Abstract
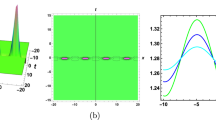
Spiral waves are a mathematical concept that organizes spatio-temporal dynamics in dissipative, spatially extended biological, physical and chemical systems. They support a variety of important phenomena, such as re-entrant cardiac arrhythmias and spatial patterns in chemical reactions. In this paper we consider a two-dimensional (2D) disturbance wave that can make the pulse wave travel around the disturbance and generate a self-sustaining spiral wave. The use of a region temporarily refractory as a disturbance in format wave is a novel mechanism for generating activity in spiral shape. In addition, it is robust for a wide variety of refractory areas and geometry shapes. This situation models the appearance of abnormal electrical activity in the heart, where the disturbance is a cardiac tissue in damage. We present a Finite Element Method (FEM) scheme for the two-dimensional FitzHugh-Nagumo (FHN) system to simulate the spiral-generation mechanism in cardiac tissue. This scheme is based on the semi implicit Eyres algorithm and we present some numerical results to demonstrate the effectiveness and usefulness of the present technique.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliev, R.R., Panilov, A.V.: A simple two-variable model of cardiac excitation. Chaos Solitons Frac. 7, 293–301 (1996)
Alonso, S., Bär, M., Echebarria, B.: Nonlinear physics of electrical wave propagation in the heart: a review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 79(9), 096601 (2016)
Arrieta, J.M., Carvalho, A.N., Rodríguez-Bernal, A.: Parabolic problems with nonlinear boundary conditions and critical nonlinearities. J. Differ. Equ. 156(2), 376–406 (1999)
Arrieta, J.M., Carvalho, A.N., Rodríguez-Bernal, A.: Attractors for Parabolic Problems with Nonlinear Boundary Condition. Unif. Bounds, Commun. Partial Differ. Equ. 25(1–2), 1–37 (2000)
Bendoukha, S., Abdelmalek, S., Kirane, M.: The global existence and asymptotic stability of solutions for a reaction-diffusion system. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 53, 103052 (2020)
Biktasheva, I., Holden, A., Biktashev, V.: Localization of response functions of spiral waves in the FitzHugh-Nagumo system. Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos 16, 1547–1555 (2006)
Bourgault, Y., Ethier, M., LeBlanc, V.G.: Simulation of Electrophysiological Waves with an Unstructured Finite Element Method. ESAIM: M2AN, 37 4, 649–661 (2003)
Bueno-Orovio, A., Kay, D., Burrage, K.: Fourier spectral methods for fractional-in-space reaction-diffusion equations. BIT Numer. Math. 54, 937–954 (2014)
Cai, L., Sun, Y., Jing, F., Li, Y.: A fully discrtet implicit-explicit fnite element method for solving the ftzhugh-nagumo model. J. Comput. Math. 38(3), 469–486 (2020)
Comtois, P., Vinet, A.: Multistability of reentrant rhythms in an ionic model of a two-dimensional annulus of cardiac tissue. Phys. Rev. E 72, 051927 (2005)
Courtemanche, M., Winfree, A.T.: Re-entrant rotating waves in a Beeler-Reuter based model of two-dimensional cardiac electrical activity. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 1, 431–444 (1991)
Fenton, F.H., Karma, A.: Vortex dynamics in three dimensional continuous myocardium with fiber rotation: filament instability and fibrillation. Chaos 8, 20–47 (1998)
Fenton, F.H., Cherry, E.M., Hastings, H.M., Evans, S.J.: Multiple mechanisms of spiral wave breakup in a model of cardiac electrical activity. Chaos 12, 852–892 (2002)
FitzHugh, R.: Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J . 1–2, 445–466 (1961)
Ganesan, P., Sterling, M., Ladavich, S., Ghoraani, B.: Computer-aided Technologies - Applications in Engineering and Medicine. Open access peer-reviewed Edited Volume, Chapter 5, 91–118 (2016)
Glass, L., Josephson, M.E.: Resetting and annihilation of reentrant abnormally rapid heartbeat. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75(10), 2059–2062 (1995)
Glass, L., Nagai, Y., Hall, K., Talajic, M., Nattel, S.: Predicting the entrainment of reentrant cardiac waves using phase resetting curves. Phys. Rev. E 65, 021908 (2002)
Göktepe, S., Kuhl, E.: Computational modeling of cardiac electrophysiology: A novel finite element approach. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng 79(2), 156–178 (2009)
Goldstein, R. E., Muraki, D. J., Petrich, D. M.: Interface proliferation and the growth of labyrinths in a reaction-diffusion system. Phys. Rev. E 53(4), 3933–3957 (1996)
Hastings, S.P.: Some mathematical problems from neurobiology. Amer. Math. Monthly 82, 881–895 (1975)
