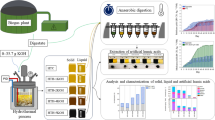
Abstract
Pyrolysis and hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) are potential technologies for renewable energy production and waste valorization using municipal wastewater sewage sludge and other lignocellulosic biomass. However, the organic-rich aqueous pyrolysis liquid (APL) and HTL aqueous phase (HTL-AP) produced currently have no apparent use and are challenging to manage. Furthermore, the toxic organic compounds in them can be harmful to the environment. Anaerobic digestion (AD) may be a viable method to manage the liquids and recover energy in APL and HTL-AP in form of methane-rich biogas. Integrating thermochemical processes with AD could promote a circular economy by recovering resources and reducing environmental pollution. The challenge, however, is the presence of toxic compounds recalcitrant to anaerobic biodegradation such as phenols and nitrogen-containing organics that can inhibit methane-producing microbes. This review presents information on APL and HTL-AP characterization and biodegradability. Feedstock composition and process operational parameters are major factors affecting APL and HTL-AP composition, subsequent toxicity, and degradability. Feedstocks with high nitrogen content as well as increased thermochemical processing temperature and retention time result in a more toxic aqueous liquid and lower methane yield. Dilution and low AD organic loading are required to produce methane. More comprehensive APL and HTL-AP chemical characterization is needed to adopt suitable treatment strategies. Pretreatments such as overliming, air stripping, partial chemical oxidation, adsorption, and solvent extraction of toxic constituents as well as co-digestion and microbial acclimatization successfully reduce toxicity and increase methane yield.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya B, Dutta A, Minaret J (2015) Review on comparative study of dry and wet torrefaction. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 12:26–37
Araya P, Chamy R, Mota M, Alves M (2000) Biodegradability and toxicity of styrene in the anaerobic digestion process. Biotechnol Lett 22:1477–1481. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005636030693
Black BA, Michener WE, Ramirez KJ et al (2016) Aqueous stream characterization from biomass fast pyrolysis and catalytic fast pyrolysis. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01766
Blum DJW, Speece RE (1991) A database environmental interspecies of chemical bacteria to toxicity in and its use and correlations comparisons. Water Environ Fed 63:198–207
Cantero-Tubilla B, Cantero DA, Martinez CM et al (2018) Characterization of the solid products from hydrothermal liquefaction of waste feedstocks from food and agricultural industries. J Supercrit Fluids 133:665–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2017.07.009
Cao Y, Pawłowski A (2012) Sewage sludge-to-energy approaches based on anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis: brief overview and energy efficiency assessment. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:1657–1665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.12.014
Carey DE, McNamara PJ, Zitomer DH (2015) Biochar from pyrolysis of biosolids for nutrient adsorption and turfgrass cultivation. Water Environ Res 87:2098–2106. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143015x14362865227391
Chen H, Wan J, Chen K et al (2016) Biogas production from hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater (HTLWW): focusing on the microbial communities as revealed by high-throughput sequencing of full-length 16S rRNA genes. Water Res 106:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.052
Chen H, Zhang C, Rao Y et al (2017) Methane potentials of wastewater generated from hydrothermal liquefaction of rice straw: focusing on the wastewater characteristics and microbial community compositions. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0830-0
Chen H, Rao Y, Cao L et al (2019) Hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge: focusing on the characterization of liquid products and their methane yields. Chem Eng J 357:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.180
Cheng J-R, Liu X-M, Chen Z-Y et al (2016) A novel mesophilic anaerobic digestion system for biogas production and in situ methane enrichment from coconut shell pyroligneous. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178:1303–1314
Cordova LT, Lad BC, Ali SA et al (2020) Valorizing a hydrothermal liquefaction aqueous phase through co-production of chemicals and lipids using the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Bioresour Technol 313:123639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123639
Demirel B, Scherer P (2008) The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:173–190
Donlon BA, Razo-Flores E et al (1995) Toxicity of N-substituted aromatics to acetoclastic methanogenic activity in granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3889–3893
