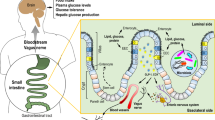
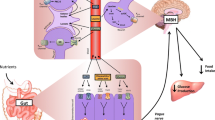
Abstract
The mechanisms by which the gut senses and responds to nutrients involve the interplay of multiple complex pathways. In addition to regulating digestion and absorption, the pathways stimulated by molecules in the gut lumen mediate gastric motility, food intake, and satiety. Furthermore, protective mechanisms are activated as necessary to prevent injury, promote healing, and limit intake and absorption of potentially toxic substances. This review provides an update on the current knowledge and recent findings related to gastric sensing of nutrients, highlighting recent research and future endeavors in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Roche JR, Blache D, Kay JK, et al.: Neuroendocrine and physiological regulation of intake with particular reference to domesticated ruminant animals. Nutr Res Rev 2008, 21:207–234.
Cummings DE, Overduin J: Gastrointestinal regulation of food intake. J Clin Invest 2007, 117:13–23.
Zhou SY, Lu YX, Owyang C: Gastric relaxation induced by hyperglycemia is mediated by vagal afferent pathways in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2008, 294:G1158–G1164.
Yuan PQ, Yang H: Neuronal activation of brain vagal-regulatory pathways and upper gut enteric plexuses by insulin hypoglycemia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2002, 283:E436–E448.
Wang WG, Chen X, Jiang H, Jiang ZY: Effects of ghrelin on glucose-sensing and gastric distension sensitive neurons in rat dorsal vagal complex. Regul Pept 2008, 146:169–175.
Darcel NP, Liou AP, Tome D, Raybould HE: Activation of vagal afferents in the rat duodenum by protein digests requires PepT1. J Nutr 2005, 135:1491–1495.
Tome D: From gut nutrient sensing to nutrient perception: a cooperative role involving CCK and 5-HT? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2007, 292:R1061–R1062.
Liddle RA: Regulation of cholecystokinin secretion by intraluminal releasing factors. Am J Physiol 1995, 269:G319–G327.
Choi S, Lee M, Shiu AL, et al.: GPR93 activation by protein hydrolysate induces CCK transcription and secretion in STC-1 cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2007, 292:G1366–G1375.
Choi S, Lee M, Shiu AL, et al.: Identification of a protein hydrolysate responsive G protein-coupled receptor in enterocytes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2007, 292:G98–G112.
Foltz M, Ansems P, Schwarz J, et al.: Protein hydrolysates induce CCK release from enteroendocrine cells and act as partial agonists of the CCK1 receptor. J Agric Food Chem 2008, 56:837–843.
Hira T, Nakajima S, Eto Y, Hara H: Calcium-sensing receptor mediates phenylalanine-induced cholecystokinin secretion in enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. FEBS J 2008, 275:4620–4626.
Bachmanov AA, Beauchamp GK: Taste receptor genes. Annu Rev Nutr 2007, 27:389–414.
Chandrashekar J, Hoon MA, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS: The receptors and cells for mammalian taste. Nature 2006, 444:288–294.
Chandrashekar J, Mueller KL, Hoon MA, et al.: T2Rs function as bitter taste receptors. Cell 2000, 100:703–711.
Sternini C, Anselmi L, Rozengurt E: Enteroendocrine cells: a site of ‘taste’ in gastrointestinal chemosensing. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2008, 15:73–78.
Margolskee RF: Molecular mechanisms of bitter and sweet taste transduction. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:1–4.
Caicedo A, Pereira E, Margolskee RF, Roper SD: Role of the G-protein subunit alpha-gustducin in taste cell responses to bitter stimuli. J Neurosci 2003, 23:9947–9952.
Wong GT, Gannon KS, Margolskee RF: Transduction of bitter and sweet taste by gustducin. Nature 1996, 381:796–800.
Chen MC, Wu SV, Reeve JR Jr, Rozengurt E: Bitter stimuli induce Ca2+ signaling and CCK release in enteroendocrine STC-1 cells: role of L-type voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2006, 291:C726–C739.
Bennett MK, Seo YK, Datta S, et al.: Selective binding of sterol regulatory element-binding protein isoforms and coregulatory proteins to promoters for lipid metabolic genes in liver. J Biol Chem 2008, 283:15628–15637.
Jeon TI, Zhu B, Larson JL, Osborne TF: SREBP-2 regulates gut peptide secretion through intestinal bitter taste receptor signaling in mice. J Clin Invest 2008, 118:3693–3700.
Dotson CD, Zhang L, Xu H, et al.: Bitter taste receptors influence glucose homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3:e3974.
Hansen MB, Witte AB: The role of serotonin in intestinal luminal sensing and secretion. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2008, 193:311–323.
Freeman SL, Bohan D, Darcel N, Raybould HE: Luminal glucose sensing in the rat intestine has characteristics of a sodium-glucose cotransporter. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006, 291:G439–G445.
Hansen MB, Skadhauge E: Signal transduction pathways for serotonin as an intestinal secretagogue. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 1997, 118:283–290.
Tack J: Chemosensitivity of the human gastrointestinal tract in health and in disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2007, 19:241–244.
Dockray GJ: Clinical endocrinology and metabolism. Gastrin Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 18:555–568.
Lindstrom E, Chen D, Norlen P, et al.: Control of gastric acid secretion: the gastrin-ECL cell-parietal cell axis. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 2001, 128:505–514.
Ceglia L, Harris SS, Rasmussen HM, Dawson-Hughes B: Activation of the calcium sensing receptor stimulates gastrin and gastric acid secretion in healthy participants. Osteoporos Int 2009, 20:71–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
deFonseka, A., Kaunitz, J. Gut sensing mechanisms. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 11, 442–447 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-009-0068-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-009-0068-5