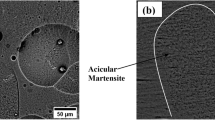
Abstract
Ti-6Al-4V specimens were fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM) to study the effect of thermal treatment on the phase transformation, elemental diffusion, microstructure, and mechanical properties. The results show that vanadium enriches around the boundary of α phases with increasing annealing temperature to 973 K, and α′ phases transform into α+β at 973 K. The typical α′ martensite microstructure transforms to fine-scale equiaxed microstructure at 973 K and the equiaxed microstructure significantly coarsens with increasing annealing temperature to 1273 K. The SLM Ti-6Al-4V alloy annealed at 973 K exhibits a well-balanced combination of strength and ductility ((1305±25) MPa and (37±3) %, respectively).
摘要
利用激光选区熔化技术(SLM)制备 Ti-6Al-4V 合金,并研究退火处理对该合金的相转变、元素扩散、显微组织结构以及力学性能的影响。结果表明,随着退火温度的升高,钒元素富集在 α′相并且α′相在973 K 转变为 α+β双相组织。在973 K,α′相所形成的马氏体组织转变为细小等轴显微组织,且该等轴组织随温度的升高发生显著粗化。经过973 K 退火的SLM Ti-6Al-4V 合金表现出良好且均衡的强度和延展性,分别为(1305±25) MPa,(37±3)%。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BANERJEE D, WILLIAMS J C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(3): 844–879.
EHTEMAM HAGHIGHI S, LU H B, JIAN G Y, CAO G H, HABIBI D, ZHANG L C. Effect of α″ martensite on the microstructure and mechanical properties of beta-type Ti-Fe-Ta alloys [J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 76: 47–54.
GEETHA M, SINGH A K, ASOKAMANI R, GOGIA A K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants-A review [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2009, 54(3): 397–425.
DONOGHUE J, ANTONYSAMY A A, MARTINA F, COLEGROVE P A, WILLIAMS S W, PRANGNELL P B. The effectiveness of combining rolling deformation with wire-arc additive manufacture on β-grain refinement and texture modification in Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Characterization, 2016, 114: 103–114.
WANG Shao-gang, WU Xin-qiang. Investigation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy joints with electron beam welding [J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 36: 663–670.
ATTAR H, CALIN M, ZHANG L C, SCUDINO S, ECKERT J. Manufacture by selective laser melting and mechanical behavior of commercially pure titanium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 593: 170–177.
ATTAR H, BOENISCH M, CALIN M, ZHANG L C, SCUDINO S, ECKERT J. Selective laser melting of in situ titanium-titanium boride composites: Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 76: 13–22.
ZHANG Shuang-yin, LIN Xin, CHEN Jing, HUANG Wei-dong. Heat-treated microstructure and mechanical properties of laser solid forming Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 28(6): 537–544.
ZHOU Li-bo, YUAN Tie-chui, LI Rui-di, TANG Jian-zhong, WANG Min-bo, MEI Fang-sheng. Anisotropic mechanical behavior of biomedical Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 762: 289–300.
WANG Pei, ECKERT J, PRASHANTH K G, WU Ming-wei, KABAN I, XI Li-xia, SCUDINO S. A review of particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(8): 2001–2034.
YANG Xin, REN Yao-jia, LIU Shi-feng, WANG Qing-juan, SHI Ming-jun. Microstructure and tensile property of SLM 316L stainless steel manufactured with fine and coarse powder mixtures [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(2): 334–343.
GU Dong-dong, HAGEDORN Y C, MEINERS Wilhelm, MENG Guang-bin, BATISTA R J S, WISSENBACH K, POPRAWE R. Densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and wear performance of selective laser melting processed commercially pure titanium [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(9): 3849–3860.
ZHOU Li-bo, YUAN Tie-chui, TANG Jian-zhong, HE Jianjun, LI Rui-di. Mechanical and corrosion behavior of titanium alloys additively manufactured by selective laser melting-A comparison between nearly β titanium, α titanium and α+β titanium [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 119: 105625.
LU Sheng-lu, TANG Hui-ping, QIAN M, HONG Quan, ZENG Li-ying, STJOHN D H. A yttrium-containing high-temperature titanium alloy additively manufactured by selective electron beam melting [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(8): 2857–2863.
WANG Pei, LAO Chang-shi, CHEN Zhang-wei, LIU Ying-kuo, WANG Hao, WENDROCK H, ECKERT J, SCUDINO S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-12Si and Al-3.5Cu-1.5Mg-1Si bimetal fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2020, 36: 18–26.
PAULY S, WANG Pei, KUEHN U, KOSIBA K. Experimental determination of cooling rates in selectively laser-melted eutectic Al-33Cu [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 22: 753–757.
LIU Shun-yu, SHIN Y C. Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V alloy: A review [J]. Materials & Design, 2019, 164: 107552.
SCHWAB H, PALM F, KUEHN U, ECKERT J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the near-beta titanium alloy Ti-5553 processed by selective laser melting [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 105: 75–80.
