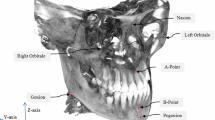
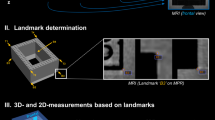
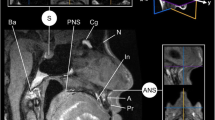
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the accuracy of three-dimensional cephalometric measurements obtained through an automatic landmark detection algorithm compared to those obtained through manual identification.
Methods
The study demonstrates a comparison of 51 cephalometric measurements (28 linear, 16 angles and 7 ratios) on 30 CBCT (cone beam computed tomography) images. The analysis was performed to compare measurements based on 21 cephalometric landmarks detected automatically and those identified manually by three observers.
Results
Inter-observer ICC for each landmark was found to be excellent (\({>}0.9\)) among three observers. The unpaired t-test revealed that there was no statistically significant difference in the measurements based on automatically detected and manually identified landmarks. The difference between the manual and automatic observation for each measurement was reported as an error. The highest mean error in the linear and angular measurements was found to be 2.63 mm (\(\hbox {Or}_{\mathrm{L}}\hbox {-Or}_{\mathrm{R}}\) distance) and \(2.12^{\circ }\) (\(\hbox {Co}_{\mathrm{L}}\hbox {-Go}_{\mathrm{L}}\)-Me angle), respectively. The highest mean error in the group of distance ratios was 0.03 (for N-Me/N-ANS and \(\hbox {Go}_{\mathrm{R}}\hbox {-Gn/S-N}\)).
Conclusion
Cephalometric measurements computed from automatic detection of landmarks on 3D CBCT image were as accurate as those computed from manual identification.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broadbent BH (1931) A new X-ray technique and its application to orthodontia. Angle Orthod 1(2):45–66. doi:10.1043/0003-3219(1931)001<0045:anxtai>2.0.co;2
Hofrath H (1931) Die Bedeutung der Röntgen, Fern-und Abstandsaufnahme für die Diagnostik der Kieferanomalien. Fortschr Orthod 1:232–242
Baumrind S, Frantz RC (1971) The reliability of head film measurements. 1. Landmark identification. Am J Orthod 60(2):111–127
Chien P, Parks E, Eraso F, Hartsfield J, Roberts W, Ofner S (2009) Comparison of reliability in anatomical landmark identification using two-dimensional digital cephalometrics and three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography in vivo. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 38(5):262–273. doi:10.1259/dmfr/81889955
Kragskov J, Bosch C, Gyldensted C, Sindet-Pedersen S (1997) Comparison of the reliability of craniofacial anatomic landmarks based on cephalometric radiographs and three-dimensional CT scans. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 34(2):111–116
Tulunoglu O, Esenlik E, Gulsen A, Tulunoglu I (2011) A comparison of three-dimensional and two-dimensional cephalometric evaluations of children with cleft lip and palate. Eur J Dent 5(4):451–458
Park CS, Park JK, Kim H, Han SS, Jeong HG, Park H (2012) Comparison of conventional lateral cephalograms with corresponding CBCT radiographs. Imaging Sci Dent 42(4):201–205
Nur M, Kayipmaz S, Bayram M, Celikoglu M, Kilkis D, Sezgin OS (2012) Conventional frontal radiographs compared with frontal radiographs obtained from cone beam computed tomography. Angle Orthod 82(4):579–584
Olmez H, Gorgulu S, Akin E, Bengi AO, Tekdemir I, Ors F (2011) Measurement accuracy of a computer-assisted three-dimensional analysis and a conventional two-dimensional method. Angle Orthod 81(3):375–382
Moshiri M, Scarfe WC, Hilgers ML, Scheetz JP, Silveira AM, Farman AG (2007) Accuracy of linear measurements from imaging plate and lateral cephalometric images derived from cone-beam computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 132(4):550–560
Gribel BF, Gribel MN, Frazao DC, McNamara JA Jr, Manzi FR (2011) Accuracy and reliability of craniometric measurements on lateral cephalometry and 3D measurements on CBCT scans. Angle Orthod 81(1):26–35
Damstra J, Fourie Z, Huddleston Slater JJ, Ren Y (2011) Reliability and the smallest detectable difference of measurements on 3-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography images. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 140(3):e107–114
Scarfe WC, Farman AG, Sukovic P (2006) Clinical applications of cone-beam computed tomography in dental practice. J Can Dent Assoc 72(1):75–80
Rossini G, Cavallini C, Cassetta M, Barbato E (2011) 3D cephalometric analysis obtained from computed tomography. Review of the literature. Ann Stomatol (Roma) 2(3–4):31–39
Hassan B, van der Stelt P, Sanderink G (2009) Accuracy of three-dimensional measurements obtained from cone beam computed tomography surface-rendered images for cephalometric analysis: influence of patient scanning position. Eur J Orthod 31(2):129–134
Zamora N, Llamas JM, Cibrian R, Gandia JL, Paredes V (2012) A study on the reproducibility of cephalometric landmarks when undertaking a three-dimensional (3D) cephalometric analysis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 17(4):e678–688
Lagravere MO, Gordon JM, Guedes IH, Flores-Mir C, Carey JP, Heo G, Major PW (2009) Reliability of traditional cephalometric landmarks as seen in three-dimensional analysis in maxillary expansion treatments. Angle Orthod 79(6):1047–1056
