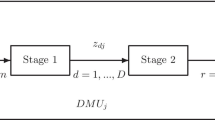
Abstract
The range-adjusted measure (RAM) as one of the non-radial data envelopment analysis (DEA) models has been broadly used in the assessment of decision-making units (DMUs). In many situations, the DMUs have a multi-component (network) structure, where the output of each component can be used as the input of another component, which is referred to as intermediate output. Various methods with different forms of production possibility sets (PPSs) have been suggested to formulate the intermediate output in efficiency calculations that link network components and each of these methods leads to different efficiency scores. These different forms of PPSs include independent, relational, and cooperative, which can appraise the efficiency of a DMU from internal and external perspectives. This paper aims to clarify the relationship among different forms of PPSs for the network RAM-DEA model from internal and external perspectives by emphasizing the development of a network RAM-DEA model. This study shows that from internal evaluation, a DMU with a network structure may operate efficiently while it is inefficient from external evaluation. This study proves that to evaluate a DMU with a network structure, the cooperative form of PPS is more suitable from both internal and external perspectives. The independent form of PPS does not exactly define the relationships among the components, so it is not recommended for computing the efficiency of a network. Models associated with the relational form of PPS may cause excess supply (waste) in the network, which is not appropriate for internal evaluation. Finally, a real example illustrates the applicability of the presented model.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The concept of weak disposability was first defined by Färe et al. (1989). This concept means that undesirable outputs can be reduced by the same reduction factor so that the relative proportions between the resulting outputs are kept constant. With this concept, the RAM-DEA model in this study can easily increase desirable outputs and simultaneously reduce undesirable outputs. The classification of technologies based on the hypothesis of weak disposability of outputs is reviewed in detail by Pham and Zelenyuk (2019).
References
Andersen P, Petersen NC (1993) A procedure for ranking efficient units in data envelopment analysis. Manage Sci 39(10):1261–1264
Avkiran NK, McCrystal A (2012) Sensitivity analysis of network DEA: NSBM versus NRAM. Appl Math Comput 218(22):11226–11239
Banker RD, Charnes A, Cooper WW (1984) Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Manage Sci 30(9):1078–1092
Bardhan I, Bowlin W, Cooper WW, Sueyoshi T (1996) Models for measuring amounts of efficiency dominance in DEA: part i additive models and MED measures. J Operat Res Soc Japan 39:322–332
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2(6):429–444
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Golany B, Seiford L, Stutz J (1985) Foundations of data envelopment analysis for Pareto-Koopmans efficient empirical production functions. J Econ 30(1–2):91–107
Chen K, Zhu J (2020) Additive slacks-based measure: computational strategy and extension to network DEA. Omega 91:102022
Chen C, Zhu J, Yu JY, Noori H (2012) A new methodology for evaluating sustainable product design performance with two-stage network data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 221(2):348–359
Chen Y, Li Y, Liang L, Salo A, Wu H (2016) Frontier projection and efficiency decomposition in two-stage processes with slacks-based measures. Eur J Oper Res 250(2):543–554
Conover WJ (1999) Practical nonparametric statistics, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, p 578
Cook WD, Hababou M (2001) Sales performance measurement in bank branches. Omega 29(4):299–307
Cook WD, Zhu J, Bi G, Yang F (2010) Network DEA: additive efficiency decomposition. Eur J Oper Res 207(2):1122–1129
Cooper WW, Park KS, Pastor JT (1999) RAM: a range adjusted measure of inefficiency for use with additive models, and relations to other models and measures in DEA. J Prod Anal 11(1):5–42
Cooper WW, Park KS, Pastor JT (2001) The range adjusted measure (RAM) in DEA: a response to the comment by steinmann and Zweifel. J Prod Anal 145:152