MURR L E, QUINONES S A, GAYTAN S M, LOPEZ M I, RODELA A, MARTINEZ E Y, HERNANDEZ D H, MARTINEZ E, MEDINA F, WICKER R B. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti-6Al-4V produced by rapid-layer manufacturing, for biomedical applications [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2009, 2(1): 20–32.
THOMPSON M K, MORONI G, VANEKER T, FADEL G, CAMPBELL R I, GIBSON I, BERNARD A, SCHULZ J, GRAF P, AHUJA B, MARTINA F. Design for additive manufacturing: Trends, opportunities, considerations, and constraints [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 65(2): 737–760.
ZHANG Lai-chang, ATTAR H. Selective laser melting of titanium alloys and titanium matrix composites for biomedical applications: A review [J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2016, 18(4): 463–475.
KARIMZADEH F, HEIDARBEIGY M, SAATCHI A. Effect of heat treatment on corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy weldments [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 206(1–3): 388–394.
ZHANG A-li, LIU Dong, WU Xin-hua, WANG Hua-ming. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser deposited Ti60A alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 585: 220–228.
VRANCKEN B, THIJS L, KRUTH J P, HUMBEECK J V. Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting: Microstructure and mechanical properties [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 541: 177–185.
WU S Q, LU Y J, GAN Y L, HUANG T T, ZHAO C Q, LIN J J, GUO S, LIN J X. Microstructural evolution and microhardness of a selective-laser-melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy after post heat treatments [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 672: 643–652.
VILARO T, COLIN C, BARTOUT J D. As-fabricated and heat-treated microstructures of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy processed by selective laser melting [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(10): 3190–3199.
ZENG L, BIELER T R. Effects of working, heat treatment, and aging on microstructural evolution and crystallographic texture of α, α′, α″ and β phases in Ti-6Al-4V wire [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 392(1, 2): 403–414.
MCQUILLAN M K. Phase transformations in titanium and its alloys [J]. Metallurgical Reviews, 1963, 8(1): 41–104.
JANDAGHI M R, POURALIAKBAR H, SABOORI A. Effect of second-phase particles evolution and lattice transformations while ultrafine graining and annealing on the corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity of Al-Mn-Si alloy [J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(10): 1065d9.
XU W, BRANDT M, SUN S, ELAMBASSERIL J, LIU Q, LATHAM K, XIA K, QIAN M. Additive manufacturing of strong and ductile Ti-6Al-4V by selective laser melting via in situ martensite decomposition [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 85: 74–84.
QAZI J I, SENKOV O N, RAHIM J, GENC A, FORES F H. Phase transformations in Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2001, 32(10): 2453–2463.
AHMED T, RACK H J. Phase transformations during cooling in α+β titanium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243(1): 206–211.
SAFDAR A, WEI L Y, SNIS A, LAI Z. Evaluation of microstructural development in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 65: 8–15.
PATTERSON A L. The Scherrer Formula for X-ray particle size determination [J]. Physical Review, 1939, 56(10): 978–982.
LOH L E, CHUA C K, YEONG W Y, SONG Jie, MAPAR M, SING S L, LIU Zhong-hong, ZHANG Dan-qing. Numerical investigation and an effective modelling on the selective laser melting (SLM) process with aluminium alloy 6061 [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 80: 288–300.
PRASHANTH K G, DAMODARAM R, MAITY T, WANG Pei, ECKERT J. Friction welding of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V parts [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 704: 66–71.
LUETJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium [M]. Berlin: Springer, 2003.
DOBROMYSLOV A V, ELKIN V A. Martensitic transformation and metastable beta-phase in binary titanium alloys with d-metals of 4–6 periods [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 44(6): 905–910.
LIU Z, WELSCH G. Literature survey on diffusivities of oxygen, aluminum, and vanadium in alpha titanium, beta titanium, and in rutile [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1988, 19(4): 1121–1125.
EHTEMAM-HAGHIGHI S, LIU Yu-jing, CAO Guang-hui, ZHANG Lai-chang. Phase transition, microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Ti-Nb-Fe alloys induced by Fe addition [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 97: 279–286.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WANG Pei provided the concept and edited the draft of manuscript. The overarching research goals were developed by J. ECKERT, S. SCUDINO, and K. G. PRASHANTH. CHEN Feng-hua and S. PILZ analyzed the calculated results. The initial draft of the manuscript was written by WANG Pei and K.G. PRASHANTH. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of interest
WANG Pei, CHEN Feng-hua, J. ECKERT, S. PILZ, S. SCUDINO, and K. G. PRASHANTH declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Foundation item: Project (2020A1515110869) supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, China; Project(GJHZ20190822095418365) supported by Shenzhen International Cooperation Research, China; Project(51775351) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019011) supported by the NTUT-SZU Joint Research Program, China; Project(2019040) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of SZU, China; Project(ASTRA6-6) supported by the European Regional Development Fund, European Union
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Chen, Fh., Eckert, J. et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V induced by annealing treatment. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 1068–1077 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4680-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4680-3