Abstract
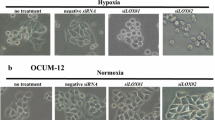
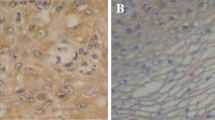
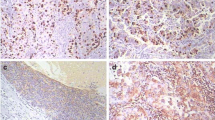
The purpose of this study is to explore the role of hypoxia on the invasion and metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma. The invasion and migration ability of laryngeal cancer SCC10A cell was detected by transwell assay. Western blot was applied to analyze the expression of EMT-related proteins. Fifty-seven samples from postoperative patients with laryngeal cancer were collected to study. Immunohistochemistry was used to examine the expression of GLUT-1 and EMT-related proteins (Vim, E-cad, N-cad) in normal laryngeal squamous epithelial tissue, laryngeal cancer adjacent tissues and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma tissues. Hypoxia promoted laryngeal cancer cell invasion and migration. Hypoxia also enhanced the expression of GLUT-1, vimentin and N-cad, which exist statistically significant correlation with the clinical staging and lymph node metastases (P < 0.05). The expression of GLUT-1 is positively correlated with Vim and N-cad expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma tissues, but negatively correlated with E-cad expression. The patient survival rate with the positive expression of GLUT-1, Vim and N-cad becomes much shorter compared with those with negative expression of GLUT-1, Vim and N-cad (P < 0.05). Hypoxia promoted laryngeal cancer cell invasion and migration via EMT.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia C-X, Zhu Q, Zhao H-X, Yan F, Li S-L, Zhang S-M. Usefulness of ultrasonography in assessment of laryngeal carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 2013;86(1030):20130343.
Markou K, Christoforidou A, Karasmanis I, Tsiropoulos G, Triaridis S, Constantinidis I, Vital V, Nikolaou A. Laryngeal cancer: epidemiological data from Νorthern Greece and review of the literature. Hippokratia. 2013;17(4):313–8.
Dan Yu, Jin C, Liu Y, Yang J, Zhao Y, Wang H, Zhao X, Cheng J, Liu X, Liu C. Clinical implications of cancer stem cell-like side population cells in human laryngeal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(6):3603–10.
Harris AL. Hypoxia—a key regulatory factor in tumor growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:38–47.
Tsaiand JH, Yang J. Epithelial–mesenchymal plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 2013;27(20):2192–206.
Mendichovszky I, Jackson A. Imaging hypoxia in gliomas. Br J Radiol. 2011;84(Spec Iss 2):S145–58.
Ponnusamy MP, Seshacharyulu P, Lakshmanan I, Vaz AP, Chugh S, Batra SK. Emerging role of mucins in epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013;13(9):945–56.
Steinestel K, Eder S, Schrader AJ, Steinestel J. Clinical significance of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Clin Transl Med. 2014;3:17.
Hazan RB, Phillips GR, Qiao RF, Norton L, Aaronson SA. Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. J Cell Biol. 2000;148(4):779–90.
Qian X, Anzovino A, Kim S, Suyama K, Yao J, Hulit J, Agiostratidou G, Chandiramani N, McDaid HM, Nagi C, Cohen HW, Phillips GR, Norton L, Hazan RB. N-cadherin/FGFR promotes metastasis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem/progenitor cell-like properties. Oncogene. 2014;33(26):3411–21.
Chung S, Yao J, Suyama K, Bajaj S, Qian X, Loudig OD, Eugenin EA, Phillips GR, Hazan RB. N-cadherin regulates mammary tumor cell migration through Akt3 suppression. Oncogene. 2013;32(4):422–30.
Su Y, Li J, Witkiewicz AK, Brennan D, Neill T, Talarico J, Radice GL. N-cadherin haploinsufficiency increases survival in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31(41):4484–9.
Kallergi G, Papadaki MA, Politaki E, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V, Agelaki S. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers expressed in circulating tumour cells of early and metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(3):R59.
Ulirsch J, Fan C, Knafl G, Wu MJ, Coleman B, Perou CM, Swift-Scanlan T. Vimentin DNA methylation predicts survival in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2353-5.
Wendt MK, Taylor MA, Schiemann BJ, Schiemann WP. Down-regulation of epithelial cadherin is required to initiate metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22(14):2423–35.
Reinhold WC, Reimers MA, Lorenzi P, Ho J, Shankavaram UT, Ziegler MS, Bussey KJ, Nishizuka S, Ikediobi O, Pommier YG, Weinstein JN. Multifactorial regulation of E-cadherin expression: an integrative study. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(1):1.
Zuo J-h, Zhu W, Li Mao-Yu, Li X-H, Yi H, Zeng G-Q, Wan X-X, He Q-Y, Li J-H, Jia-Quan Q, Xiao Z-Q. Activation of EGFR promotes squamous carcinoma SCC10A cell migration and invasion via inducing EMT-like phenotype change and MMP-9-mediated degradation of E-cadherin. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:2508–17.
Chou CC, Chuang HC, Salunke SB, Kulp SK, Chen CS. A novel HIF-1α-integrin-linked kinase regulatory loop that facilitates hypoxia-induced HIF-1α expression and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6(10):8271–85.
Lu X, Kang Y. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors:master regulators of metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:5928–35.
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC. Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell. 2010;40:294–309.
Tsai YP, Wu KJ. Hypoxia-regulated target genes implicated in tumor metastasis. J Biomed Sci. 2012;19:102.
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Cox TR, Lang G, Bird D, Koong A, et al. Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:35–44.
Huang X, Zuo J. Emerging roles of miR-210 and other non-coding RNAs in the hypoxic response. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014;46(3):220–32.
