Abstract
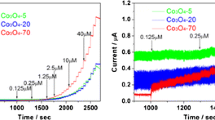
The glassy carbon electrode (GCE) embellished with porous Co3O4 as a non-enzymatic amperometric sensor is applied to the determination of glucose concentration. Spinel porous Co3O4 samples are synthesized by a facile coprecipitation method using sodium oxalate (SO) and ammonia water (AW) as different precipitants. The influence of the different precipitants on the morphology, structure, and catalytic performance is systematically studied. The electrochemical measurements reveal that the Co3O4 synthesized using sodium oxalate (SO) precipitant exhibits higher sensitivity of 1060.1 μA mM−1 cm−2 and better long-term stability with maintain in 90% after 30 days than the Co3O4 (37.25 μA mM−1 cm−2) synthesized using ammonia water (AW) precipitant. The limit of detection for Co3O4 (using SO as precipitant)/GCE is estimated to be 0.32 μM less than 0.51 μM of Co3O4 (using AW as precipitant)/GCE (S/N = 3). The reason may be that theCo3O4 (using SO as precipitant) has fluffy porous structure and higher specific surface area than the Co3O4 (using AW as precipitant), which can provide the large electroactive sites and improve the diffusion of electrolyte ions and reduces their diffusion resistance.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang XL, Liu EL, Zhang XL (2014) Non-enzymatic glucose biosensor based on copperoxide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites synthesized from water isopropanol solution. Electrochim Acta 130:253–260
Huo HH, Guo CY, Li GL, Han X, Xu CL (2014) Reticular-vein-like Cu@Cu2O/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. RSC Adv 4:20459–20465
Sun AL, Zheng JB, Sheng QL (2012) A highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel and multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanohybrid films fabricated by one-step co-electrodeposition in ionic liquids. Electrochim Acta 65:64–69
Yoo EH, Lee SY (2010) Glucose biosensors: an overview of use inclinical practice. Sensors 10:4558–4576
Lu LM, Li HB, Qu F, Zhang XB, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2011) In situ synthesis of palladium nanoparticle–graphene nanohybrids and their application in nonenzymatic glucose biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3500–3504
Jiang LC, Zhang WD (2010) A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on CuO nanoparticles-modified carbon nanotube electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1402–1407
Li K, Fan GL, Yang L, Li F (2014) Novel ultrasensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on controlled flower-like CuO hierarchical films. Sensors Actuators B Chem 199:175–182
Cui ZZ, Yin HY, Nie QL, Qin DY, Wu WW, He XL (2015) Hierarchical flower-like NiO hollow microspheres for non-enzymatic glucose sensors. J Electroanal Chem 757:51–57
Khun K, Ibupoto ZH, Liu X, Beni V, Willander M (2015) The ethylene glycol template assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Co3O4 nanowires; structural characterization and their application as glucose non-enzymatic sensor. Mater Sci Eng B 194:94–100
Chen YC, Hsu JH, Chen ZB, Lin YG, Hsu YK (2017) Fabrication of Fe3O4 nanotube arrays for high-performance non-enzymatic detection of glucose. J Electroanal Chem 788:144–149
Soomro RA, Ibupoto ZH, Uddin S, Sherazi STH, Abro MI, Willander M, Mahesar SA, Kalwar NH (2015) Glycine-assisted preparation of Co3O4 nanoflakes with enhanced performance for non-enzymaticglucose sensing. Mater Express 5:437–444
Fan SS, Zhao MG, Ding LJ, Liang JJ (2016) Synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous Co3O4 film by eggshell membrane for non-enzymatic glucose detection. J Electroanal Chem 775:52–57
Xiao XC, Peng BG, Cai LP, Zhang XM, Liu SR, Wang YD (2018) The high efficient catalytic properties for thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate using mesoporous ZnCo2O4 rods synthesized by oxalate co-precipitation method. Sci Rep 8:7571
Zhang E, Xie Y, Ci SQ, Jia JC, Wen ZH (2016) Porous Co3O4 hollow nano-dodecahedra for non-enzymatic glucose biosensor and biofuelcell. Biosens Bioelectron 81:46–53
