Abstract
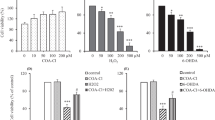
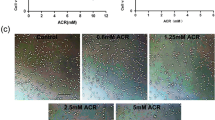
Alterations in lysosomal proteases have been implicated in many neurodegenerative diseases. The current study demonstrates a concentration-dependent decrease in PC12 cell viability and transient changes in cystatin C (CYSC), cathepsin B (CATB), cathepsin D (CATD) and caspase-3 following exposure to H2O2. Furthermore, activation of CATD occurred following exposure to H2O2 and cysteine protease suppression, while inhibition of CATD with pepstatin A significantly improved cell viability. Additionally, significant PARP cleavage, suggestive of caspase-3-like activity, was observed following H2O2 exposure, while inhibition of caspase-3 significantly increased cell viability compared to H2O2 administration alone. Collectively, our data suggest that H2O2 induced cell death is regulated at least in part by caspase-3 and CATD. Furthermore, cysteine protease suppression increases CATD expression and activity. These studies provide insight for alternate pathways and potential therapeutic targets of cell death associated with oxidative stress and lysosomal protease alterations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olanow CW, Tatton WG (1999) Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Rev Neurosci 22:123–144
Avshalumov MV, Chen BT et al (2003) Glutamate-dependent inhibition of dopamine release in striatum is mediated by a new diffusible messenger, H2O2. J Neurosci 23(7):2744–2750
Cadet JL, Brannock C (1998) Free radicals and the pathobiology of brain dopamine systems. Neurochem Res 32:117–131
Del Rio M, Velez-Pardo C (2002) Monoamine neurotoxins-induced apoptosis in lymphocytes by a common oxidative stress mechanism: involvement of hydrogen preoxide, caspase-3, and nuclear factor kappa-B, p53, c-Jun transcription factors. Biochem Pharmacol (63):677–688
Gruss-Fischer T, Fabian I (2002) Protection by ascorbic acid from denaturation and release of cytochrome c, alterations in mitochondrial membrane potential and activation of multiple capases induced by hydrogen peroxide in human leukemia cells. Biochem Pharmacol 63:1325–1335
Takuma K, Kiriu M et al (2002) Roles of cathepsins in reperfusion-induced apoptosis in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem Internatl 1246:1–7
Vancompernolle K, Herreweghe FV et al (1998) Atractyloside-induced release of cathepsin B, a protease with caspase-processing activity. FEBS Lett 438:150–158
Roberg K, Johansson U et al (1999) Lysosomal release of cathepsin D precedes relocation of cytochrome C and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential during apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. Free Rad Biol Med 27(11/12): 1228–1237
Foghsgaard L, Wissing D et al (2001) Cathepsin B acts as a dominant execution protease in tumor cell apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor. J Cell Biol 153(5):999–1009
Kagedal K, Johansson U et al (2001) The lysosomal protease cathepsin D mediates apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. FASEB J 15:1592–1594
Boland B, Campbell V (2004) A B-mediated activation the apoptotic cascade in cultured cortical neurones: a role for cathepsin L. Neurobiol Aging 25:83–91
Nakanishi H, Tominaga K et al (1994) Age related changes in activites and localizations of cathepsins D, E, B and L in rat brain tissues. Exp Neurol 126:119–128
Brunk U, Zhang H et al (1995) Exposure of cells to nonlethal concentrations of hydrogen peroxide induces degeneration-repair mechanisms involving lysosomal destablization. Free Rad Biol Med 19(6):813–822
Jung H, Lee E et al (1999) Age-related changes in ultrastructural features cathepsin B- and D-containing neurons in rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res 844(1–2):43–54
Hawkins HK, Ericsson JLE et al (1977) Lysosomes and phagosome stability in lethal cell injury. Am J Pathol 68:255–288
Nixon RA, Cataldo AM et al (1992) The lysosomal system in neurons; involvement at multiple stages of Alzheimers disease pathogenesis. Ann NY Acad Sci 674:65–88
Shibata M, Kanamori S et al (1998) Participation of cathepsins B and D in apoptosis of PC12 cells following serum deprivation. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 251:199–203
Isahara K, Ohsawa Y et al (1999) Regulation of a novel pathway for cell death by lysosomal aspartic and cysteine proteinases. Neuroscience 91(1):233–249
Yamashima T (2000) Implication of cysteine protease calpain, cathepsin and caspase in ischemic neuronal death of primates. Prog Neurobiol 62:273–295
Bahr BA, Bendiske J (2002) The neuropathogenic contributions of lysosomal dysfunction. J Neurochem 83:481–489
Bahr BA (1995) Long term hippocampal slices: a model system for investigating synaptic mechanisms and pathologic processes. J Neurosci Res 42:294–305
Barrett A (1981) Cystatin, the egg white inhibitor of cysteine proteinases. Meth Enzymol 80:771–778
Warfel AH, Sucker-Franklin D et al (1987) Constitutive secretion of cystatin C (gamma-trace) by monocytes and macrophages and its downregulation after stimulation. J Exp Med 166:1912–1917
