Abstract
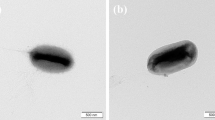
Two novel Gram-negative, aerobic, asporogenous, motile, rod-shaped, orange and white pigmented, designated as LEGU1T and G19T, were isolated from the roots of rice plants, collected from Goyang, South Korea. Phylogenetic analysis based on their 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that they belonged to the genus Devosia and formed a different lineage and clusters with different members of the genus Devosia. These strains shared common chemotaxonomic features. In particular, they had Q-10 as the sole quinone, phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol as the principal polar lipids and C16:0, C18:1ω7c 11-methyl and summed feature 8 (comprising C18:1ω7c/C18:1ω6c) as the main fatty acids. The draft genome sequences of strains LEGU1T and G19T were 3,524,978 and 3,495,520 bp in size, respectively. Their average nucleotide identity (ANI) and digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) values were 72.8–81.9% and 18.7–25.1%, respectively, with each other and type strains of related species belonging to the genus Devosia, suggesting that these two strains represent novel species. The G + C content of strains LEGU1T and G19T were 62.1 and 63.8%, respectively. Of the two strains, only LEGU1T produced carotenoid and flexirubin-type pigment. Both strains produced siderophore and indole acetic acid (IAA) in the presence of l-tryptophan. Siderophore biosynthesis genes, auxin responsive genes and tryptophan biosynthesis genes were present in their genomes. The present study aimed to determine the detailed taxonomic positions of the strains using the modern polyphasic approach. Based on the results of polyphasic analysis, these strains are suggested to be two novel bacterial species within the genus Devosia. The proposed names are D. rhizoryzae sp. nov., and Devosia oryziradicis sp. nov., respectively. The plant growth promoting effects of these strains suggest that they can be exploited to improve rice crop productivity. The type strain of D. rhizoryzae is LEGU1T (KCTC 82712T = NBRC 114485T) and D. oryziradicis is G19T (KCTC 82688T = NBRC 114842T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandumula, N. 2018. Rice production in Asia: key to global food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 88, 1323–1328.
Burd, G.I., Dixon, D.G., and Glick, B.R. 2000. Plant growth promoting bacteria that decrease heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can. J. Microbiol. 46, 237–245.
Chhetri, G., Kim, J., Kim, I., Kim, H., Lee, B., Jang, W., and Seo, T. 2020. Adhaeribacter rhizoryzae sp. nov., fibrillar matrix producing bacterium isolated from the rhizosphere of rice plant. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 70, 5382–5388.
Chhetri, G., Kim, J., Kim, I., Kim, M.K., and Seo, T. 2019a. Pontibacter chitinilyticus sp. nov., a novel chitin-hydrolysing bacterium isolated from soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 1011–1018.
Chhetri, G., Kim, J., Kim, H., Kim, H., and Seo, T. 2019b. Pontibacter oryzae sp. nov., a carotenoid-producing species isolated from a rice paddy field. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 1705–1713.
Chun, J., Oren, A., Ventosa, A., Christensen, H., Arahal, D.R., Da Costa, M.S., Rooney, A.P., Yi, H., Xu, X.W., De Meyer, S., et al. 2018. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 68, 461–466.
Cleland, R.E. 1995. Auxin and cell elongation. In Davies, P.J. (ed.), Plant Hormones and Their Role in Plant Growth and Development, pp. 132–148. Kluwer, Dordrecht, Netherlands.
Collins, M.D. and Jones, D. 1981. Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implications. Microbiol. Rev. 45, 316–354.
Dua, A., Malhotra, J., Saxena, A., Khan, F., and Lal, R. 2013. Devosia lucknowensis sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) contaminated pond soil. J. Microbiol. 51, 689–694.
Fautz, E. and Reichenbach, H. 1980. A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 8, 87–91.
Felsenstein, J. 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17, 368–376.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791.
Fitch, W.M. 1971. Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 20, 406–416.
Galatis, H., Martin, K., Kämpfer, P., and Glaeser, S.P. 2013. Devosia epidermidihirudinis sp. nov. isolated from the surface of a medical leech. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103, 1165–1171.
Glick, B.R. 1995. The enhancement of plant growth by free-living bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 41, 109–117.
Hopkinson, B.M. and Barbeau, K.A. 2012. Iron transporters in marine prokaryotic genomes and metagenomes. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 114–128.
Huerta-Cepas, J., Forslund, K., Coelho, L.P., Szklarczyk, D., Jensen, L.J., von Mering, C., and Bork, P. 2017. Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol. Biol. Evol. 34, 2115–2122.
Jia, Y.Y., Sun, C., Pan, J., Zhang, W.Y., Zhang, X.Q., Huo, Y.Y., Zhu, X.F., and Wu, M. 2014. Devosia pacifica sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 2637–2641.
Kim, J., Chhetri, G., Kim, I., Kim, H., Kim, M.K., and Seo, T. 2019a. Methylobacterium terrae sp. nov., a radiation-resistant bacterium isolated from gamma ray-irradiated soil. J. Microbiol. 57, 959–966.
Kim, I., Chhetri, G., Kim, J., and Seo, T. 2019b. Amnibacterium setariae sp. nov., an endophytic actinobacterium isolated from dried foxtail. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 1731–1738.