Dong CJ, Liu X, Xiao XC, Chen G, Wang YD, Djerdj I (2014) Combustion synthesis of porous Pt-functionalized SnO2 sheets for isopropanol gas detection with a significant enhancement in response. J Mater Chem A 2:20089–20095
Xiao XC, Wang GF, Zhang MM, Wang ZZ, Zhao RJ, Wang YD (2017) Electrochemical performance of mesoporous ZnCo2O4 nanosheets as an electrode material for supercapacitor. Ionics 10:1–9
Deng SJ, Han R, Dong CJ, Xiao XX, Wu JM, Wang YD (2014) Flash synthesis of macro-/nanoporous ZnCo2O4 via self-sustained decomposition of metal-organic complexes. Mater Lett 134:138–141
Mehar SK, Ranga GR (2011) Ultralayered Co3O4 for high-performance supercapacitor applications. J Phys Chem C 115:15646–15654
Deng SJ, Xiao XC, Chen G, Wang LH, Wang YD (2016) Cd doped porous Co3O4 nanosheets as electrode material for high performance supercapacitor application. Electrochim Acta 196:316–327
Xu WN, Dai SG, Wang X, He XM, Wang MJ, Xi Y, Hu CG (2015) Nanorod-aggregated flower-like CuO grown on a carbon fiber fabric for a super high sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. J Mater Chem B 3:5777–5785
Dong XC, Xu H, Wang XW, Huang YX, Chan-Park MB, Zhang H, Wang LH, Huang W, Chen P (2012) 3D graphene-cobalt oxide electrode for high-performance supercapacitor and enzymeless glucose detection. ACS Nano 6:3206–3213
Ding Y, Wang Y, Su L, Bellagamba M, Zhang H, Lei Y (2010) Electrospun Co3O4 nanofibers for sensitive and selective glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron 26:542–548
Sun SD, Zhang XZ, Sun YX, Yang SC, Song XP, Yang ZM (2013) Facile water-assisted synthesis of cupric oxide nanourchins and their application as non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4429–4437
Huang JF, Zhu YH, Yang XL, Chen W, Zhou Y, Li CZ (2015) Flexible 3D porous CuO nanowire arrays for enzymeless glucose sensing: in situ engineered versus ex situ piled. Nanoscale 7:559–569
Zhang Z, Gu SQ, Ding YP, Jin JD (2012) A novel nonenzymatic sensor based on LaNi0.6Co0.4O3 modified electrode for hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Anal Chim Acta 745:112–117
Kung CW, Lin CY, Lai YH, Vittal R, Ho KC (2011) Cobalt oxide acicular nanorods with high sensitivity for the non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Biosens Bioelectron 27:125–131
Ho LT, Chung JS, Hur SH (2016) A highly sensitive enzyme-free glucose sensor based on Co3O4 nanoflowers and 3D grapheme oxide hydrogel fabricated via hydrothermal synthesis. Sensors Actuators B Chem 223:76–82
Kang LG, He DP, Bie LL, Jiang P (2015) Nanoporous cobalt oxide nanowires for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 220:888–894
Ding LJ, Zhao MG, Fan SS, Ma Y, Liang JJ, Wang XT, Song YW, Chen SG (2016) Preparing Co3O4 urchin-like hollow microspheres self-supporting architecture for improved glucose biosensing performance. Sensors Actuators B Chem 235:162–169
Gao YJ, Yang FY, Yu QH (2019) Three-dimensional porous Cu@Cu2O aerogels for direct voltammetric sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 186:192–201
Cao X, Wang N (2011) A novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor modified with Fe2O3 nanowire arrays. Analyst 136:4241 (6 pages)–4246
Tian LL, Liu B (2013) Fabrication of CuO nanosheets modified Cu electrode and its excellent electrocatalytic performance towards glucose. Appl Surf Sci 283:947–953
Funding
The project was supported by the Yunnan Provincial Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates 2018 and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61751107) and Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Yunnan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, X., Zhang, Z., Li, J. et al. High-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on porous Co3O4 synthesized by coprecipitation method with the different precipitants. Ionics 27, 1803–1812 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-03942-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-03942-0