Starska K, Forma E, Jóźwiak P, Bryś M, Lewy-Trenda I, Brzezińska-Błaszczyk E, Krześlak A. Gene and protein expression of glucose transporter 1 and glucose transporter 3 in human laryngeal cancer-the relationship with regulatory hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression, tumor invasiveness, and patient prognosis. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(4):2309–21.
Cui Y, Nadiminty N, Liu C, Lou W, Schwartz CT, Gao AC. Upregulation of glucose metabolism by NF-κB2/p52 mediates enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21:435–42.
Rashmi R, DeSelm C, Helms C, Bowcock A, Rogers BE, Rader J, et al. AKT inhibitors promote cell death in cervical cancer through disruption of mTOR signaling and glucose uptake. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e92948. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092948.
Zhang C, Liu J, Liang Y, Wu R, Zhao Y, Hong X, et al. Tumour-associated mutant p53 drives the Warburg effect. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2935.
Chen XH, Bao YY, Zhou SH, Wang QY, Wei Y, Fan J. Glucose transporter-1 expression in CD133 + laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8:1695–700.
Eckert AW, Lautner MH, Schütze A, Taubert H, Schubert J, Bilkenroth U. Coexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and glucose transporter-1 is associated with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Histopathology. 2011;58:1136–47.
Zuo J, Ishikawa T, Boutros S, Xiao Z, Humtsoe JO, Kramer RH. Bcl-2 over-expression induces a partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition and promotes squamous carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8(2):170–82.
Zuo J, Wen M, Lei M, Peng X, Yang X, Liu Z. MiR-210 links hypoxia with cell proliferation regulation in human laryngocarcinoma cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(6):1039–49.
Yuan TZ, Zhang HH, Tang QF, Zhang Q, Li J, Liang Y, Huang LJ, Zheng RH, Deng J, Zhang XP. Prognostic value of kisspeptin expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2014;124(5):E167–74.
Li L, Wang J, Gao L, Gong L. Expression of paxillin in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and its prognostic value. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(8):9232–9.
Tu XP, Qiu QH, Chen LS, Luo XN, Lu ZM, Zhang SY, Chen SH. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an independent prognostic marker in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2015;15(743):1–7.
Xie J, Li D, Chen X, Wang F, Dong P. Expression and significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and MDR1/P-glycoprotein in laryngeal carcinoma tissue and hypoxic Hep-2 cells. Oncol Lett. 2013;6(1):232–8.
Abdou AG, Eldien MM. Elsakka D.GLUT-1 expression in cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Surg Pathol. 2015;23(6):447–53.
Huang XQ, Chen X, Xie XX, Zhou Q, Li K, Li S, Shen LF, Su J. Co-expression of CD147 and GLUT-1 indicates radiation resistance and poor prognosis in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(4):1651–66.
Eckert AW, Lautner MH, Taubert H, Schubert J, Bilkenroth U. Expression of Glut-1 is a prognostic marker for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oncol Rep. 2008;20:1381–5.
Deron P, Vermeersch H, Mees G, Vangestel C, Pauwels P, Van de Wiele C. Expression and prognostic value of glucose transporters and hexokinases in tonsil and mobile tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26:1165–72.
Kondo Y, Yoshikawa K, Omura Y, Shinohara A, Kazaoka Y, Sano J, Mizuno Y, Yokoi T, Yamada S. Clinicopathological significance of carbonic anhydrase 9, glucose transporter-1, Ki-67 and p53 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2011;25:1227–33.
Deron P, Vangestel C, Goethals I, De Potter A, Peeters M, Vermeersch H, Van de Wiele C. FDG uptake in primary squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. The relationship between overexpression of glucose transporters and hexokinases, tumour proliferation and apoptosis. Nuklearmedizin. 2011;50:15–21.
Zhang L, Huang G, Li X, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Shen J, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhu J, Feng X, Dong J, Qian C. Hypoxia induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition via activation of SNAI1 by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:108.
Mayer A, Höckel M, Schlischewsky N, Schmidberger H, Horn LC, Vaupel P. Lacking hypoxia-mediated downregulation of E-cadherin in cancers of the uterine cervix. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(2):402–8.
Huang X, Ding L, Bennewith KL, Tong RT, Welford SM, Ang KK, Story M, Le QT, Giaccia AJ. Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression involved in tumor initiation. Mol Cell. 2009;35(6):856–67.
Talbot LJ, Bhattacharya SD, Kuo PC. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, the tumor microenvironment, and metastatic behavior of epithelial malignancies. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2012;3(2):117–36.
Huang SG, Zhang LL, Niu Q, Xiang GM, Liu LL, Jiang DN, Liu F, Li Y, Pu X. Hypoxia promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inducing GLIPR-2 expression. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(10):e77497.
Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang SY, Liu CJ, Teng SC, Wu KJ. Direct regulation of TWIST by HIF-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:295–305.
Choi JY, Jang YS, Min SY, Song JY. Overexpression of MMP-9 and HIF-1alpha in breast cancer cells under hypoxic conditions. J Breast Cancer. 2011;14:88–95.
Kaidi A, Williams AC, Paraskeva C. Interaction between beta-catenin and HIF-1 promotes cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:210–7.
Zhang W, Shi X, Peng Y, Wu M, Zhang P, Xie R, Wu Y, Yan Q, Liu S, Wang J. HIF-1α promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metastasis through direct regulation of ZEB1 in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0129603.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (81272960), Key Research Program from Science and Technology Department of Hunan Province, China (2013WK2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Jianhong Zuo and Juan Wen have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, J., Wen, J., Lei, M. et al. Hypoxia promotes the invasion and metastasis of laryngeal cancer cells via EMT. Med Oncol 33, 15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0716-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0716-6