Hecht, F.: New development in freefem++. J. Numer. Math. 20(3-4), 251–265 (2012)
Henry, D.: Geometric theory of semilinear parabolic equations. In: Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 840. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York (1981)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500–44 (1952)
Kamjoo, K., Uchida, R., Ikeda, T., Fishbein, M.C., Garfinkel, A., Weiss, J.N., Karagueuzian, H.S., Chen, P.: Importance of location and timing of electrical stimuli in terminating sustained functional reentry in isolated swine ventricular tissues. Circulation 96, 2048–2060 (1997)
Keener, J.P., Tyson, J.J.: The dynamics of scroll waves in excitable media. SIAM Rev. 34, 1–39 (1992)
Liu, F., Turner, I., Anh, V., Yang, Q., Burrage, Q.: A numerical method for the fractional Fitzhugh-Nagumo monodomain model, In: Proceedings of the 16th Biennial Computational Techniques and Applications Conferenc, vol. 54, pp. C608-C629 (2013)
Liu, F., Chen, S., Turner, I., Burrage, K., Anh, V.: Numerical simulation for two-dimensional Riesz space fractional diffusion equations with a nonlinear reaction term. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 11(10), 1221–1232 (2013)
Mesin, L.: Dynamics of spiral waves in a cardiac electromechanical model with a local electrical inhomogeneity. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 45, 1220–1230 (2012)
Mesin, L., Ambrosi, D.: Spiral waves on a contractile tissue. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 126, 21 (2011)
Nagumo, J.S., Arimoto, S., Yoshizawa, Y.: An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc. Inst. Radio. Eng. 50, 2061–2070 (1962)
Panfilov, A.V.: Spiral Breakup in an Array of Coupled Cells: The Role of the Intercellular Conductance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 118101 (2002)
Panfilov, A., Hogeweg, P.: Spiral breakup in a modified FitzHugh-Nagumo model. Phys. Lett. A 176, 295–299 (1993)
Panfilov, A.V., Keldermann, R.H., Nash, M.P.: Drift and breakup of spiral waves in reaction-diffusion-mechanics systems Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 7922–7926 (2007)
Paton, K. M.: A study of wave propagation in the FitzHugh-Nagumo System, Master thesis, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver (2011)
Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Numerical Approximation of Partial Differential Equations, vol. 5. Springer, Berlin (1992)
Rogers, J.M.: Wave front fragmentation due to ventricular geometry in a model of the rabbit heart. Chaos 12, 779–787 (2002)
Rogers, J.M., McCulloch, A.D.: A collocation-Galerkin finite element model of cardiac action potential propagation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 41(8), 743–757 (1994)
Rogers, J.M., McCulloch, A.D.: Nonuniform muscle fiber orientation causes spiral wave drift in a finite element model of cardiac action potential propagation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 5(6), 496–509 (1994)
Sandstede, B., Scheel, A.: Absolute and convective instabilities of waves on unbounded and large bounded domains. Physica D 145, 233–277 (2000)
Shajahan, T.K., Sinha, S., Pandit, R.: Spiral-wave dynamics depend sensitively on inhomogeneities in mathematical models of ventricular tissue. Phys. Rev. E 75, 011929 (2007)
Sweers, G., Troy, W.C.: On the bifurcation curve for an elliptic system of FitzHugh- Nagumo type. Phys. D 177, 1–22 (2003)
Wang, Y., Cai, L., Luo, X., Ying, W., Gao, H.: Simulation of action potential propagation based on the ghost structure method. Sci. Rep. 9, 10927 (2019)
Weise, L.D., Nash, M.P., Panfilov, A.V.: A Discrete Model to Study Reaction-Diffusion-Mechanics Systems. PLoS ONE 6(7), e21934 (2011)
Xu, B., Binczak, S., Jacquir, S., Pont, O., Yahia, H.: Parameters Analysis of FitzHugh-Nagumo Model for a Reliable Simulations, 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 4334-4337 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referee for his/her comments and suggestions which improved an earlier version of this work.
C. E.Rubio-Mercedes thanks to the Carolina Foundation for the financial support for the academic exchange at the University of Cádiz, Spain. G. Lozada-Cruz thanks to the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, (FAPESP), grant 2015/24095-6, for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubio-Mercedes, C.E., Lozada-Cruz, G. & Gallego, F.O. Spiral-generation mechanism in the two-dimensional FitzHugh-Nagumo system. Ricerche mat (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11587-022-00725-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11587-022-00725-1