Abstract
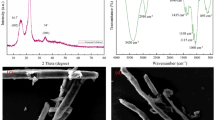
In this study, we modified microcrystalline cellulose by cross-linking it with epichlorohydrin to obtain a rapid and efficient adsorbent for the removal of Reactive Blue 4 dye from aqueous solution. Evidences of the cross-linking of the microcrystalline cellulose were obtained by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, and scanning electron microscopy. We investigated the effects of adsorbent dosage, pH, initial dye concentration, temperature, and contact time on the dye adsorption capacity. The results showed that the adsorption equilibrium time was just 20 min and the maximum adsorption capacity was 69.79 mg/g. The adsorption isotherm data fitted the Langmuir isotherm model well, and the adsorption kinetics data followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The results of the thermodynamic analysis suggest that the adsorption process was spontaneous and exothermic. Recyclability experiments demonstrated the good reusability of this adsorbent. Electrostatic interaction was found to dominate the adsorption process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nabil GM, El-Mallah NM, Mahmoud ME (2014) Enhanced decolorization of reactive black 5 dye by active carbon sorbent-immobilized-cationic surfactant (AC-CS). J Ind Eng Chem 20(3):994–1002
Lourenço ND, Novais JM, Pinheiro HM (2000) Reactive textile dye colour removal in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci Technol 42(5–6):321–328
Pearce CI, Lloyd JR, Guthrie JT (2003) The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review. Dye Pigment 58(3):179–196
Errais E, Duplay J, Darragi F et al (2011) Efficient anionic dye adsorption on natural untreated clay: kinetic study and thermodynamic parameters. Desalination 275(1–3):74–81
Novotný Č, Dias N, Kapanen A et al (2006) Comparative use of bacterial, algal and protozoan tests to study toxicity of azo- and anthraquinone dyes. Chemosphere 63(9):1436–1442
Aldegs Y, Elbarghouthi M, Elsheikh A et al (2008) Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dye Pigment 77(1):16–23
Yagub MT, Sen TK, Afroze S et al (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 209:172–184
Vikrant K, Giri BS, Raza N et al (2018) Recent advancements in bioremediation of dye: current status and challenges. Bioresour Technol 253:355–367
Pal S, Patra AS, Ghorai S et al (2015) Efficient and rapid adsorption characteristics of templating modified guar gum and silica nanocomposite toward removal of toxic reactive blue and Congo red dyes. Bioresour Technol 191:291–299
Zhang ZZ, Tang JD, Sun Y et al (2013) Water effect on amine-modification of adsorbents for separation of CO2/N2. Trans Tianjin Univ 19(5):313–318
Panda J, Sahoo JK, Panda PK et al (2019) Adsorptive behavior of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 towards anionic dye in aqueous media: combined experimental and molecular docking study. J Mol Liq 278:536–545
Değermenci GD, Değermenci N, Ayvaoğlu V et al (2019) Adsorption of reactive dyes on lignocellulosic waste; characterization, equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Clean Prod 225:1220–1229
Hong GB, Wang YK (2017) Synthesis of low-cost adsorbent from rice bran for the removal of reactive dye based on the response surface methodology. Appl Surf Sci 423:800–809
Ibrahim S, Shuy WZ, Ang HM et al (2010) Preparation of bioadsorbents for effective adsorption of a reactive dye in aqueous solution. Asia-Pacific J Chem Eng 5(4):563–569
Aguayo-Villarreal IA, Ramírez-Montoya LA, Hernández-Montoya V et al (2013) Sorption mechanism of anionic dyes on pecan nut shells (Carya illinoinensis) using batch and continuous systems. Ind Crop Prod 48:89–97
Chowdhury S, Saha T (2016) Adsorption of Reactive Blue 4 (RB4) onto Rice Husk in aqueous solution. Int J Sci Eng Res 7(3):7–12
Binupriya AR, Sathishkumar M, Jung S et al (2009) A novel method in utilization of Bokbunja seed wastes from wineries in liquid-phase sequestration of Reactive Blue 4. Int J Environ Res 3(1):1–12
Jin YQ, Zhang YZ, Lü Q et al (2014) Biosorption of methylene blue by chemically modified cellulose waste. J Wuhan Univ Technol-Mat Sci Edit 29(4):817–823
Vieira Ferreira LF, Ferreira DP, Duarte P et al (2012) Surface photochemistry: 3,3′-dialkylthia and selenocarbocyanine dyes adsorbed onto microcrystalline cellulose. Int J Mol Sci 13(1):596–611
Thoorens G, Krier F, Leclercq B et al (2014) Microcrystalline cellulose, a direct compression binder in a quality by design environment: a review. Int J Pharm 473(1–2):64–72
Trache D, Hussin MH, Hui Chuin CT et al (2016) Microcrystalline cellulose: Isolation, characterization and bio-composites application: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 93:789–804
Cao J, Fei DT, Tian XL et al (2017) Novel modified microcrystalline cellulose-based porous material for fast and effective heavy-metal removal from aqueous solution. Cellulose 24(12):5565–5577
Lin FC, You YZ, Yang X et al (2017) Microwave-assisted facile synthesis of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose beads with high adsorption capacity for organic dyes. Cellulose 24(11):5025–5040
