Abstract
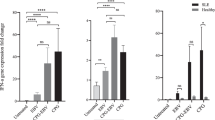
Risk posed by microbial superantigens in triggering or exacerbating SLE in genetically predisposed individuals, thereby altering the response to its treatment strategies, has not been studied. Using streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A and staphylococcal enterotoxin B as prototype superantigens, we have demonstrated that they profoundly affect the magnitude of polyclonal T cell response, particularly CD4+ T cells and expression of CD45RA and CD45RO, and cytokine secretion in vitro in SLE patient PBMCs. Also, reduced proportions of FoxP3 expressing CD4+CD25+ T cells were detected in SLE as compared to healthy control PBMCs. Furthermore, polymorphism in IL-10 and TGF-β showed significant association with SLE in our study population. These results indicate that accumulation of superantigen-reactive T cells and cytokine polymorphism may cause disease exacerbation, relapse, or therapeutic resistance in SLE patients. Attempts to contain colonizing and/or superantigen-producing microbial agents in SLE patients in addition to careful monitoring of their therapy may be worthwhile in decreasing disease severity or preventing frequent relapses. The study suggests that superantigen interference in conjunction with cytokine polymorphism may play a role in immune dysregulation, thereby contributing to autoimmunity in SLE. Therefore, changes in T cell phenotypes and cytokine secretion might be good indicators of therapeutic efficacy in these patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mok CC, Lau CS. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Pathol. 2003;56(7):481–90.
Lahita RG. The connective tissue diseases and the overall influence of gender. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud. 1996;41(2):156–65.
D’Cruz D. Autoimmune diseases associated with drugs, chemicals, and environmental factors. Toxicol Lett. 2000;112–113:421–32.
Dooley MA, Hogan SL. Environmental epidemiology and risk factors for autoimmune disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15(2):99–103.
Deapen D, Escalante A, Weinrib L, Horwitz D, Bachman B, Roy-Burman P, Walker A, Mack TM. A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35(3):311–8.
Friedman SM, Posnett DN, Tumang JR, Cole BC, Crow MK. A potential role for microbial superantigens in the pathogenesis of systemic autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1991;34(4):468–80.
Fraser JD, Proft T. The bacterial superantigen and superantigen-like proteins. Immunol Rev. 2008;225:226–43.
Sfriso P, Ghirardello A, Botsios C, Tonon M, Zen M, Bassi N, Bassetto F, Doria A. Infections and autoimmunity: the multifaceted relationship. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87:385–95.
Kissner TL, Ruthel G, Alam S, Ulrich RG, Fernandez S, Saikh KU. Activation of MyD88 signaling upon staphylococcal enterotoxin binding to MHC class II molecules. PLoS One. 2011;6:e15985.
Florquin S, Amraoui Z, Goldman M. Persistent production of TH2- type cytokines and polyclonal B cell activation after chronic administration of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in mice. J Autoimmun. 1996;9(5):609–15.
Tumang JR, Zhou JL, Gietl D, Crow MK, Elkon KB, Friedman SM. T helper cell dependent, microbial superantigen-mediated B cell activation in vivo. Autoimmunity. 1996;24(4):247–55.
Friedman SM, Tumang JR, Crow MK. Microbial superantigens as etiopathogenic agents in autoimmunity. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1993;19:207–22.
Kotzin BL, Leung DY, Kappler J, Marrack P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:99–166.
Bette M, Schafer MK, van Rooijen N, Weihe E, Fleischer B. Distribution and kinetics of superantigen-induced cytokine gene expression in mouse spleen. J Exp Med. 1993;178(5):1531–9.
Miethke T, Duschek K, Wahl C, Heeg K, Wagner H. Pathogenesis of the toxic shock syndrome: T cell mediated lethal shock caused by the superantigen TSST-1. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23(7):1494–500.
MacDonald HR, Baschieri S, Lees R. Clonal expansion precedes anergy and death of Vβ8+ peripheral T cells responding to staphylococcal enterotoxin B in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1991;21:1963.
Baschieri S, Lees RK, Lussow A, MacDonald HR. Clonal anergy to staphylococcal enterotoxin B in vivo: selective effects on T cell subsets and cytokines. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:2661.
Arend WP, Gabay C. Cytokines in the rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2004;30(1):41–67.
