Opinion statement
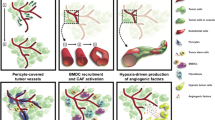
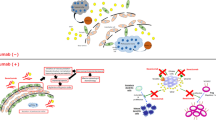
Adults with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most common primary brain tumor, have an unacceptably poor outcome with conventional cytotoxic therapies. Malignant gliomas are remarkably angiogenic, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is the dominant pro-angiogenic factor. Recent clinical trials targeting VEGF signaling have achieved unprecedented rates of durable radiographic and clinical response, while also confirming adequate safety among recurrent malignant glioma patients. An array of additional clinical trials evaluating anti-angiogenic strategies are underway for both recurrent and newly diagnosed malignant glioma patients. Promising results of these approaches suggest that the treatment of GBM may represent an emerging paradigm of anti-angiogenic therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, has been highlighted as: •Of importance ••Of major importance
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al.: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005, 352(10):987–996
Simpson L, Galanis E: Recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: advances in treatment and promising drug candidates. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2006, 6(11):1593–1607
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 1971, 285(21):1182–1186
Hanahan D, Folkman J: Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996, 86(3):353–364
Vajkoczy P, Schilling L, Ullrich A, Schmiedek P, Menger MD: Characterization of angiogenesis and microcirculation of high-grade glioma: an intravital multifluorescence microscopic approach in the athymic nude mouse. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1998, 18(5):510–520
Brem S, Cotran R, Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: a quantitative method for histologic grading. J Natl Cancer Inst 1972, 48(2):347–356
Schueneman AJ, Himmelfarb E, Geng L, Tan J, Donnelly E, Mendel D, et al.: SU11248 maintenance therapy prevents tumor regrowth after fractionated irradiation of murine tumor models. Cancer Res 2003, 63(14):4009–4016
Saleh M, Stacker SA, Wilks AF: Inhibition of growth of C6 glioma cells in vivo by expression of antisense vascular endothelial growth factor sequence. Cancer Res 1996;56(2):393–401
Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S, Keir ST, Kieran MW, Laforme A, Kaipainen A, et al.: ZD6474, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor, inhibits tumor growth of multiple nervous system tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2005, 11(22):8145–8157
Millauer B, Shawver LK, Plate KH, Risau W, Ullrich A: Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature 1994, 367(6463):576–579
Machein MR, Risau W, Plate KH: Antiangiogenic gene therapy in a rat glioma model using a dominant-negative vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Hum Gene Ther 1999, 10(7):1117–1128
Kunkel P, Ulbricht U, Bohlen P, Brockmann MA, Fillbrandt R, Stavrou D, et al.: Inhibition of glioma angiogenesis and growth in vivo by systemic treatment with a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res 2001, 61(18):6624–6628
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, et al.: Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362(6423):841–844
Jones-Bolin S, Zhao H, Hunter K, Klein-Szanto A, Ruggeri B: The effects of the oral, pan-VEGF-R kinase inhibitor CEP-7055 and chemotherapy in orthotopic models of glioblastoma and colon carcinoma in mice. Mol Cancer Ther 2006, 5(7):1744–1753
Jane EP, Premkumar DR, Pollack IF: Coadministration of sorafenib with rottlerin potently inhibits cell proliferation and migration in human malignant glioma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006, 319(3):1070–1080
Goudar RK, Shi Q, Hjelmeland MD, Keir ST, McLendon RE, Wikstrand CJ, et al.: Combination therapy of inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (AEE788) and the mammalian target of rapamycin (RAD001) offers improved glioblastoma tumor growth inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther 2005, 4(1):101–112
Goldbrunner RH, Bendszus M, Wood J, Kiderlen M, Sasaki M, Tonn JC: PTK787/ZK222584, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, decreases glioma growth and vascularization. Neurosurgery 2004, 55(2):426–432; discussion 432
Frederick B, Gustafson D, Bianco C, Ciardiello F, Dimery I, Raben D: ZD6474, an inhibitor of VEGFR and EGFR tyrosine kinase activity in combination with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006, 64(1):33–37
de Bouard S, Herlin P, Christensen JG, Lemoisson E, Gauduchon P, Raymond E, et al.: Antiangiogenic and anti-invasive effects of sunitinib on experimental human glioblastoma. Neuro-oncology 2007, 9(4):412–423
Damiano V, Melisi D, Bianco C, Raben D, Caputo R, Fontanini G, et al.: Cooperative antitumor effect of multitargeted kinase inhibitor ZD6474 and ionizing radiation in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2005, 11(15):5639–5644
Cheng SY, Huang HJ, Nagane M, Ji XD, Wang D, Shih CC, et al. Suppression of glioblastoma angiogenicity and tumorigenicity by inhibition of endogenous expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996, 93(16):8502–8507
Albert JM, Cao C, Geng L, Leavitt L, Hallahan DE, Lu B: Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonist Cilengitide enhances efficacy of radiotherapy in endothelial cell and non-small-cell lung cancer models. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006, 65(5):1536–1543
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE II, Marcello J, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, et al.: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 2007, 25(30):4722–4729