Kim, I., Kim, J., Chhetri, G., and Seo, T. 2019c. Flavobacterium humi sp. nov., a flexirubin-type pigment producing bacterium, isolated from soil. J. Microbiol. 57, 1079–1085.
Kimura, M. 1980. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111–120.
Komagata, K. and Suzuki, K.I. 1988. Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol. 19, 161–207.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., and Tamura, K. 2016. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 1870–1874.
Lee, S.D. 2007. Devosia subaequoris sp. nov., isolated from beach sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2212–2215.
Meier-Kolthoff, J.P., Auch, A.F., Klenk, H.P., and Göker, M. 2013. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 14, 60.
Minnikin, D.E., O’Donnell, A.G., Goodfellow, M., Alderson, G., Athalye, M., Schaal, A., and Parlett, J.H. 1984. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2, 233–241.
Na, S.I., Kim, Y.O., Yoon, S.H., Ha, S.M., Baek, I., and Chun, J. 2018. UBCG: up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J. Microbiol. 56, 281–285.
Nakagawa, Y., Sakane, T., and Yokota, A. 1996. Transfer of “Pseudomonas riboflavina” (Foster 1944), a Gram-negative, motile rod with long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids, to Devosia riboflavina gen. nov., sp. nov., nom. rev. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46, 16–22.
Parks, D.H., Imelfort, M., Skennerton, C.T., Hugenholtz, P., and Tyson, G.W. 2015. CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 25, 1043–1055.
Quan, X.T., Siddiqi, M.Z., Liu, Q.Z., Lee, S.M., and Im, W.T. 2020. Devosia ginsengisoli sp. nov., isolated from ginseng cultivation soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 70, 1489–1495.
Rivas, R., Willems, A., Subba-Rao, N.S., Mateos, P.F., Dazzo, F.B., Kroppenstedt, R.M., Martínez-Molina, E., Gillis, M., and Velázquez, E. 2003. Description of Devosia neptuniae sp. nov. that nodulates and fixes nitrogen in symbiosis with Neptunia natans, an aquatic legume from India. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 26, 47–53.
Romanenko, L.A., Tanaka, N., and Svetashev, V.I. 2013. Devosia submarina sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea surface sediments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63, 3079–3085.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Schuster, C.F. and Bertram, R. 2013. Toxin-antitoxin systems are ubiquitous and versatile modulators of prokaryotic cell fate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 340, 73–85.
Stackebrandt, E. and Goebel, B.M. 1994. Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 44, 846–849.
Talwar, C., Nagar, S., Kumar, R., Scaria, J., Lal, R., and Negi, R.K. 2020. Defining the environmental adaptations of genus Devosia: Insights into its expansive short peptide transport system and positively selected genes. Sci. Rep. 10, 1151.
Tatusov, R.L., Galperin, M.Y., Natale, D.A., and Koonin, E.V. 2000. The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 33–36.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D.G. 1997. The CLUSTAL-X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882.
Toral, G.M., Stillman, R.A., Santoro, S., and Figuerola, J. 2012. The importance of rice fields for glossy ibis (Plegadis falcinellus): management recommendations derived from an individual-based model. Biol. Conserv. 148, 19–27.
Ueji, M. and Inao, K. 2001. Rice paddy field herbicides and their effects on the environment and ecosystems. Weed Biol. Manag. 1, 71–79.
Vanparys, B., Heylen, K., Lebbe, L., and De Vos, P. 2005. Devosia limi sp. nov., isolated from a nitrifying inoculum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 1997–2000.
Verma, M., Kumar, M., Dadhwal, M., Kaur, J., and Lal, R. 2009. Devosia albogilva sp. nov. and Devosia crocina sp. nov., isolated from a hexachlorocyclohexane dump site. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 795–799.
Wang, G., Wang, Y., Ji, F., Xu, L., Yu, M., Shi, J., and Xu, J. 2019. Biodegradation of deoxynivalenol and its derivatives by Devosia insulae A16. Food Chem. 276, 436–442.
Yoo, S.H., Weon, H.Y., Kim, B.Y., Hong, S.B., Kwon, S.W., Cho, Y.H., Go, S.J., and Stackebrandt, E. 2006. Devosia soli sp. nov., isolated from greenhouse soil in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 2689–2692.
Yoon, S.H., Ha, S.M., Lim, J., Kwon, S., and Chun, J. 2017. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 1281–1286.
Zhang, D.C., Redzic, M., Liu, H.C., Zhou, Y.G., Schinner, F., and Margesin, R. 2012. Devosia psychrophila sp. nov. and Devosia glacialis sp. nov., two novel bacteria from alpine glacier cryoconite. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 710–715.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) grant, funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of the Republic of Korea (NIBR2020-02203/NIBR202102205), and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2020R1F1A1072647).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study does not describe any experimental work related to human.
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic Supplementary Material
12275_2022_1474_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Devosia rhizoryzae sp. nov., and Devosia oryziradicis sp. nov., novel plant growth promoting members of the genus Devosia, isolated from the rhizosphere of rice plants
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chhetri, G., Kim, I., Kang, M. et al. Devosia rhizoryzae sp. nov., and Devosia oryziradicis sp. nov., novel plant growth promoting members of the genus Devosia, isolated from the rhizosphere of rice plants. J Microbiol. 60, 1–10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-022-1474-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-022-1474-8