Grainger DJ, Heathcote K, Chiano M, Snieder H, Kemp PR, Metcalfe JC, Carter ND, Spector TD. Genetic control of the circulating concentration of transforming growth factor type beta 1. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8(1):93–7.
Terry C, Loukaci V, Green F. Cooperative influence of genetic polymorphisms on interleukin 6 transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(24):18138–44.
Bidwell J, Keen L, Gallagher G, Kimberly R, Huizinga T, McDermott MF, Oksenberg J, McNicholl J, Pociot F, Hardt C, D’Alfonso S. Cytokine gene polymorphism in human disease: on-line databases. Genes Immun. 1999;1(1):3–19.
Ahmad YA, Bruce IN. Genetic epidemiology: systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2001;3(6):331–6.
Magnusson V, Nakken B, Bolstad A, Alarcon-Riquelme M. Cytokine polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome. Scand J Immunol. 2001;54(1–2):55–61.
Lu LY, Cheng HH, Sung PK, Yeh JJ, Shiue YL, Chen A. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of transforming growth factor-beta1 gene in Taiwanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2004;37(3):145–52.
Boyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Investig. 1968;97:77–89.
Fuleihan R, Mourad W, Geha RS, Chatila T. Engagement of MHC-class II molecules by staphylococcal exotoxins delivers a co-mitogenic signal to human B cells. J Immunol. 1991;146(5):1661–6.
Leitenberg D, Boutin Y, Lu DD, Bottomly K. Biochemical association of CD45 with the T cell receptor complex: regulation by CD45 isoform and during T cell activation. Immunity. 1999;10(6):701–11.
Davis MM, Boniface JJ, Reich Z, Lyons D, Hamp J, Arden B, Chien Y. Ligand recognition by αβ T cell receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:523–44.
Crispin JC, Martinez A, Alcocer-Varela J. Quantification of regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2003;21(3):273–6.
Liu MF, Wang CR, Fung LL, Wu CR. Decreased CD4+ CD25+ T cells in peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 2004;59(2):98–202.
Sabry A, Sheashaa H, El-Husseini A, Mahmoud K, Eldahshan KF, George SK, Abdel-Khalek E, El-Shafey EM, Abo-Zenah H. Proinflammatory cytokines (TNFalpha and IL-6) in Egyptian patients with SLE: its correlation with disease activity. Cytokine. 2006;35(3–4):148–53.
Kimura A, Naka T, Kishimoto T. IL-6-dependent and -independent pathways in the development of interleukin 17-producing T helper cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(29):12099104.
Zhang B, Zhang X, Tang F, Zhu L, Liu Y. Reduction of forkhead box P3 levels in CD4+CD25high T cells in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;153(2):182–7.
Salomon B, Bluestone JA. Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:225–52.
Al-Mutairi S, Al-Awadhi A, Raghupathy R, Al-Khawari H, Sada P, Al-Herz A, Rawoot P. Lupus patients with pulmonary involvement have a pro-inflammatory cytokines profile. Rheumatol Int. 2007;27(7):621–30.
Ishida H, Muchamuel T, Sakaguchi S, Andrade S, Menon S, Howard M. Continuous administration of anti-interleukin 10 antibodies delays onset of autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1994;179:305–10.
Awad MR, El-Gamel A, Hasleton P, Turner DM, Sinnott PJ, Hutchinson IV. Genotypic variation in the transforming growth factor beta1 gene: association with transforming growth factor production, fibrotic lung disease, and graft fibrosis after lung transplantation. Transplantation. 1998;66(8):1014–20.
Guarnizo-Zuccardi P, Lopez Y, Giraldo M, Garcia N, Rodriguez L, Ramirez L, Uribe O, Garcia L, Vasquez G. Cytokine gene polymorphisms in Colombian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens. 2007;70(5):376–82.
Kurreeman FA, Schonkeren JJ, Heijmans BT, Toes RE, Huizinga TW. Transcription of the IL10 gene reveals allele-specific regulation at the mRNA level. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13(16):1755–62.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported in parts by the grants from (1) SERB, Department of Science and Technology [F.No. SR/SO/SH-82/2005], Govt. of India, New Delhi, and (2) the University Grants Commission [F.No. 40-116/2011(SR)], Govt. of India, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dar, S.A., Janahi, E.M.A., Haque, S. et al. Superantigen influence in conjunction with cytokine polymorphism potentiates autoimmunity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Immunol Res 64, 1001–1012 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8768-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8768-4