Abstract
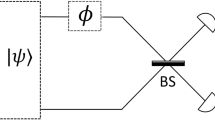
A simple protocol is described for transferring spatial orientation from Alice to Bob (two spatially separated observers). The two observers are assumed to share quantum singlet states and classical communication. The protocol assumes that Alice and Bob have complete free will (measurement independence) and is based on maximizing the Shannon mutual information between Alice and Bob’s measurement outcomes. Repeated use of this protocol for each spatial axis of Alice allows transfer of a complete three-dimensional reference frame, up to inversion of each of the axes. The technological complexity of this protocol is similar to that needed for BB84 quantum key distribution and hence is much simpler to implement than recently proposed schemes for transmission of reference frames. A second protocol based on a Bayesian formalism is also discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sagnac, Georges: The demonstration of the luminiferous aether by an interferometer in uniform rotation. Comptes Rendus 157, 708–710 (1913)
Sagnac, Georges: On the proof of the reality of the luminiferous aether by the experiment with a rotating interferometer. Comptes Rendus 157, 1410–1413 (1913)
Sagnac, G.: Circulation of the ether in rotating interferometer. Le Journal de Physique et Le Radium, 5th Ser. 4, 177-195, (1914)
Post, E.J.: Sagnac effect. Rev. Mod. Phys. 39, 475–493 (1967)
Lefevre, H.: The fiber-optic gyroscope. Artech House, Boston (1993)
Titterton, D.H., Weston, J.: Strapdown Inertial Navigation Technology, 2nd edn.In: The Institution of Engineering and Technology and The American Institute of Aeronautics, London, UK and Reston, Virginia, USA (2004)
Bertocchi, G., Alibart, O., Ostrowsky, D.B., Tanzilli, S., Baldi, P.: Single-photon Sagnac interferometer. J. Phys. B 39, 1011–1016 (2006)
Gustavson, T.L., Landragin, A., Kasevich, M.A.: Rotation sensing with a dual atom-interferometer Sagnac gyroscope. Class. Quantum Grav. 17, 2385–2398 (2000)
Gilowski, M., Schubert, C., Wendrich, T., Berg, P., Tackmann, G., Ertmer, W., Rasel E.M. : IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium, 2009 Joint with the 22nd European Frequency and Time forum, pp. 1173–1175 (2009)
Gupta, S., Murch, K.W., Moore, K.L., Purdy, T.P., Stamper-Kurn, D.M.: Bose-Einstein Condensation in a Circular Waveguide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 143201–1–143201–4 (2005)
Wang, Y.J., Anderson, D.Z., Bright, V.M., Cornell, E.A., Diot, Q., Kishimoto, T., Prentiss, M., Saravanan, R.A., Segal, S.R., Wu, S.: Atom Michelson Interferometer on a Chip Using a Bose-Einstein Condensate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 090405–1–090405–4 (2005)
Tolstikhin, O.I., Morishita, T., Watanabe, S.: Gyroscopic effects in interference of matter waves. Phys. Rev. A 72, pp. 051603(R) to 051603-4 (2005)
Kolkiran, A., Agarwal, G.S.: Heisenberg limited Sagnac interferometry. Opt. Exp. 15(11): 6798–6808; (2007)
Cooper, J.J., Hallwood, D.W., Dunningham, J.A.: Entanglement-enhanced atomic gyroscope. Phys. Rev. A 81, pp. 43624–1 to 043624–8 (2010)
Bahder, T.B.: Upper Bound on Fidelity of Classical Sagnac Gyroscope, pp. 1–5, Jan 25 (2011) quant-ph arXiv:1101.4634v1
Massar, S.: Phys. Rev. A 62(040101):040101–1 to 040101–4 (2000). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.62.040101
Massar, S., Popescu, S.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 74: 1259–1263 (1995). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.1259
Peres, A., Scudo, P.F.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 86: 4160–4162 (2001). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.4160
Bagan, E., Baig, M., Munoz Tapia, R.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 87: 257903–1 to 257903–4 (2001). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.257903
Chiribella, G., Chao, R., Yang, Y.: Superactivation of quantum gyroscopes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.3439, pp. 1–11 (2014)
Peres, A., Scudo, P. F.: Unspeakable quantum information. In: Khrennikov, A. (ed.) Quantum Theory: Reconsideration of Foundations, Series Math. Modelling in Physics, Engineering and Cognitive Sciences, pp. 283–298. Växjö Univ. Press, Växjö (2002)