Cui Q, Li Y (2018) Airline environmental efficiency measures considering materials balance Principles: an application of a network range-adjusted measure with weak-G disposability. J Environ Planning Manage 61(13):2298–2318
FakhrMousavi SM, Amirteimoori A, Kordrostami S, Vaez-Ghasemi M (2022) Estimation of efficiency of two-stage processes using a fully fuzzy range-adjusted measure approach and strong complementary slackness conditions. Modern Res Decis Making 7(2):29–51
Faramarzi GR, Khodakarami M, Shabani A, Saen RF, Azad F (2015) New network data envelopment analysis approaches: an application in measuring sustainable operation of combined cycle power plants. J Clean Prod 108:232–246
Färe R, Grosskopf S (1997) Intertemporal production frontiers: with dynamic DEA. J Operat Res Soc 48(6):656–656
Färe R, Grosskopf S (2000) Network DEA. Socioecon Plann Sci 34:35–49
Färe R, Grosskopf S, Lovell CAK, Pasurka C (1989) Multilateral productivity comparisons when some outputs are undesirable: A nonparametric approach. Rev Econ Stat 71:90–98
Färe R, Grosskopf S, Pasurka CA Jr (2007) Environmental production functions and environmental directional distance functions. Energy 32(7):1055–1066
Heydari C, Omrani H, Taghizadeh R (2020) A fully fuzzy network DEA-Range adjusted measure model for evaluating airlines efficiency: a case of Iran. J Air Transp Manag 89:101923
Huang HC, Hu CF (2021) Performance measurement for the recycling production system using cooperative game network data envelopment analysis. Sustainability 13(19):11060
Hwang SN, Tong-Liang K (2006) Measuring managerial efficiency in non-life insurance companies: an application of two-stage data envelopment analysis. Int J Manag 23(3):699
Kalantary M, Farzipoor Saen R, Toloie Eshlaghy A (2018) Sustainability assessment of supply chains by inverse network dynamic data envelopment analysis. Sci Iranica 25(6):3723–3743
Kao C (2014) Efficiency decomposition in network data envelopment analysis with slacks-based measures. Omega 45:1–6
Kao C (2016) Efficiency decomposition and aggregation in network data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 255(3):778–786
Kao C (2018) A classification of slacks-based efficiency measures in network data envelopment analysis with an analysis of the properties possessed. Eur J Oper Res 270(3):1109–1121
Kao C, Hwang SN (2008) Efficiency decomposition in two-stage data envelopment analysis: An application to non-life insurance companies in Taiwan. Eur J Oper Res 185(1):418–429
Kao C, Hwang SN (2010) Efficiency measurement for network systems: IT impact on firm performance. Decis Support Syst 48(3):437–446
Khalili-Damghani K, Tavana M (2013) A new fuzzy network data envelopment analysis model for measuring the performance of agility in supply chains. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(1):291–318
Li Y, Cui Q (2017) Carbon neutral growth from 2020 strategy and airline environmental inefficiency: a network range adjusted environmental data envelopment analysis. Appl Energy 199:13–24
Li Y, Cui Q (2018) Airline efficiency with optimal employee allocation: an input-shared network range adjusted measure. J Air Transp Manag 73:150–162
Mahmoudabadi MZ, Azar A, Emrouznejad A (2018) A novel multilevel network slacks-based measure with an application in electric utility companies. Energy 158:1120–1129
Omrani H, Soltanzadeh E (2016) Dynamic DEA models with network structure: An application for Iranian airlines. J Air Transp Manag 57:52–61
Petridis K, Ünsal MG, Dey PK, Örkcü HH (2019) A novel network data envelopment analysis model for performance measurement of Turkish electric distribution companies. Energy 174:985–998
Pham MD, Zelenyuk V (2019) Weak disposability in nonparametric production analysis: a new taxonomy of reference technology sets. Eur J Oper Res 274(1):186–198
Sarkhosh-Sara A, Tavassoli M, Heshmati A (2020) Assessing the sustainability of high-, middle-, and low-income countries: A network DEA model in the presence of both zero data and undesirable outputs. Sustainable Production and Consumption 21:252–268
Sexton TR, Silkman RH, Hogan AJ (1986) Data envelopment analysis: critique and extensions. Direct Progr Eval 1986(32):73–105
Shermeh HE, Najafi SE, Alavidoost MH (2016) A novel fuzzy network SBM model for data envelopment analysis: a case study in Iran regional power companies. Energy 112:686–697
Statistics and Information of Ministry Energy (2017), http://isn.moe.gov.ir//.
