Abstract
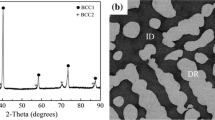
In this work, a new refractory high-entropy alloy, the Co-Cr-Mo-Nb-Ti system, was proposed as a family of candidate materials for high-temperature structural applications. CoCrMoNbTi x (x values in terms of molar ratios, x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.5 and 1.0) alloys were prepared by vacuum arc melting. The effects of variations in the Ti content on the phase constituents, microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloys were investigated using x-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy and compressive testing. The results showed that the CoCrMoNbTi0.4 alloy possessed a typical cast dendritic microstructure consisting of a single body-centered cubic (BCC) solid solution. Laves phases (Cr2Nb and Co2Ti) were formed in other alloys with different Ti contents. The results were discussed in terms of the mixing enthalpy, atomic size difference, electronegativity difference and valance electron concentrations among the elements within alloys. The alloy hardness exhibited a slightly decreasing trend as the Ti content increased, resulting from the coarser microstructure and reduced amount of Laves phases. Augmented Ti content increased the compressive strength, but decreased the ductility. Particularly, for the CoCrMoNbTi0.2 alloy, the hardness, compressive strength and fracture strain were as high as 916.46 HV0.5, 1906 MPa and 5.07%, respectively. The solid solution strengthening of the BCC matrix and the formation of hard Laves phases were two main factors contributing to alloy strengthening.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, p 299–303
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, J. Shi, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, and Q.J. Zhang, Annealing on the Structure and Properties Evolution of the CoCrFeNiCuAl High-Entropy Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 502, p 295–299
X.C. Li, D. Dou, Z.Y. Zheng, and J.C. Li, Microstructure and Properties of FeAlCrNiMox High-Entropy Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 2164–2169
Bingfeng Wang, Fu Ao, Xiaoxia Huang, Bin Liu, Yong Liu, Zezhou Li, and Xiang Zan, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of the CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloy Under High Strain Rate Compression, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 2985–2992
J.M. Zhu, H.M. Fu, H.F. Zhang, A.M. Wang, H. Li, and Z.Q. Hu, Synthesis and Properties of Multiprincipal Component AlCoCrFeNiSix Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 7210–7214
W.H. Liu, J.Y. He, H.L. Huang, H. Wang, Z.P. Lu, and C.T. Liu, Effects of Nb Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Property of CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2015, 60, p 1–8
C. Zhang, G.F. Wu, and P.Q. Dai, Phase Transformation and Aging Behavior of Al0.5CoCrFeNiSi0.2 High-Entropy Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 1918–1925
Y. Dong, L. Yiping, J. Kong, J. Zhang, and T. Li, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multi-component AlCrFeNiMox High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 573, p 96–101
M. Chuang, M. Tsai, W. Wang, S. Lin, and J. Yeh, Microstructure and Wear Behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 6308–6317
J.J. Licavoli, M.C. Gao, J.S. Sears, P.D. Jablonski, and J.A. Hawk, Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of High-Entropy Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 3685–3698
X. Qiu, Y. Zhang, L. He, and C. Liu, Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of AlCrFeCuCo High Entropy Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 549, p 195–199
Y. Chang and A. Yeh, The Evolution of Microstructures and High Temperature Properties of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy High Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 653, p 379–385
A. Li, D. Ma, and Q. Zheng, Effect of Cr on Microstructure and Properties of a Series of AlTiCrxFeCoNiCu High-Entropy Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23, p 1197–1203
C. Sajith Babu, K. Sivaprasad, V. Muthupandi, and J.A. Szpunar, Characterization of Nanocrystalline AlCoCrNiFeZn high entropy alloy produced by mechanical alloying, Proc. Mater. Sci., 2014, 5, p 1020–1026
B. Zhang, M.C. Gao, Y. Zhang, S. Yang, and S.M. Guo, Senary refractory high entropy alloy MoNbTaTiVW, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, 31, p 1207–1213
H. Jiang, L. Jiang, K. Han, L. Yiping, T. Wang, Z. Cao, and T. Li, Effects of Tungsten on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CrFeNiV0.5Wx and CrFeNi2V0.5Wx High-Entropy Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 4594–4600
N.N. Guo, L. Wang, L.S. Luo, X.Z. Li, R.R. Chen, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory High Entropy (Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi)BCC/M5Si3 In-Situ Compound, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 660, p 197–203
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, J.M. Scott, and D.B. Miracle, Mechanical Properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 Refractory High Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2011, 19, p 698–706
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, D.B. Miracle, C.P. Chuang, and P.K. Liaw, Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2010, 18, p 1758–1765
O.N. Senkov, J.M. Scott, S.V. Senkova, D.B. Miracle, and C.F. Woodward, Microstructure and Room Temperature Properties of a High-Entropy TaNbHfZrTi Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2011, 509, p 6043–6048
O.N. Senkov, J.M. Scott, S.V. Senkova, F. Meisenkothen, D.B. Miracle, and C.F. Woodward, Microstructure and Elevated Temperature Properties of a Refractory TaNbHfZrTi Alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 2012, 47, p 4062–4074
O.N. Senkov and C.F. Woodward, Microstructure and Properties of a Refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5TiZr Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, 529, p 311–320
C.-C. Juan, K.-K. Tseng, W.-L. Hsu, M.-H. Tsai, C.-W. Tsai, C.-M. Lin, S.-K. Chen, S.-J. Lin, and J.-W. Yeh, Solution Strengthening of Ductile Refractory HfMoxNbTaTiZr High-Entropy Alloys, Mater. Lett., 2016, 175, p 284–287
N.N. Guo, L. Wang, L.S. Luo, X.Z. Li, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory MoNbHfZrTi High-Entropy Alloy, Mater. Des., 2015, 81, p 87–94
O.N. Senkov, C. Woodward, and D.B. Miracle, Microstructure and Properties of Aluminum-Containing Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, JOM, 2014, 66, p 2030–2042
X. Yang, Y. Zhang, and P.K. Liaw, Microstructure and Compressive Properties of NbTiVTaAlx High Entropy Alloys, Proc. Eng., 2012, 36, p 292–298
C.-M. Lin, C.-C. Juan, C.-H. Chang, C.-W. Tsai, and J.-W. Yeh, Effect of Al Addition on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Refractory AlxHfNbTaTiZr Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 624, p 100–107
International Tables for X-ray Crystallography, Birmingham, England; 1968
B.D. Cullity and S.R. Stock, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, Pearson, Upper Saddle River, 2001
X. Yang and Y. Zhang, Prediction of High-Entropy Stabilized Solid-Solution in Multi-component Alloys, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 132, p 233–238
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue, Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element, Mater. Trans., 2005, 46, p 2817–2829
S. Guo and C.T. Liu, Phase Stability in High Entropy Alloys: Formation of Solid-Solution Phase or Amorphous Phase, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater., 2011, 21, p 433–436
N.N. Guo, L. Wang, L.S. Luo, X.Z. Li, R.R. Chen, Y.Q. Su, J.J. Guo, and H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of In-Situ MC-Carbide Particulates-Reinforced Refractory High-Entropy Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi Matrix Alloy Composite, Intermetallics, 2016, 69, p 74–77
Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y.X. Li, X. Chen, and H.W. Zhang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Refractory HfNbTiVSi0.5 High-Entropy Alloy Composite, Mater. Lett., 2016, 174, p 82–85
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51271034) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. FRF-BR-16-023A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Zhou, X. & Li, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Refractory CoCrMoNbTi High-Entropy Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 3657–3665 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2799-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2799-z