Abstract
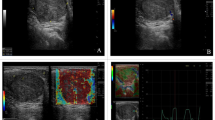
The study evaluated the value of ultrasound elastography in differentiating the benign and malignant superficial lymph nodes. A total of 112 subjects, including 82 patients with enlarged lymph nodes and 30 healthy volunteers, were recruited. All the subjects were examined by B-mode ultrasonography, power Doppler ultrasonography and elastography. Most of the patients were histopathologically confirmed by needle aspiration cytology and some patients were diagnosed by clinical data combined with follow-up findings. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of B-mode ultrasonography were 59.8%, 76.5% and 67.1%, those of the blood flow classification by power Doppler ultrasonography 77.0%, 82.3% and 79.4% and those of elastographic classification 74.7%, 97.1% and 84.5%, respectively. The elasticity of the lymph nodes was quantitatively measured and defined as stiffness value. When the stiffness value of 2.395 was taken as the cutoff point, the sensitivity and specificity of elastography were 78.41% and 98.51%, and the Youden index reached the highest, with the value being 0.7692. The stiffness values of two indeterminate benign lymph nodes, the elastrographic findings of which were rated as patterns 2 and 3, were below the cutoff point. The elastographic findings of 10 malignant lymph nodes were also classified as pattern 2 or 3. Only one of them had the stiffness values below the cutoff point. It was concluded that ultrasound elastography is a novel, noninvasive and convenient tool for the differentiation of the nature of the superficial lymph nodes in clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrari F S, Cozza S, Guazzi G, Della Sala L, Leoncini L, Lazzi S, Stefani P. Role of Doppler color in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant adenopathies. Radiol Med (Torino), 1997, 93(3): 242–245
Yang W T, Chang J, Metreweli C. Patients with breast cancer: differences in color Doppler flow and gray-scale US features of benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes. Radiology, 2000, 215(2): 568–573
Ho S S, Metrewefi C, Ahuja A T. Does anybody know how we should measure Doppler parameters in lymph nodes? Clin Radiol, 2001, 56(2): 124–126
Ophir J, Céspedes I, Ponnekanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X. Elastography: a quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason Imaging, 1991, 13(2): 111–134
Sohn Y M, Kim M J, Kim E K, Kwak J Y, Moon H J, Kim S J. Sonographic elastography combined with conventional sonography: how much is it helpful for diagnostic performance? J Ultrasound Med, 2009, 28(4): 413–420
Thitaikumar A, Mobbs L M, Kraemer-Chant C M, Garra B S, Ophir J. Breast tumor classification using axial shear strain elastography: a feasibility study. Phys Med Biol, 2008, 53(17): 4809–4823
Saleem S. Elastography and its role in breast cancer screening. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak, 2009, 19(3): 203–204
Thomas A, Kümmel S, Fritzsche F, Warm M, Ebert B, Hamm B, Fischer T. Real-time sonoelastography performed in addition to B-mode ultrasound and mammography: improved differentiation of breast lesions? Acad Radiol, 2006, 13(12): 1496–1504
Tardivon A, El Khoury C, Thibault F, Wyler A, Barreau B, Neuenschwander S. Elastography of the breast: a prospective study of 122 lesions. J Radiol, 2007, 88(5 Pt 1): 657–662
Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E, Kamma H, Takahashi H, Shiina T, Yamakawa M, Matsumura T. Breast disease: clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology, 2006, 239(2): 341–350
Ou B, Luo B M, Feng X, Yang H Y, Zhi H, Wen Y L. The value of ultrasonic elastography in differential diagnosing breast small masses. Zhonghua Chaosheng Yingxiangxue Zazhi, 2007, 16(6): 506–508 (in Chinese)
Zhi H, Xiao X Y, Yang H Y, Wen Y L, Ou B, Luo B M, Liang B L. Semi-quantitating stiffness of breast solid lesions in ultrasonic elastography. Acad Radiol, 2008, 15(11): 1347–1353
Adler D D, Carson P L, Rubin J M, Quinn-Reid D. Doppler ultrasound color flow imaging in the study of breast cancer: preliminary findings. Ultrasound Med Biol, 1990, 16(6): 553–559