Fabbri D, Torri C (2016) Linking pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion (Py-AD) for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Curr Opin Biotechnol 38:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.02.004
Feng Q, Lin Y (2017) Integrated processes of anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis for higher bioenergy recovery from lignocellulosic biomass: a brief review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 77:1272–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.022
Fernandez S, Srinivas K, Schmidt AJ et al (2018) Anaerobic digestion of organic fraction from hydrothermal liquefied algae wastewater byproduct. Bioresour Technol 247:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.030
Fonts I, Gea G, Azuara M et al (2012) Sewage sludge pyrolysis for liquid production: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:2781–2805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.02.070
Fuchs G, Boll M, Heider J (2011) Microbial degradation of aromatic compounds: from one strategy to four. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:803–816. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2652
Gai C, Zhang Y, Chen WT et al (2015) Characterization of aqueous phase from the hydrothermal liquefaction of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Bioresour Technol 184:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.118
Gollakota ARK, Kishore N, Gu S (2018) A review on hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:1378–1392
Hübner T, Mumme J (2015) Integration of pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion: use of aqueous liquor from digestate pyrolysis for biogas production. Bioresour Technol 183:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.037
Jarboe LR, Wen Z, Choi D, Brown RC (2011) Hybrid thermochemical processing: fermentation of pyrolysis-derived bio-oil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1519–1523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3495-9
Jayakody LN, Johnson CW, Whitham JM et al (2018) Thermochemical wastewater valorization: via enhanced microbial toxicity tolerance. Energy Environ Sci 11:1625–1638. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ee00460a
Kappell AD, Kimbell LK, Seib MD et al (2018) Removal of antibiotic resistance genes in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating primary clarifier effluent at 20 °C. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 4:1783–1793. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ew00270c
Kumar M, Olajire Oyedun A, Kumar A (2018) A review on the current status of various hydrothermal technologies on biomass feedstock. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:1742–1770
Leng L, Zhou W (2018) Chemical compositions and wastewater properties of aqueous phase (wastewater) produced from the hydrothermal treatment of wet biomass: a review. Energy Sour Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 40:2648–2659
Li H, Feng K (2018) Life cycle assessment of the environmental impacts and energy efficiency of an integration of sludge anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis. J Clean Prod 195:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.259
Li Y, Gu G, Zhao J, Yu H (2001) Anoxic degradation of nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds by acclimated activated sludge. Process Biochem 37:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(01)00176-5
Li R, Liu D, Zhang Y et al (2019) Improved methane production and energy recovery of post-hydrothermal liquefaction waste water via integration of zeolite adsorption and anaerobic digestion. Sci Total Environ 651:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.175
Liaw S-S, Perez VH, Westerhof R, et al (2020) Biomethane Production from pyrolytic aqueous phase: biomass acid washing and condensation temperature effect on the bio-oil and aqueous phase composition. BioEnergy Res
Liu Z, McNamara P, Zitomer D (2017) Autocatalytic pyrolysis of wastewater biosolids for product upgrading. Environ Sci Technol 51:9808–9816. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02913
Liu Z, Singer S, Tong Y et al (2018) Characteristics and applications of biochars derived from wastewater solids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 90:650–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.02.040
Liu Z, Mayer BK, Venkiteshwaran K et al (2020) The state of technologies and research for energy recovery from municipal wastewater sludge and biosolids. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 14:31–36
López Barreiro D, Prins W, Ronsse F, Brilman W (2013) Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) of microalgae for biofuel production: state of the art review and future prospects. Biomass Bioenergy 53:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.12.029