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE II, Dowell JM, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, et al.: Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13(4):1253–1259
Yap R, Veliceasa D, Emmenegger U, Kerbel RS, McKay LM, Henkin J, et al.: Metronomic low-dose chemotherapy boosts CD95-dependent antiangiogenic effect of the thrombospondin peptide ABT-510: a complementation antiangiogenic strategy. Clin Cancer Res 2005, 11(18):6678–6685
Batchelor TT, Sorensen AG, di Tomaso E, Zhang WT, Duda DG, Cohen KS, et al.: AZD2171, a Pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Cell 2007, 11(1):83–95
Taga T, Suzuki A, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Gilles FH, Stins M, Shimada H, et al.: Alpha v-Integrin antagonist EMD 121974 induces apoptosis in brain tumor cells growing on vitronectin and tenascin. Int J Cancer 2002, 98(5):690–697
Smith JW: Cilengitide Merck. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2003, 4(6):741–745
Yamada S, Bu XY, Khankaldyyan V, Gonzales-Gomez I, McComb JG, Laug WE: Effect of the angiogenesis inhibitor Cilengitide (EMD 121974) on glioblastoma growth in nude mice. Neurosurgery 2006;59(6):1304–1312; discussion 1312
Chatterjee S, Matsumura A, Schradermeier J, Gillespie GY: Human malignant glioma therapy using anti-alpha(v)beta3 integrin agents. J Neurooncol 2000, 46(2):135–144
Lamfers ML, Grill J, Dirven CM, Van Beusechem VW, Geoerger B, Van Den Berg J, et al. Potential of the conditionally replicative adenovirus Ad5-Delta24RGD in the treatment of malignant gliomas and its enhanced effect with radiotherapy. Cancer Res 2002, 62(20):5736–5742
Tonn JC, Wunderlich S, Kerkau S, Klein CE, Roosen K: Invasive behaviour of human gliomas is mediated by interindividually different integrin patterns. Anticancer Res 1998, 18(4A):2599–2605
Nabors LB, Mikkelsen T, Rosenfeld SS, Hochberg F, Akella NS, Fisher JD, et al.: Phase I and correlative biology study of cilengitide in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 2007, 25(13):1651–1657
Eskens FA, Dumez H, Hoekstra R, Perschl A, Brindley C, Bottcher S, et al.: Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of continuous twice weekly intravenous administration of Cilengitide (EMD 121974), a novel inhibitor of the integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 2003, 39(7):917–926
Reardon DA, Fink K, Nabors LB, Cloughesy T, Plotkin S, Schiff D, et al.: Phase IIa trial of cilengitide (EMD121974) single-agent therapy in patients (pts) with recurrent glioblastoma (GBM): EMD 121974-009. In 43rd Annual Meeting of American Society of Clinical Oncology. Edited by Grunberg SM. Chicago, IL: Lisa Greaves; 2007:75s
Stupp R, Goldbrunnr R, Neyns B, Schlegel U, Clement P, Grabenbauer GG, et al.: Phase I/IIa trial of cilengitide (EMD121974) and temozolomide with concomitant radiotherapy, followed by temozolomide and cilengitide maintenance therapy in patients (pts) with newly diagnosed glioblastoma (GBM). In 2007 ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings. Edited by Grunberg SM. Chicago, IL: Lisa Greaves; 2007:75s
Singh RK, Gutman M, Bucana CD, Sanchez R, Llansa N, Fidler IJ: Interferons alpha and beta down-regulate the expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995, 92(10):4562–4566
Buckner JC, Brown LD, Kugler JW, Cascino TL, Krook JE, Mailliard JA, et al.: Phase II evaluation of recombinant interferon alpha and BCNU in recurrent glioma. J Neurosurg 1995, 82(3):430–435
Brandes AA, Scelzi E, Zampieri P, Rigon A, Rotilio A, Amista P, et al.: Phase II trial with BCNU plus alpha-interferon in patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas. Am J Clin Oncol 1997, 20(4):364–367
Fine HA, Wen PY, Robertson M, O’Neill A, Kowal J, Loeffler JS, et al.: A phase I trial of a new recombinant human beta-interferon (BG9015) for the treatment of patients with recurrent gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 1997, 3(3):381–387
Yung WK, Prados M, Levin VA, Fetell MR, Bennett J, Mahaley MS, et al.: Intravenous recombinant interferon beta in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas: a phase I/II study. J Clin Oncol 1991, 9(11):1945–1949
Kerbel RS, Kamen BA: The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2004, 4(6):423–436
Kim JT, Kim JS, Ko KW, Kong DS, Kang CM, Kim MH, et al.: Metronomic treatment of temozolomide inhibits tumor cell growth through reduction of angiogenesis and augmentation of apoptosis in orthotopic models of gliomas. Oncol Rep 2006, 16(1):33–39
Son MJ, Kim JS, Kim MH, Song HS, Kim JT, Kim H, et al.: Combination treatment with temozolomide and thalidomide inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in an orthotopic glioma model. Int J Oncol 2006, 28(1):53–59
Bello L, Carrabba G, Giussani C, Lucini V, Cerutti F, Scaglione F, et al.: Low-dose chemotherapy combined with an antiangiogenic drug reduces human glioma growth in vivo. Cancer Res 2001, 61(20):7501–7506
Herrlinger U, Rieger J, Steinbach JP, Nagele T, Dichgans J, Weller M: UKT-04 trial of continuous metronomic low-dose chemotherapy with methotrexate and cyclophosphamide for recurrent glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 2005, 71(3):295–299
Tuettenberg J, Grobholz R, Korn T, Wenz F, Erber R, Vajkoczy P Continuous low-dose chemotherapy plus inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 as an antiangiogenic therapy of glioblastoma multiforme. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2005, 131(1):31–40
Kesari S, Schiff D, Doherty L, Gigas DC, Batchelor TT, Muzikansky A, et al.: Phase II study of metronomic chemotherapy for recurrent malignant gliomas in adults. Neuro-oncology 2007, 9(3):354–363
Kieran MW, Turner CD, Rubin JB, Chi SN, Zimmerman MA, Chordas C, et al.: A feasibility trial of antiangiogenic (metronomic) chemotherapy in pediatric patients with recurrent or progressive cancer. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2005, 27(11):573–581