Zhi H, Ou B, Luo BM, Feng X, Wen Y L, Yang H Y. Comparison of ultrasound elastography, mammography, and sonography in the diagnosis of solid breast lesions. J Ultrasound Med, 2007, 26(6): 807–815
Luo B M, Ou B, Zhi H. Factors affecting the performance of ultrasonic elastography in breast tumors and its solutions. Zhongguo Yixue Kexueyuan Xuebao, 2008, 30(1): 112–115 (in Chinese)
Luo B M, Zeng J, Ou B, Zhi H. Effects of pressure and compression frequency on diagnosis of breast masses by ultrasonic elastography. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiang Jishu, 2007, 23(8): 1152–1154 (in Chinese)
Luo B M, Zeng J, Ou B, Zhi H. Effects of region of interesting on diagnostic results of ultrasonic elastography. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiang Jishu, 2007, 23(9): 1330–1332 (in Chinese)
Jank S, Robatscher P, Emshoff R, Strobl H, Gojer G, Norer B. The diagnostic value of ultrasonography to detect occult lymph node involvement at different levels in patients with squamous cell carcinoma in the maxillofacial region. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2003, 32(1): 39–42
Dangore S B, Degwekar S S, Bhowate R R. Evaluation of the efficacy of colour Doppler ultrasound in diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopathy. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2008, 37(4): 205–212
Chan JM, Shin L K, Jeffrey R B. Ultrasonography of abnormal neck lymph nodes. Ultrasound Q, 2007, 23(1): 47–54
Li P, Cai S, Jiang Y X. Ultrasonography differential diagnosis and development of superficial lymph node diseases. Zhongguo Yixue Yingxiang Jishu, 2007, 23(9): 1409–1413 (in Chinese)
Ghirardelli M L, Jemos V, Gobbi P G. Diagnostic approach to lymph node enlargement. Haematologica, 1999, 84(3): 242–247
Miyagawa T, Tsutsumi M, Matsumura T, Kawazoe N, Ishikawa S, Shimokama T, Miyanaga N, Akaza H. Real-time elastography for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: evaluation of elastographic moving images. Jpn J Clin Oncol, 2009, 39(6): 394–398
Kamoi K, Okihara K, Ochiai A, Ukimura O, Mizutani Y, Kawauchi A, Miki T. The utility of transrectal real-time elastography in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2008, 34(7): 1025–1032
Alam F, Naito K, Horiguchi J, Fukuda H, Tachikake T, Ito K. Accuracy of sonographic elastography in the differential diagnosis of enlarged cervical lymph nodes: comparison with conventional B-mode sonography. Am J Roentgenol, 2008, 191(2): 604–610
Dighe M, Bae U, Richardson M L, Dubinsky T J, Minoshima S, Kim Y. Differential diagnosis of thyroid nodules with US elastography using carotid artery pulsation. Radiology, 2008, 248(2): 662–669
Uchida H, Hirooka Y, Itoh A, Kawashima H, Hara K, Nonogaki K, Kasugai T, Ohno E, Ohmiya N, Niwa Y, Katano Y, Ishigami M, Goto H. Feasibility of tissue elastography using transcutaneous ultrasonography for the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases. Pancreas, 2009, 38(1): 17–22
Kolokythas O, Gauthier T, Fernandez A T, Xie H, Timm B A, Cuevas C, Dighe M K, Mitsumori L M, Bruce M F, Herzka D A, Goswami G K, Andrews R T, Oas K M, Dubinsky T J, Warren B H. Ultrasound-based elastography: a novel approach to assess radio frequency ablation of liver masses performed with expandable ablation probes: a feasibility study. J Ultrasound Med, 2008, 27(6): 935–946
Salomon G, Köllerman J, Thederan I, Chun F K, Budäus L, Schlomm T, Isbarn H, Heinzer H, Huland H, Graefen M. Evaluation of prostate cancer detection with ultrasound real-time elastography: a comparison with step section pathological analysis after radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol, 2008, 54(6): 1354–1362
Furukawa M K, Kubota A, Hanamura H, Furukawa M. Clinical application of real-time tissue elastography to head and neck cancer-evaluation of cervical lymph node metastasis with realtime tissue elastography. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho, 2007, 110(7): 503–505
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Lv, Q., Yin, Y. et al. The value of ultrasound elastography in differential diagnosis of superficial lymph nodes. Front. Med. China 3, 368–374 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-009-0063-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-009-0063-0