Du KF, Li SK, Zhao LS et al (2018) One-step growth of porous cellulose beads directly on bamboo fibers via oxidation-derived method in aqueous phase and their potential for heavy metal ions adsorption. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(12):17068–17075
Jia QJ, Li DP, Gao XC et al (2016) Hydrazinolyzed cellulose-g-polymethyl acrylate as adsorbent for efficient removal of Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91(5):1378–1386
Wang Z, Huang WX, Yang GH et al (2019) Preparation of cellulose-base amphoteric flocculant and its application in the treatment of wastewater. Carbohydr Polym 215:179–188
Dong Z, Yuan WJ, Li Y et al (2019) Radiation synthesis of crown ether functionalized microcrystalline cellulose as bifunctional adsorbent: a preliminary investigation on its application for removal of ReO4- as analogue for TcO4-. Radiat Phys Chem 159:147–153
Zhou CG, Ni JD, Zhang D et al (2019) Cellulosic adsorbent functionalized with macrocyclic pyridone pentamer for selectively removing metal cations from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr Polym 217:1–5
Rafieian F, Mousavi M, Yu QL et al (2019) Amine functionalization of microcrystalline cellulose assisted by (3-chloropropyl)triethoxysilane. Int J Biol Macromol 130:280–287
Xue F, He H, Zhu HX et al (2019) Structural design of a cellulose-based solid amine adsorbent for the complete removal and colorimetric detection of Cr(VI). Langmuir 35(39):12636–12646
Dehabadi L, Wilson LD (2014) Polysaccharide-based materials and their adsorption properties in aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 113:471–479
Udoetok IA, Dimmick RM, Wilson LD et al (2016) Adsorption properties of cross-linked cellulose-epichlorohydrin polymers in aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 136:329–340
Udoetok IA, Wilson LD, Headley JV (2018) “pillaring effects” in cross-linked cellulose biopolymers: A study of structure and properties. Int J Polym Sci 2018:1–13
Pellicer JA, Rodríguez-López MI, Fortea MI et al (2018) Removing of Direct Red 83: 1 using α- and HP-α-CDs polymerized with epichlorohydrin: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Dye Pigment 149:736–746
Anirudhan TS, Rauf TA (2013) Adsorption performance of amine functionalized cellulose grafted epichlorohydrin for the removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions. J Ind Eng Chem 19(5):1659–1667
Song W, Gao BY, Xu X et al (2016) Adsorption of nitrate from aqueous solution by magnetic amine-crosslinked biopolymer based corn stalk and its chemical regeneration property. J Hazard Mater 304:280–290
Luo XG, Zhang LN (2009) High effective adsorption of organic dyes on magnetic cellulose beads entrapping activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):340–347
Bai YX, Li YF (2006) Preparation and characterization of crosslinked porous cellulose beads. Carbohydr Polym 64(3):402–407
Chen JN, Yan SQ, Ruan JY (1996) A study on the preparation, structure, and properties of microcrystalline cellulose. J Macromol Sci Part A 33(12):1851–1862
El-Naggar ME, Radwan EK, El-Wakeel ST et al (2018) Synthesis, characterization and adsorption properties of microcrystalline cellulose based nanogel for dyes and heavy metals removal. Int J Biol Macromol 113:248–258
Sing KSW (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl Chem 57(4):603–619
Pratt DY, Wilson LD, Kozinski JA et al (2010) Preparation and sorption studies of β-cyclodextrin/epichlorohydrin copolymers. J Appl Polym Sci 116(5):2982–2989
Liu HG, Dong XM, Xia JP et al (2019) Preparation of γ-Al2O3 via hydrothermal synthesis using ρ-Al2O3 as raw material for propane dehydrogenation. Trans Tianjin Univ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-019-00225-8
Trache D, Donnot A, Khimeche K et al (2014) Physico-chemical properties and thermal stability of microcrystalline cellulose isolated from Alfa fibres. Carbohydr Polym 104:223–230
Udoetok IA, Wilson LD, Headley JV (2018) Ultra-sonication assisted cross-linking of cellulose polymers. Ultrason Sonochem 42:567–576
Hou LP, Tao ML (2020) Oxadiazole-functionalized polyacrylonitrile fiber as selective adsorbent for mercury ion. Trans Tianjin Univ 26(1):49–56
Vakili M, Rafatullah M, Salamatinia B et al (2015) Elimination of reactive blue 4 from aqueous solutions using 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane modified chitosan beads. Carbohydr Polym 132:89–96
Zhu HY, Fu YQ, Jiang R et al (2011) Adsorption removal of Congo red onto magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 173(2):494–502
Nascimento MA, Cruz JC, Rodrigues GD et al (2018) Synthesis of polymetallic nanoparticles from spent lithium-ion batteries and application in the removal of reactive blue 4 dye. J Clean Prod 202:264–272
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Analytical and Testing Center of Tianjin University for the characterization support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Y., Qu, H., Li, Z. et al. Rapid and Efficient Adsorption Removal of Reactive Blue 4 from Aqueous Solution by Cross-Linked Microcrystalline Cellulose–Epichlorohydrin Polymers: Isothermal, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Study. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 27, 77–86 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-020-00245-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-020-00245-9