Conrad C, Friedman HS, Reardon DA, Provenzale JM, Jackson E, Serajuddin H, et al.: A Phase I/II trial of single-agent PTK 787/ZK 222584 (PTK/ZK), a novel, oral angiogenesis inhibitor, in patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). In Proceedings of American Society of Clinical Oncology. Edited by Grunberg SM. New Orleans, LA: Lisa Greaves;2004:110
Reardon DA, Friedman HS, Yung WKA, Brada M, Conrad C, Provenzale JM, et al.: A phase I/II trial of PTK787/ZK 222584 (PTK/ZK), a novel, oral angiogenesis inhibitor, in combination with either temozolomide or lomustine for patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). In Proceedings of American Society of Clinical Oncology. Edited by Grunberg SM. New Orleans, LA: Lisa Greaves; 2004:110
Pope WB, Lai A, Nghiemphu P, Mischel P, Cloughesy TF: MRI in patients with high-grade gliomas treated with bevacizumab and chemotherapy. Neurology 2006, 66(8):1258–1260
Chen W, Delaloye S, Silverman DH, Geist C, Czernin J, Sayre J, et al.: Predicting treatment response of malignant gliomas to bevacizumab and irinotecan by imaging proliferation with [18F] fluorothymidine positron emission tomography: a pilot study. J Clin Oncol 2007, 25(30):4714–4721
Raiser J, Gallot L, Levy RM, Getch C, Mellot A, Newman S, et al.: A phase II safety study of bevacizumab in patients with multiple recurrent or progressive malignant gliomas. In Twelfth Annual Meeting of the Society of Neuro-Oncology 2007, Dallas, TX. Edited by Yung A. 2007:530
Gonzalez J, Kumar AJ, Conrad CA, Levin VA: Effect of bevacizumab on radiation necrosis of the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007, 67(2):323–326
D’Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E, Folkman J: Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994, 91(9):4082–4085
Marx GM, Pavlakis N, McCowatt S, Boyle FM, Levi JA, Bell DR, et al.: Phase II study of thalidomide in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 2001, 54(1):31–38
Short SC, Traish D, Dowe A, Hines F, Gore M, Brada M: Thalidomide as an anti-angiogenic agent in relapsed gliomas. J Neurooncol 2001, 51(1):41–45
Fine HA, Figg WD, Jaeckle K, Wen PY, Kyritsis AP, Loeffler JS, et al.: Phase II trial of the antiangiogenic agent thalidomide in patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas. J Clin Oncol 2000, 18(4):708–715
Fine HA, Wen PY, Maher EA, Viscosi E, Batchelor T, Lakhani N, et al.: Phase II trial of thalidomide and carmustine for patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas. J Clin Oncol 2003, 21(12):2299–2304
Baumann F, Bjeljac M, Kollias SS, Baumert BG, Brandner S, Rousson V, et al.: Combined thalidomide and temozolomide treatment in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 2004, 67(1–2):191–200
Chang SM, Lamborn KR, Malec M, Larson D, Wara W, Sneed P, et al.: Phase II study of temozolomide and thalidomide with radiation therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004, 60(2):353–357
Konner J, Dupont J: Use of soluble recombinant decoy receptor vascular endothelial growth factor trap (VEGF Trap) to inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor activity. Clin Colorectal Cancer 2004, 4(Suppl 2):S81–S85
Holash J, Davis S, Papadopoulos N, Croll SD, Ho L, Russell M, et al.: VEGF-Trap: a VEGF blocker with potent antitumor effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002, 99(17):11393–11398
Wachsberger PR, Burd R, Cardi C, Thakur M, Daskalakis C, Holash J, et al.: VEGF trap in combination with radiotherapy improves tumor control in u87 glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007, 67(5):1526–1537
Baish JW, Jain RK: Fractals and cancer. Cancer Res 2000, 60(14):3683–3688
Yuan F, Salehi HA, Boucher Y, Vasthare US, Tuma RF, Jain RK: Vascular permeability and microcirculation of gliomas and mammary carcinomas transplanted in rat and mouse cranial windows. Cancer Res 1994, 54(17):4564–4568
Plate KH, Mennel HD: Vascular morphology and angiogenesis in glial tumors. Exp Toxicol Pathol 1995, 47(2–3):89–94
Bullitt E, Zeng D, Gerig G, Aylward S, Joshi S, Smith JK, et al.: Vessel tortuosity and brain tumor malignancy: a blinded study. Acad Radiol 2005, 12(10):1232–1240
Deeken JF, Loscher W: The blood-brain barrier and cancer: transporters, treatment, and Trojan horses. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13(6):1663–1674
Cecchelli R, Berezowski V, Lundquist S, Culot M, Renftel M, Dehouck MP, et al.: Modelling of the blood-brain barrier in drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007, 6(8):650–661
Pardridge WM: Blood-brain barrier drug targeting: the future of brain drug development. Mol Interv 2003;3(2):90–105, 51
Bart J, Groen HJ, Hendrikse NH, van der Graaf WT, Vaalburg W, de Vries EG: The blood-brain barrier and oncology: new insights into function and modulation. Cancer Treat Rev 2000, 26(6):449–462
Liebner S, Fischmann A, Rascher G, Duffner F, Grote EH, Kalbacher H, et al.: Claudin-1 and claudin-5 expression and tight junction morphology are altered in blood vessels of human glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2000, 100(3):323–331
Shibata S: Ultrastructure of capillary walls in human brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1989, 78(6):561–571
Hobbs SK, Monsky WL, Yuan F, Roberts WG, Griffith L, Torchilin VP, et al.: Regulation of transport pathways in tumor vessels: role of tumor type and microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998, 95(8):4607–4612
Becker I, Becker KF, Meyermann R, Hollt V The multidrug-resistance gene MDR1 is expressed in human glial tumors. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1991, 82(6):516–519
Haga S, Hinoshita E, Ikezaki K, Fukui M, Scheffer GL, Uchiumi T, et al.: Involvement of the multidrug resistance protein 3 in drug sensitivity and its expression in human glioma. Jpn J Cancer Res 2001, 92(2):211–219