Lü F, Hua Z, Shao L, He P (2018) Loop bioenergy production and carbon sequestration of polymeric waste by integrating biochemical and thermochemical conversion processes: a conceptual framework and recent advances. Renew Energy 124:202–211
Maddi B, Panisko E, Wietsma T et al (2017) Quantitative characterization of aqueous byproducts from hydrothermal liquefaction of municipal wastes. Food Ind Wastes Biomass Grown Waste. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02367
Madigou C, Poirier S, Bureau C, Chapleur O (2016) Acclimation strategy to increase phenol tolerance of an anaerobic microbiota. Bioresour Technol 216:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.045
Monlau F, Sambusiti C, Antoniou N et al (2015) A new concept for enhancing energy recovery from agricultural residues by coupling anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis process. Appl Energy 148:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.03.024
Mukarakate C, Evans RJ, Deutch S et al (2017) Reforming biomass derived pyrolysis bio-oil aqueous phase to fuels. Energy Fuels 31:1600–1607. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02463
Nelson M, Zhu L, Thiel A et al (2013) Microbial utilization of aqueous co-products from hydrothermal liquefaction of microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata. Bioresour Technol 136:522–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.074
Pecchi M, Baratieri M (2019) Coupling anaerobic digestion with gasification, pyrolysis or hydrothermal carbonization: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 105:462–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.02.003
Pokorna E, Postelmans N, Jenicek P et al (2009) Study of bio-oils and solids from flash pyrolysis of sewage sludges. Fuel 88:1344–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.02.020
Posmanik R, Labatut RA, Kim AH et al (2017) Coupling hydrothermal liquefaction and anaerobic digestion for energy valorization from model biomass feedstocks. Bioresour Technol 233:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.095
Ran H, Zhang J, Gao Q et al (2014) Analysis of biodegradation performance of furfural and 5- hydroxymethylfurfural by Amorphotheca resinae ZN1. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-7-51
Righi S, Bandini V, Marazza D et al (2016) Life Cycle Assessment of high ligno-cellulosic biomass pyrolysis coupled with anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 212:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.04.052
Rivard CJ, Grohmann K (1991) Degradation of furfural (2- furaldehyde) to methane and carbon dioxide by an anaerobic consortium. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 28–29:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02922608
Ross JJ, Zitomer DH, Miller TR et al (2016) Emerging investigators series: pyrolysis removes common microconstituents triclocarban, triclosan, and nonylphenol from biosolids. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 2:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ew00229j
Seiple TE, Coleman AM, Skaggs RL (2017) Municipal wastewater sludge as a sustainable bioresource in the United States. J Environ Manage 197:673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.032
Seyedi S (2018) Anaerobic Co-digestion of Aqueous Liquid from Biosolids Pyrolysis. Master’s Thesis. Marquette University. Milwaukee, WI. USA
Seyedi S, Venkiteshwaran K, Zitomer D (2019) Toxicity of various pyrolysis liquids from biosolids on methane production yield. Front Energy Res 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2019.00005
Seyedi S, Venkiteshwaran K, Benn N, Zitomer D (2020) Inhibition during anaerobic co-digestion of aqueous pyrolysis liquid from wastewater solids and synthetic primary sludge. Sustainability 12:3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083441
Shanmugam SR, Adhikari S, Wang Z, Shakya R (2017) Treatment of aqueous phase of bio-oil by granular activated carbon and evaluation of biogas production. Bioresour Technol 223:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.008
Si B, Li J, Zhu Z et al (2018) Inhibitors degradation and microbial response during continuous anaerobic conversion of hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater. Sci Total Environ 630:1124–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.310
Si B, Yang L, Zhou X et al (2019) Anaerobic conversion of the hydrothermal liquefaction aqueous phase: fate of organics and intensification with granule activated carbon/ozone pretreatment. Green Chem 21:1305–1318. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8gc02907e
Skaggs RL, Coleman AM, Seiple TE, Milbrandt AR (2017) Waste-to-Energy biofuel production potential for selected feedstocks in the conterminous United States. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:2640–2651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.09.107