Sueyoshi T, Goto M (2012) Efficiency-based rank assessment for electric power industry: a combined use of data envelopment analysis (DEA) and DEA-discriminant analysis (DA). Energy Economics 34(3):634–644
Sueyoshi T, Sekitani K (2009) An occurrence of multiple projections in DEA-based measurement of technical efficiency: theoretical comparison among DEA models from desirable properties. Eur J Oper Res 196(2):764–794
Sueyoshi T, Goto M, Ueno T (2010) Performance analysis of US coal-fired power plants by measuring three DEA efficiencies. Energy Policy 38:1675–1688
Tavassoli M, Saen RF (2022) A new fuzzy network data envelopment analysis model for measuring efficiency and effectiveness: assessing the sustainability of railways. Appl Intell 52(12):13634–13658
Tavassoli M, Faramarzi GR, Saen RF (2014) Efficiency and effectiveness in airline performance using a SBM-NDEA model in the presence of shared input. J Air Transp Manag 34:146–153
Tavassoli M, Fathi A, Saen RF (2021) Assessing the sustainable supply chains of tomato paste by fuzzy double frontier network DEA model. Ann Operat Res 12:1–33
Tavassoli M, Ketabi S, Ghandehari M (2022) A novel fuzzy network DEA model to evaluate efficiency of Iran’s electricity distribution network with sustainability considerations. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 52:102269
Tone K (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 130(3):498–509
Tone K, Tsutsui M (2009) Network DEA: a slacks-based measure approach. Eur J Oper Res 197(1):243–252
Tone K, Tsutsui M (2010) Dynamic DEA: a slacks-based measure approach. Omega 38(3–4):145–156
Wang M, Chen Y, Zhou Z (2021) Assessing environmental efficiency of China’s industry system using two-stage range-adjusted measure model. Manag Environ Qual Int J 32(6):1401–1421
Wu J, Xu G, Zhu Q, Zhang C (2021) Two-stage DEA models with fairness concern: modelling and computational aspects. Omega 105:102521
Yu MM, Lin ET (2008) Efficiency and effectiveness in railway performance using a multi-activity network DEA model. Omega 36(6):1005–1017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT is an Assistant Professor at the Department of Industrial Management, Lorestan University, in Iran. MT has published over 25 refereed papers in peer-reviewed journals. His H-index in Google Scholar is 15. He has 10 years of industrial and consultation experience. He has published several refereed papers in many prestigious journals such as Operations Management Research, Sustainable production and consumption, Annals of Operations Research, Journal of Air Transport Management, international Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems. MG is an Associate Professor at the Department of Industrial Management, University of Esfahan, in Iran. In 2006, he obtained his PhD in Industrial Management from Sharif University, in Iran. He has published several papers in many prestigious journals such as Computers & Industrial Engineering, Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering, International Journal of Mathematics in Operational Research. MT is a member of faculty in area of finance and accounting. He received his BS and MA in Accounting from Allameh Tabatabai University, Tehran, in Iran. He obtained his PhD in Accounting from Pune University, in India. He has published several refereed papers in many journals such as The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business (JAFEB), International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, Advances in Mathematical Finance and Applications, Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance Journal, International Journal of Finance & Managerial Accounting, Journal of Management Accounting and Auditing Knowledge, Journal of Accounting and Social Interests, International Journal of Nonlinear Analysis and Applications, Empirical Research in Accounting and Journal of Hunan University Natural Sciences.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tavassoli, M., Ghandehari, M. & Taherinia, M. Rang-adjusted measure: modelling and computational aspects from internal and external perspectives for network DEA. Oper Res Int J 23, 62 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-023-00802-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-023-00802-9