Regina A, Demeule M, Laplante A, Jodoin J, Dagenais C, Berthelet F, et al.: Multidrug resistance in brain tumors: roles of the blood-brain barrier. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2001, 20(1–2):13–25
Toth K, Vaughan MM, Peress NS, Slocum HK, Rustum YM: MDR1 P-glycoprotein is expressed by endothelial cells of newly formed capillaries in human gliomas but is not expressed in the neovasculature of other primary tumors. Am J Pathol 1996, 149(3):853–858
Muldoon LL, Soussain C, Jahnke K, Johanson C, Siegal T, Smith QR, et al.: Chemotherapy delivery issues in central nervous system malignancy: a reality check. J Clin Oncol 2007, 25(16):2295–2305
Jain RK, Tong RT, Munn LL: Effect of vascular normalization by antiangiogenic therapy on interstitial hypertension, peritumor edema, and lymphatic metastasis: insights from a mathematical model. Cancer Res 2007, 67(6):2729–2735
Fukumura D, Xu L, Chen Y, Gohongi T, Seed B, Jain RK Hypoxia and acidosis independently up-regulate vascular endothelial growth factor transcription in brain tumors in vivo. Cancer Res 2001, 61(16):6020–6024
Ewing JR, Brown SL, Lu M, Panda S, Ding G, Knight RA, et al.: Model selection in magnetic resonance imaging measurements of vascular permeability: Gadomer in a 9L model of rat cerebral tumor. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2006, 26(3):310–320
Kaur B, Tan C, Brat DJ, Post DE, Van Meir EG: Genetic and hypoxic regulation of angiogenesis in gliomas. J Neurooncol 2004, 70(2):229–243
Kowanetz M, Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathways: therapeutic perspective. Clin Cancer Res 2006, 12(17):5018–5022
Keyt BA, Berleau LT, Nguyen HV, Chen H, Heinsohn H, Vandlen R, et al.: The carboxyl-terminal domain (111–165) of vascular endothelial growth factor is critical for its mitogenic potency. J Biol Chem 1996, 271(13):7788–7795
Park JE, Keller GA, Ferrara N: The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) isoforms: differential deposition into the subepithelial extracellular matrix and bioactivity of extracellular matrix-bound VEGF. Mol Biol Cell 1993, 4(12):1317–1326
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, et al.: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2000, 2(10):737–744
Salven P, Orpana A, Joensuu H: Leukocytes and platelets of patients with cancer contain high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 1999, 5(3):487–491
Verheul HM, Hoekman K, Luykx-de Bakker S, Eekman CA, Folman CC, Broxterman HJ, et al.: Platelet: transporter of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 1997, 3(12 Pt 1):2187–2190
Mohle R, Green D, Moore MA, Nachman RL, Rafii S: Constitutive production and thrombin-induced release of vascular endothelial growth factor by human megakaryocytes and platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997, 94(2):663–668
Leon SP, Folkerth RD, Black PM: Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with astroglial brain tumors. Cancer 1996, 77(2):362–372
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Mennel HD, Risau W: Vascular endothelial growth factor and glioma angiogenesis: coordinate induction of VEGF receptors, distribution of VEGF protein and possible in vivo regulatory mechanisms. Int J Cancer 1994, 59(4):520–529
Plate KH, Risau W: Angiogenesis in malignant gliomas. Glia 1995, 15(3):339–347
Plate KH, Breier G, Millauer B, Ullrich A, Risau W: Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its cognate receptors in a rat glioma model of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 1993, 53(23):5822–5827
Samoto K, Ikezaki K, Ono M, Shono T, Kohno K, Kuwano M, et al.: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its possible relation with neovascularization in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 1995, 55(5):1189–1193
Schmidt NO, Westphal M, Hagel C, Ergun S, Stavrou D, Rosen EM, et al.: Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in human gliomas and their relation to angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 1999, 84(1):10–18
Fischer I, Gagner JP, Law M, Newcomb EW, Zagzag D: Angiogenesis in gliomas: biology and molecular pathophysiology. Brain Pathol 2005, 15(4):297–310
Kargiotis O, Rao JS, Kyritsis AP: Mechanisms of angiogenesis in gliomas. J Neurooncol 2006, 78(3):281–293
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E: Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 1992, 359(6398):843–845
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J: The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 2003, 9(6):669–676
Parliament MB, Allalunis-Turner MJ, Franko AJ, Olive PL, Mandyam R, Santos C, et al.: Vascular endothelial growth factor expression is independent of hypoxia in human malignant glioma spheroids and tumours. Br J Cancer 2000, 82(3):635–641
Mizukami Y, Kohgo Y, Chung DC: Hypoxia inducible factor-1 independent pathways in tumor angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13(19):5670–5674
Zagzag D, Zhong H, Scalzitti JM, Laughner E, Simons JW, Semenza GL: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in brain tumors: association with angiogenesis, invasion, and progression. Cancer 2000, 88(11):2606–2618
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995, 92(12):5510–5514
Lando D, Peet DJ, Whelan DA, Gorman JJ, Whitelaw ML: Asparagine hydroxylation of the HIF transactivation domain a hypoxic switch. Science 2002, 295(5556):858–861
Kaur B, Khwaja FW, Severson EA, Matheny SL, Brat DJ, Van Meir EG: Hypoxia and the hypoxia-inducible-factor pathway in glioma growth and angiogenesis. Neuro-oncology 2005, 7(2):134–153
Pore N, Liu S, Haas-Kogan DA, O’Rourke DM, Maity A: PTEN mutation and epidermal growth factor receptor activation regulate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA expression in human glioblastoma cells by transactivating the proximal VEGF promoter. Cancer Res 2003, 63(1):236–241