Speece RE (1996) Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial wastewaters. Archae Press, Nashville
Speece RE (2008) Anaerobic biotechnology and odor/corrosion control for municipalities and industries. Archae Press, Nashville
Syed-Hassan SSA, Wang Y, Hu S et al (2017) Thermochemical processing of sewage sludge to energy and fuel: fundamentals, challenges and considerations. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 80:888–913
Tommaso G, Chen WT, Li P et al (2015) Chemical characterization and anaerobic biodegradability of hydrothermal liquefaction aqueous products from mixed-culture wastewater algae. Bioresour Technol 178:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.011
Torri C, Fabbri D (2014) Biochar enables anaerobic digestion of aqueous phase from intermediate pyrolysis of biomass. Bioresour Technol 172:335–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.021
Torri C, Pambieri G, Gualandi C et al (2020) Evaluation of the potential performance of hyphenated pyrolysis-anaerobic digestion (Py-AD) process for carbon negative fuels from woody biomass. Renew Energy 148:1190–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.10.025
Ul Islam Z, Barbary Hassan E, Zhisheng Y et al (2015) Microbial conversion of pyrolytic products to biofuels: a novel and sustainable approach toward second-generation biofuels. Artic J Ind Microbiol 42:1557–1579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1687-5
Venkiteshwaran K, Bocher B, Maki J, Zitomer D (2016) Relating anaerobic digestion microbial community and process function. Microbiol Insights 8:37. https://doi.org/10.4137/MBI.S33593
Watson GK, Caint RB (1975) Microbial metabolism of the pyridine ring metabolic pathways of pyridine biodegradation by soil bacteria. Biochem J 146:157–172
Watson J, Zhang Y, Si B et al (2018) Gasification of biowaste: a critical review and outlooks. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 83:1–17
Watson J, Wang T, Si B et al (2020) Valorization of hydrothermal liquefaction aqueous phase: pathways towards commercial viability. Prog Energy Combust Sci 77:100819
Wen C, Moreira CM, Rehmann L, Berruti F (2020) Feasibility of anaerobic digestion as a treatment for the aqueous pyrolysis condensate (APC) of birch bark. Bioresour Technol 307:123199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123199
Wierckx N, Koopman F, Ruijssenaars HJ, De Winde JH (2011) Microbial degradation of furanic compounds: biochemistry, genetics, and impact. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:1095–1105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3632-5
Xu D, Lin G, Liu L et al (2018) Comprehensive evaluation on product characteristics of fast hydrothermal liquefaction of sewage sludge at different temperatures. Energy 159:686–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.191
Yang Y, Heaven S, Venetsaneas N et al (2018) Slow pyrolysis of organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW): characterisation of products and screening of the aqueous liquid product for anaerobic digestion. Appl Energy 213:158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.01.018
Yang Z, Liu Y, Zhang J et al (2020) Improvement of biofuel recovery from food waste by integration of anaerobic digestion, digestate pyrolysis and syngas biomethanation under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. J Clean Prod 256:120594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120594
Yu X, Zhang C, Qiu L et al (2020) Anaerobic digestion of swine manure using aqueous pyrolysis liquid as an additive. Renew Energy 147:2484–2493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.10.096
Zheng M, Schideman LC, Tommaso G et al (2017) Anaerobic digestion of wastewater generated from the hydrothermal liquefaction of Spirulina: toxicity assessment and minimization. Energy Convers Manag 141:420–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.10.034
Zhou Y, Schideman L, Zheng M et al (2015) Anaerobic digestion of post-hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater for improved energy efficiency of hydrothermal bioenergy processes. Water Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.435
Zhou H, Brown RC, Wen Z (2019) Anaerobic digestion of aqueous phase from pyrolysis of biomass: reducing toxicity and improving microbial tolerance. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121976
Zhu Y, Biddy MJ, Jones SB et al (2014) Techno-economic analysis of liquid fuel production from woody biomass via hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) and upgrading. Appl Energy 129:384–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seyedi, S., Venkiteshwaran, K. & Zitomer, D. Current status of biomethane production using aqueous liquid from pyrolysis and hydrothermal liquefaction of sewage sludge and similar biomass. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 20, 237–255 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09560-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09560-y