Gribel BF, Gribel MN, Manzi FR, Brooks SL, McNamara JA Jr (2011) From 2D to 3D: an algorithm to derive normal values for 3-dimensional computerized assessment. Angle Orthod 81(1):3–10
Fuyamada M, Nawa H, Shibata M, Yoshida K, Kise Y, Katsumata A, Ariji E, Goto S (2011) Reproducibility of landmark identification in the jaw and teeth on 3-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography images. Angle Orthod 81(5):843–849. doi:10.2319/010711-5.1
de Oliveira AE, Cevidanes LH, Phillips C, Motta A, Burke B, Tyndall D (2009) Observer reliability of three-dimensional cephalometric landmark identification on cone-beam computerized tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107(2):256–265
Ludlow JB, Gubler M, Cevidanes L, Mol A (2009) Precision of cephalometric landmark identification: cone-beam computed tomography vs conventional cephalometric views. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 136(3):312–313
Hassan B, Nijkamp P, Verheij H, Tairie J, Vink C, van der Stelt P, van Beek H (2013) Precision of identifying cephalometric landmarks with cone beam computed tomography in vivo. Eur J Orthod 35(1):38–44. doi:10.1093/ejo/cjr050
Shahidi S, Bahrampour E, Soltanimehr E, Zamani A, Oshagh M, Moattari M, Mehdizadeh A (2014) The accuracy of a designed software for automated localization of craniofacial landmarks on CBCT images. BMC Med Imaging 14(1):1471–2342
Makram M, Kamel H (2014) Reeb graph for automatic 3D cephalometry. Int J Image Process (IJIP) 8(2):17–65
Gupta A, Kharbanda O, Sardana V, Balachandran R, Sardana H (2015) A knowledge-based algorithm for automatic detection of cephalometric landmarks on CBCT images. Int J CARS:1–16. doi:10.1007/s11548-015-1173-6
Yang J, Ling X, Lu Y, Wei M, Ding G (2001) Cephalometric image analysis and measurement for orthognathic surgery. Med Biol Eng Comput 39(3):279–284
Lagravere MO, Low C, Flores-Mir C, Chung R, Carey JP, Heo G, Major PW (2010) Intraexaminer and interexaminer reliabilities of landmark identification on digitized lateral cephalograms and formatted 3-dimensional cone-beam computerized tomography images. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 137(5):598–604
Tomasi C, Bressan E, Corazza B, Mazzoleni S, Stellini E, Lith A (2011) Reliability and reproducibility of linear mandible measurements with the use of a cone-beam computed tomography and two object inclinations. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 40(4):244–250
Swennen GRJ, Schutyser FAC, Hausamen JE (2005) Three-dimensional cephalometry: a color atlas and manual. Springer, Berlin
Kharbanda OP (2009) Orthodontics: Diagnosis and Management of Malocclusion and Dentofacial Deformities, 1st edn. Elsevier, Chennai
Clinical recommendations regarding use of cone beam computed tomography in orthodontics. [corrected]. Position statement by the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology (2013). Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 116 (2):238–257
Dula K, Bornstein MM, Buser D, Dagassan-Berndt D, Ettlin DA, Filippi A, Gabioud F, Katsaros C, Krastl G, Lambrecht JT, Lauber R, Luebbers HT, Pazera P, Turp JC (2014) SADMFR guidelines for the use of cone-beam computed tomography/digital volume tomography. Swiss Dent J 124(11):1169–1183
Michele C, Federica A, Roberto DG, Alessandro S (2015) Two-dimensional and three-dimensional cephalometry using cone beam computed tomography scans. J Craniofac Surg 26(4):e311–e315. doi:10.1097/scs.0000000000001700
Silva MA, Wolf U, Heinicke F, Bumann A, Visser H, Hirsch E (2008) Cone-beam computed tomography for routine orthodontic treatment planning: a radiation dose evaluation. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 133(5):019
Swennen GJ, Schutyser, Filip, Hausamen, Jarg-Erich (2006). In: Three-dimensional cephalometry: a color atlas and manual. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/3-540-29011-7_3
Olszewski R, Cosnard G, Macq B, Mahy P, Reychler H (2006) 3D CT-based cephalometric analysis: 3D cephalometric theoretical concept and software. Neuroradiology 48(11):853–862
Lee M, Kanavakis G, Miner RM (2014) Newly defined landmarks for a three-dimensionally based cephalometric analysis: a retrospective cone-beam computed tomography scan review. Angle Orthod 27:27
Bayome M, Park JH, Kook YA (2013) New three-dimensional cephalometric analyses among adults with a skeletal class I pattern and normal occlusion. Korean J Orthod 43(2):62–73
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge National Informatics Centre (NIC), Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY), New Delhi, as a funding agency in partial support of this research work. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Shilpa Kalra and Dr. Sushma Chaurasia from All India Institute of Medical Sciences—Centre for Dental Education and Research, New Delhi, India, for manual plotting of cephalometric landmarks on the dataset used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Kharbanda, O.P., Sardana, V. et al. Accuracy of 3D cephalometric measurements based on an automatic knowledge-based landmark detection algorithm. Int J CARS 11, 1297–1309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1334-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1334-7