Maity A, Pore N, Lee J, Solomon D, O’Rourke DM: Epidermal growth factor receptor transcriptionally up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human glioblastoma cells via a pathway involving phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase and distinct from that induced by hypoxia. Cancer Res 2000, 60(20):5879–5886
Ostman A: PDGF receptors-mediators of autocrine tumor growth and regulators of tumor vasculature and stroma. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2004, 15(4):275–286
Ma D, Nutt CL, Shanehsaz P, Peng X, Louis DN, Kaetzel DM: Autocrine platelet-derived growth factor-dependent gene expression in glioblastoma cells is mediated largely by activation of the transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein and is associated with altered genotype and patient survival in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 2005, 65(13):5523–5534
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N, Bergsland E, Hanahan D: Benefits of targeting both pericytes and endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors. J Clin Invest 2003, 111(9):1287–1295
Abounader R, Laterra J: Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis. Neuro-oncology 2005, 7(4):436–451
Trojan J, Cloix JF, Ardourel MY, Chatel M, Anthony DD: Insulin-like growth factor type I biology and targeting in malignant gliomas. Neuroscience 2007, 145(3):795–811
Clarke K, Smith K, Gullick WJ, Harris AL Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor enhances induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by hypoxia and insulin-like growth factor-1 via a PI3 kinase dependent pathway. Br J Cancer 2001, 84(10):1322–1329
Sun L, Hui AM, Su Q, Vortmeyer A, Kotliarov Y, Pastorino S, et al.: Neuronal and glioma-derived stem cell factor induces angiogenesis within the brain. Cancer Cell 2006, 9(4):287–300
Li VW, Folkerth RD, Watanabe H, Yu C, Rupnick M, Barnes P, et al.: Microvessel count and cerebrospinal fluid basic fibroblast growth factor in children with brain tumours. Lancet 1994, 344(8915):82–86
Lamszus K, Heese O, Westphal M: Angiogenesis-related growth factors in brain tumors. Cancer Treat Res 2004, 117:169–190
Zagzag D, Miller DC, Sato Y, Rifkin DB, Burstein DE: Immunohistochemical localization of basic fibroblast growth factor in astrocytomas. Cancer Res 1990, 50(22):7393–7398
Vajkoczy P, Farhadi M, Gaumann A, Heidenreich R, Erber R, Wunder A, et al.: Microtumor growth initiates angiogenic sprouting with simultaneous expression of VEGF, VEGF receptor-2, and angiopoietin-2. J Clin Invest 2002, 109(6):777–785
Grau SJ, Trillsch F, Herms J, Thon N, Nelson PJ, Tonn JC, et al.: Expression of VEGFR3 in glioma endothelium correlates with tumor grade. J Neurooncol 2007, 82(2):141–150
Dvorak HF: Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol 2002, 20(21):4368–4380
Papapetropoulos A, Garcia-Cardena G, Madri JA, Sessa WC: Nitric oxide production contributes to the angiogenic properties of vascular endothelial growth factor in human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 1997, 100(12):3131–3139
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, van der Zee R, Li T, et al.: Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 1997, 275(5302):964–967
Rajantie I, Ilmonen M, Alminaite A, Ozerdem U, Alitalo K, Salven P: Adult bone marrow-derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells. Blood 2004, 104(7):2084–2086
Bertolini F, Shaked Y, Mancuso P, Kerbel RS: The multifaceted circulating endothelial cell in cancer: towards marker and target identification. Nat Rev Cancer 2006, 6(11):835–845
Santarelli JG, Udani V, Yung CY, Cheshier S, Wagers A, Brekken RA, et al.: Preuss Resident Research Award: bone marrow-derived Flk-1-expressing CD34+ cells contribute to the endothelium of tumor vessels in mouse brain. Clin Neurosurg 2005, 52:384–388
Lamszus K, Heese O, Westphal M: Angiogenesis-related growth factors in brain tumors. Cancer Treat Res 2004, 117:169–190
Stefanik DF, Rizkalla LR, Soi A, Goldblatt SA, Rizkalla WM: Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors are present in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 1991, 51(20):5760–5765
Ryuto M, Ono M, Izumi H, Yoshida S, Weich HA, Kohno K, et al.: Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by tumor necrosis factor alpha in human glioma cells. Possible roles of SP-1. J Biol Chem 1996, 271(45):28220–28228
Brat DJ, Bellail AC, Van Meir EG: The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro-oncology 2005, 7(2):122–133
Desbaillets I, Diserens AC, de Tribolet N, Hamou MF, Van Meir EG: Regulation of interleukin-8 expression by reduced oxygen pressure in human glioblastoma. Oncogene 1999, 18(7):1447–1456
Salmaggi A, Eoli M, Frigerio S, Silvani A, Gelati M, Corsini E, et al.: Intracavitary VEGF, bFGF, IL-8, IL-12 levels in primary and recurrent malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 2003, 62(3):297–303
Heyns AD, Eldor A, Vlodavsky I, Kaiser N, Fridman R, Panet A: The antiproliferative effect of interferon and the mitogenic activity of growth factors are independent cell cycle events. Studies with vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 1985, 161(2):297–306
Deininger MH, Weller M, Streffer J, Mittelbronn M, Meyermann R: Patterns of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 expression in human gliomas in vivo. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1999, 98(3):240–244
Harrigan MR: Angiogenic factors in the central nervous system. Neurosurgery 2003, 53(3):639–660; discussion 660–61
Guo W, Giancotti FG: Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev 2004, 5(10):816–826
Lakka SS, Gondi CS, Rao JS: Proteases and glioma angiogenesis. Brain Pathol 2005, 15(4):327–341