Bartlett, S.D., Rudolph, T., Spekkens, R.W.: “Reference frames, superselection rules, and quantum information”, Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 555–609 (2007). doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.79.555
Peres, A., Scudo, P.F.: Transmission of a Cartesian Frame by a Quantum System. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 167901–1 to 167901–4 (2001). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.167901
Lindner, N.H., Peres, A., Terno, D.R.: Elliptic Rydberg states as direction indicators. Phys. Rev. A 68, pp. 042308–1 to 042308–11 (2003). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.68.042308
Helstrom, C.W.: Quantum Detection and Estimation Theory. Academic Press, New York (1976)
Chiribella, G., D’Ariano, G.M., Perinotti, P., Sacchi, M.F.: Efficient use of quantum resources for the transmission of a reference frame. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 180503–1 to 180503–4 (2004). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.180503
Chiribella, G., Maccone, L., Perinotti, P.: Secret quantum communication of a reference frame. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 120501–1 to 120501–4 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.120501
Kolenderski, P., Demkowicz-Dobrzanski, R.: Optimal state for keeping reference frames aligned and the platonic solids. Phys. Rev. A 78, 052333–1 to 052333–5 (2008). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.78.052333
Kofler, J., Paterek, T., Brukner, Ĉ.: Experimenter’s freedom in Bell’s theorem and quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 73, 022104–1 to 022104–7 (2006). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.73.022104
Hall, M.J.W.: Local deterministic model of singlet state correlations based on relaxing measurement independence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 0404–1 to 250404–4 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.250404
Hall, M.J.W.: Complementary contributions of indeterminism and signaling to quantum correlations. Phys. Rev. A 82, 62117–1 to 062117–5 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.82.062117
Banik, M., Gazil, M.R., Das, S., Rai, A., Kunkri, S.: Optimal free will on one side in reproducing the singlet correlation. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 45(205301), 1–6 (2012)
Thinh, L.P., Sheridan, L., Scarani, V.: Bell tests with min-entropy sources. Phys. Rev. A 87, 062121–10 (2013). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.87.062121
Pope, J.E., Kay, A.: Limited measurement dependence in multiple runs of a Bell test. Phys. Rev. A 88, 032110–1 to 032110–7 (2013). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.88.032110
Koh, D.E., Hall, M.J.W., Setiawan, Pope, J.E., Marletto, C., Kay, A., Scarani, V., Ekert, A.: Effects of Reduced Measurement independence on Bell-based randomness expansion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 160404–1 to 160404–5 (2012). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.160404
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp. 175–189 (1984)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum public-key distribution system. IBM Tech. Discl. Bull. 28, 3153–3163 (1985)
Barnett, S.M.: Quantum Information. Oxford University Press Inc, New York (2009)
Cover, T.M., Thomas, J.A.: Elements of Information Theory, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2006)
Gisin, N.: Quantum gloves: physics and information. arXiv:quant-ph/0408095, pp 1–3 (2004)
Collins, D., Diósi, L., Gisin, N., Massar, S., Popescu, S.: Quantum gloves: quantum states that encode as much as possible chirality and nothing else. Phys. Rev. A 72, 022304–1 to 022304–9, (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.72.022304
Abromowitz, M., Stegun, I.: Handbook of Mathematical Functions, 10th edn. Dover Publications Inc, New York (1972)
Acknowledgments
I dedicate this paper, with fond memory, to my friend Dr. Howard Brandt. The author is grateful to Dr. Paul Ashley for suggesting this problem.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahder, T.B. Transfer of spatial reference frame using singlet states and classical communication. Quantum Inf Process 15, 1069–1080 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-1212-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-1212-9