Serini G, Valdembri D, Bussolino F: Integrins and angiogenesis: a sticky business. Exp Cell Res 2006, 312(5):651–658
Wang D, Anderson JC, Gladson CL The role of the extracellular matrix in angiogenesis in malignant glioma tumors. Brain Pathol 2005, 15(4):318–326
Bello L, Francolini M, Marthyn P, Zhang J, Carroll RS, Nikas DC, et al.: Alpha(v)beta3 and alpha(v)beta5 integrin expression in glioma periphery. Neurosurgery 2001, 49(2):380–389; discussion 390
Abdollahi A, Griggs DW, Zieher H, Roth A, Lipson KE, Saffrich R, et al.: Inhibition of alpha(v)beta3 integrin survival signaling enhances antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2005, 11(17):6270–6279
Stan AC, Nemati MN, Pietsch T, Walter GF, Dietz H: In vivo inhibition of angiogenesis and growth of the human U-87 malignant glial tumor by treatment with an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. J Neurosurg 1995, 82(6):1044–1052
Yamada SM, Yamaguchi F, Brown R, Berger MS, Morrison RS: Suppression of glioblastoma cell growth following antisense oligonucleotide-mediated inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptor expression. Glia 1999, 28(1):66–76
Brockmann MA, Papadimitriou A, Brandt M, Fillbrandt R, Westphal M, Lamszus K: Inhibition of intracerebral glioblastoma growth by local treatment with the scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor-antagonist NK4. Clin Cancer Res 2003, 9(12):4578–4585
Bello L, Lucini V, Giussani C, Carrabba G, Pluderi M, Scaglione F, et al.: IS20I, a specific alphavbeta3 integrin inhibitor, reduces glioma growth in vivo. Neurosurgery 2003;52(1):177–185; discussion 185–186
Portnow J, Suleman S, Grossman SA, Eller S, Carson K: A cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor compared with dexamethasone in a survival study of rats with intracerebral 9L gliosarcomas. Neuro-oncology 2002, 4(1):22–25
Bello L, Giussani C, Carrabba G, Pluderi M, Lucini V, Pannacci M, et al.: Suppression of malignant glioma recurrence in a newly developed animal model by endogenous inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 2002, 8(11):3539–3548
Read TA, Farhadi M, Bjerkvig R, Olsen BR, Rokstad AM, Huszthy PC, et al.: Intravital microscopy reveals novel antivascular and antitumor effects of endostatin delivered locally by alginate-encapsulated cells. Cancer Res 2001, 61(18):6830–6837
Kirsch M, Strasser J, Allende R, Bello L, Zhang J, Black PM: Angiostatin suppresses malignant glioma growth in vivo. Cancer Res 1998, 58(20):4654–4659
Haviv F, Bradley MF, Kalvin DM, Schneider AJ, Davidson DJ, Majest SM, et al.: Thrombospondin-1 mimetic peptide inhibitors of angiogenesis and tumor growth: design, synthesis, and optimization of pharmacokinetics and biological activities. J Med Chem 2005, 48(8):2838–2846
Willett CG, Kozin SV, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Kozak KR, Boucher Y, et al.: Combined vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy and radiotherapy for rectal cancer: theory and clinical practice. Semin Oncol 2006, 33(5 Suppl 10):S35–40
Kerbel RS: Antiangiogenic therapy: a universal chemosensitization strategy for cancer? Science 2006, 312(5777):1171–1175
Shaked Y, Kerbel RS: Antiangiogenic strategies on defense: on the possibility of blocking rebounds by the tumor vasculature after chemotherapy. Cancer Res 2007, 67(15):7055–7058
Gorski DH, Beckett MA, Jaskowiak NT, Calvin DP, Mauceri HJ, Salloum RM, et al.: Blockage of the vascular endothelial growth factor stress response increases the antitumor effects of ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 1999, 59(14):3374–3378
Jain RK: Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 2001, 7(9):987–989
Jain RK: Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005, 307(5706):58–62
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS, Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, et al. Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell 2004, 6(6):553–563
Jain RK, Safabakhsh N, Sckell A, Chen Y, Jiang P, Benjamin L, et al.: Endothelial cell death, angiogenesis, and microvascular function after castration in an androgen-dependent tumor: role of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998, 95(18):10820–10825
Tong RT, Boucher Y, Kozin SV, Winkler F, Hicklin DJ, Jain RK: Vascular normalization by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 blockade induces a pressure gradient across the vasculature and improves drug penetration in tumors. Cancer Res 2004, 64(11):3731–3736
Willett CG, Boucher Y, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, et al.: Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med 2004, 10(2):145–147
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, Squire J, et al.: Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 2003, 63(18):5821–5828
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Hide T, Dirks PB: Cancer stem cells in nervous system tumors. Oncogene 2004, 23(43):7267–7273
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, et al.: Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 2004, 64(19):7011–7021
Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, Hao Y, Li Z, Hjelmeland AB, et al.: Stem cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res 2006, 66(16):7843–7848
Calabrese C, Poppleton H, Kocak M, Hogg TL, Fuller C, Hamner B, et al.: A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell 2007, 11(1):69–82
Folkins C, Man S, Xu P, Shaked Y, Hicklin DJ, Kerbel RS: Anticancer therapies combining antiangiogenic and tumor cell cytotoxic effects reduce the tumor stem-like cell fraction in glioma xenograft tumors. Cancer Res 2007, 67(8):3560–3564
Gilbertson RJ, Rich JN: Making a tumour’s bed: glioblastoma stem cells and the vascular niche. Nat Rev Cancer 2007, 7(10):733–736
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW, Loeffler JS: Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2006, 3(1):24–40
Goli KJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE, Rich J, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, et al.: Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in the treatment of malignant gliomas. In 43rd Annual Meeting of American Society of Clinical Oncology. Edited by Grunberg SM. Chicago, IL; 2007:75S
Friedman HS, Petros WP, Friedman AH, Schaaf LJ, Kerby T, Lawyer J, et al.: Irinotecan therapy in adults with recurrent or progressive malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 1999, 17(5):1516–1525
Batchelor TT, Gilbert MR, Supko JG, Carson KA, Nabors LB, Grossman SA, et al.: Phase 2 study of weekly irinotecan in adults with recurrent malignant glioma: final report of NABTT 97-11. Neuro-oncol 2004, 6(1):21–27
Cloughesy TF, Filka E, Kuhn J, Nelson G, Kabbinavar F, Friedman H, et al.: Two studies evaluating irinotecan treatment for recurrent malignant glioma using an every-3-week regimen. Cancer 2003, 97(9 Suppl):2381–2386
Prados MD, Lamborn K, Yung WK, Jaeckle K, Robins HI, Mehta M, et al.: A phase 2 trial of irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma: a North American Brain Tumor Consortium study. Neuro-oncology 2006, 8(2):189–193
Chamberlain MC Salvage chemotherapy with CPT-11 for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 2002, 56(2):183–188
Gilbert MR, Supko JG, Batchelor T, Lesser G, Fisher JD, Piantadosi S, et al. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan in adults with recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 2003, 9(8):2940–2949
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr, Cairncross JG: Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 1990, 8(7):1277–1280
Yung WK, Prados MD, Yaya-Tur R, Rosenfeld SS, Brada M, Friedman HS, et al.: Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma or anaplastic oligoastrocytoma at first relapse. Temodal Brain Tumor Group. J Clin Oncol 1999, 17(9):2762–2771
Yung WK, Albright RE, Olson J, Fredericks R, Fink K, Prados MD, et al.: A phase II study of temozolomide vs. procarbazine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Br J Cancer 2000, 83(5):588–593
Wong ET, Hess KR, Gleason MJ, Jaeckle KA, Kyritsis AP, Prados MD, et al.: Outcomes and prognostic factors in recurrent glioma patients enrolled onto phase II clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 1999, 17(8):2572–2578
Geng L, Donnelly E, McMahon G, Lin PC, Sierra-Rivera E, Oshinka H, et al.: Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling leads to reversal of tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Cancer Res 2001, 61(6):2413–2419
Kozin SV, Boucher Y, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P, Jain RK, Suit HD: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2-blocking antibody potentiates radiation-induced long-term control of human tumor xenografts. Cancer Res 2001, 61(1):39–44
Gingras MC, Roussel E, Bruner JM, Branch CD, Moser RP: Comparison of cell adhesion molecule expression between glioblastoma multiforme and autologous normal brain tissue. J Neuroimmunol 1995, 57(1–2):143–153
Gladson CL: Expression of integrin alpha v beta 3 in small blood vessels of glioblastoma tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1996, 55(11):1143–1149
Tucker GC: Integrins: molecular targets in cancer therapy. Curr Oncol Rep 2006, 8(2):96–103
Taal W, Brandsma D, de Bruin HG, Bromberg JE, Swaak-Kragten AT, Eijkenboom WM, et al.: The Incidence of Pseudo-progression in a cohort of malignant glioma patients treated with chemo-radiation with temozolomide. In The American Society of Clinical Oncology 43rd Annual Meeting. Edited by Grunberg SM. Chicago, IL: Lisa Greaves; 2007:77s
Chen W, Silverman DH, Delaloye S, Czernin J, Kamdar N, Pope W, et al.: 18F-FDOPA PET imaging of brain tumors: comparison study with 18F-FDG PET and evaluation of diagnostic accuracy. J Nucl Med 2006, 47(6):904–911
Popperl G, Kreth FW, Herms J, Koch W, Mehrkens JH, Gildehaus FJ, et al.: Analysis of 18F-FET PET for grading of recurrent gliomas: is evaluation of uptake kinetics superior to standard methods? J Nucl Med 2006, 47(3):393–403
Chen W, Cloughesy T, Kamdar N, Satyamurthy N, Bergsneider M, Liau L, et al.: Imaging proliferation in brain tumors with 18F-FLT PET: comparison with 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med 2005, 46(6):945–952
Rock JP, Hearshen D, Scarpace L, Croteau D, Gutierrez J, Fisher JL, et al.: Correlations between magnetic resonance spectroscopy and image-guided histopathology, with special attention to radiation necrosis. Neurosurgery 2002, 51(4):912–919; discussion 919–920
Cha S, Yang L, Johnson G, Lai A, Chen MH, Tihan T, et al.: Comparison of microvascular permeability measurements, K(trans), determined with conventional steady-state T1-weighted and first-pass T2*-weighted MR imaging methods in gliomas and meningiomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006, 27(2):409–417
Hylton N: Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as an imaging biomarker. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24(20):3293–3298
Jackson A, O’Connor JP, Parker GJ, Jayson GC: Imaging tumor vascular heterogeneity and angiogenesis using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13(12):3449–3459
Fuss M, Wenz F, Essig M, Muenter M, Debus J, Herman TS, et al.: Tumor angiogenesis of low-grade astrocytomas measured by dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MRI (DSC-MRI) is predictive of local tumor control after radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001, 51(2):478–482
Essig M, Wenz F, Scholdei R, Bruning R, Berchtenbreiter C, Meurer M, et al.: Dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced echo-planar imaging of cerebral gliomas. Effect of contrast medium extravasation. Acta Radiol 2002, 43(4):354–359
Provenzale JM, Wang GR, Brenner T, Petrella JR, Sorensen AG: Comparison of permeability in high-grade and low-grade brain tumors using dynamic susceptibility contrast MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002, 178(3):711–716
Warmuth C, Gunther M, Zimmer C: Quantification of blood flow in brain tumors: comparison of arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2003, 228(2):523–532
Brubaker LM, Bullitt E, Yin C, Van Dyke T, Lin W: Magnetic resonance angiography visualization of abnormal tumor vasculature in genetically engineered mice. Cancer Res 2005, 65(18):8218–8223
Bullitt E, Reardon DA, Smith JK: A review of micro- and macrovascular analyses in the assessment of tumor-associated vasculature as visualized by MR. NeuroImage 2007, 37(Suppl 1):S116–S119
Verheul HM, Pinedo HM: Possible molecular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of angiogenesis inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer 2007, 7(6):475–485
Scappaticci FA, Skillings JR, Holden SN, Gerber HP, Miller K, Kabbinavar F, et al.: Arterial thromboembolic events in patients with metastatic carcinoma treated with chemotherapy and bevacizumab. J Natl Cancer Inst 2007, 99(16):1232–1239
Glusker P, Recht L, Lane B: Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and bevacizumab. N Engl J Med 2006, 354(9):980–982; discussion 982
Ozcan C, Wong SJ, Hari P: Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and bevacizumab. N Engl J Med 2006, 354(9):980–982; discussion 982
Jubb AM, Oates AJ, Holden S, Koeppen H: Predicting benefit from anti-angiogenic agents in malignancy. Nat Rev Cancer 2006, 6(8):626–635
Miller JC, Pien HH, Sahani D, Sorensen AG, Thrall JH: Imaging angiogenesis: applications and potential for drug development. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005, 97(3):172–187
Jubb AM, Hurwitz HI, Bai W, Holmgren EB, Tobin P, Guerrero AS, et al.: Impact of vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression, thrombospondin-2 expression, and microvessel density on the treatment effect of bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24(2):217–227
Willett CG, Boucher Y, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Munn LL, Tong RT, et al.: Surrogate markers for antiangiogenic therapy and dose-limiting toxicities for bevacizumab with radiation and chemotherapy: continued experience of a phase I trial in rectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 2005, 23(31):8136–8139
Faivre S, Delbaldo C, Vera K, Robert C, Lozahic S, Lassau N, et al.: Safety, pharmacokinetic, and antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel oral multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24(1):25–35
Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Redman BG, Hudes GR, Wilding G, Figlin RA, et al.: Activity of SU11248, a multitargeted inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24(1):16–24
Drevs J, Zirrgiebel U, Schmidt-Gersbach CI, Mross K, Medinger M, Lee L, et al.: Soluble markers for the assessment of biological activity with PTK787/ZK 222584 (PTK/ZK), a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer from two phase I trials. Ann Oncol 2005, 16(4):558–565
Duda DG, Cohen KS, di Tomaso E, Au P, Klein RJ, Scadden DT, et al.: Differential CD146 expression on circulating versus tissue endothelial cells in rectal cancer patients: implications for circulating endothelial and progenitor cells as biomarkers for antiangiogenic therapy. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24(9):1449–1453
Kerbel RS, Yu J, Tran J, Man S, Viloria-Petit A, Klement G, et al.: Possible mechanisms of acquired resistance to anti-angiogenic drugs: implications for the use of combination therapy approaches. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2001, 20(1–2):79–86
Erber R, Thurnher A, Katsen AD, Groth G, Kerger H, Hammes HP, et al.: Combined inhibition of VEGF and PDGF signaling enforces tumor vessel regression by interfering with pericyte-mediated endothelial cell survival mechanisms. FASEB J 2004, 18(2):338–340
Huang J, Soffer SZ, Kim ES, McCrudden KW, Huang J, New T, et al.: Vascular remodeling marks tumors that recur during chronic suppression of angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res 2004, 2(1):36–42
De Bouard S, Guillamo JS, Christov C, Lefevre N, Brugieres P, Gola E, et al.: Antiangiogenic therapy against experimental glioblastoma using genetically engineered cells producing interferon-alpha, angiostatin, or endostatin. Hum Gene Ther 2003, 14(9):883–895
Pennacchietti S, Michieli P, Galluzzo M, Mazzone M, Giordano S, Comoglio PM: Hypoxia promotes invasive growth by transcriptional activation of the met protooncogene. Cancer Cell 2003, 3(4):347–361
Lamszus K, Kunkel P, Westphal M: Invasion as limitation to anti-angiogenic glioma therapy. Acta Neurochir Suppl 2003, 88:169–177
Rubenstein JL, Kim J, Ozawa T, Zhang M, Westphal M, Deen DF, et al.: Anti-VEGF antibody treatment of glioblastoma prolongs survival but results in increased vascular cooption. Neoplasia 2000, 2(4):306–314
Farhadi MR, Capelle HH, Erber R, Ullrich A, Vajkoczy P: Combined inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor signaling: effects on the angiogenesis, microcirculation, and growth of orthotopic malignant gliomas. J Neurosurg 2005, 102(2):363–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Institutes of Health Grant nos. 1-P50-CA108786-01, NS20023, and CA11898 and by Grant no. MO1 RR 30 through the General Clinical Research Centers Program, National Center for Research Resources, National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reardon, D.A., Desjardins, A., Rich, J.N. et al. The Emerging Role of Anti-Angiogenic Therapy for Malignant Glioma† . Curr. Treat. Options in Oncol. 9, 1–22 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-008-0052-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-008-0052-6