Bjorck L, Akesson P, Bohus M, Trojinar J, Abrahamson M, Olafsson I, Grubb A (1989) Bacterial growth blocked by a synthetic peptide based on the structure of a human proteinase inhibitor. Nature 337:385–386
Marks N, Berg MJ, Makofske RC, Danho W (1990) Synthetic domains of cystatin linked to enkephalins are novel inhibitors of brain cathepsins L/B. Peptides 11:679–682
Nishio C, Yoshida K et al (2000) Involvement of cystatin C in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of cultured rat CNS neurons. Brain Res 873:252–262
Xu L, Sheng J et al (2005) Cystatin C prevents degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons: in vitro and in vivo studies. Neurobiol Dis 18:152–165
Lee DC, Close FT et al (2006) Enhanced cystatin C and lysosomal protease expression following 6-hydroxydopamine exposure. Neurotox. 27:260–276
Lee DC, Womble TA et al (2007) 6-Hydroxydopamine induces cystatin C-mediated cysteine protease suppression and cathepsin D activation. Neurochem Int 50:607–618
Levy E, Sastre M et al (2001) Codeposition of cystatin C with amyloid-beta protein in the brain of Alzheimer disease patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:94–104
Benuusi L, Ghidoni R et al (2003) Alzheimer diseased-associated cystatin C variant undergoes impaired secretion. Neurobiol Dis 13:15–21
Okamoto K, Hirai S et al (1993) Bunina bodies in amyotrphic lateral sclerosis immunostained with rabbit anti-cystatin C serum. Neurosci Lett 162:125–128
Kikuchi H, Yamada T et al (2003) Involvement of cathepsin B in the motor neuron degeneration of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 105:462–468
Wei L, Berman Y et al (1998) Instability of amyloidogenic cystatin C variant of hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis. J Biol Chem 273:11806–11814
Palm DE, Knuckey NW et al (1995) Cystatin C, a protease inhibitor, in degenerating rat hippocampal neurons following transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res 691:1–8
Yasuda Y, Kageyama T et al (1999) Characterization of new fluorogenic substrates for the rapid and sensitive assay. J Biochem (Tokyo) 215:1137–1143
Ollinger K, Brunk UT (1995) Cellular injury induced by oxidative stress is mediated through lysosmal damage. Free Rad Biol Med 19(5):565–574
Ollinger K (2000) Inhibition of cathepsin D prevents free radical induced apoptosis in rat myocardiocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 373(2):346–351
Thibodeau MS, Giardina C et al (2004) Silica-induced apoptosis in mouse alveolar macrophages in initiated by lysosomal enzyme activity. Toxicol Sci 80:34–48
Matus A, Green GD (1987) Age-related increase in a cathepsin D-like protease that degrades microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemestry 26:8083–8086
Bednarski E, Lynch G (1996) Cytosolic proteolysis of tau by cathepsin D in the hippocampus following suppression of cathepsin B and L. J Neurochem 67:1846–1855
Johnson G, Litersky J et al (1991) Proteolysis of microtubule-associated protein 2 and tubulin by cathepsin D. J Neurochem 57:1577–1583
Bi X, Haque T et al (2000) Novel cathepsin D inhibitors block the formation of hyperphosphorylated tau fragments in hippocampus. J Neurochem 74(4):1469–1477
Nagai A, Ryu JK et al (2005) Neuronal cell death induced by cystatin C in vivo and in cultured human CNS neurons is inhibited with cathepsin B. Brain Res 1066:120–128
Olsson T, Nygren J, Hakansson K, Lundblad C, Grubb A, Smith M, Weiloch T (2004) Gene deletion of cystatin C aggravates brain damage following focal ischemia but mitigates the neuronal injury after global ischemia in the mouse. Neuroscience 128:65–71
Conner GE (1989) Isolation of procathepsin D from mature cathepsin D by pepstatin affinity chromatography. Autocatalytic proteolysis of the zymogen form of the enzyme. Biochem J 263:601–604
Keppler D (2006) Towards novel anti-cancer strategies based on cystatin function. Cancer Lett 235(2):159–176
Dreyer RN, Bausch KM, Fracasso P, Hammond LJ, Wunderlich D, Wirak DO, Davis G, Brini CM, Buckholz TM, Konig G, Kamarck ME, Tamburini PP (1994) Processing of the preamyloid protein by cathepsin D is enhanced by a familial Alzheimer’s disease mutation. Eur J Biochem 224:265–271
Hetman M, Filipkowski R et al (1995) Elevated cathepsin D expression in kainate-evoked rat brain neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol 136:53–63
Aronica E, van Viliet E, Hendriksen E, Troost D, Lopes da Silva F, Gorter J. (2001) Cystatin C, a cysteine protease inhibitor, is persistently up-regulated in neurons and glia in a rat model for mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci 14:1485–1495
Deng A, Irizarry M et al (2001) Elevation of cystatin C in susceptible neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 159:1061–1068
Lukasiuk K, Pirttila T, Pitkanen A (2002) Upregulation of cystatin C expression in the rat hippocampus during epileptogenesis in the amygdala stimulation model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 43:137–145
Laenarcic B, Krasovec M et al (1991) Inactivation of human cystatin C and human kininogen by human cathepsin D. Fed Eur Biochem Soc 280(2):211–215
Acknowlegdements
We would like to thank Mrs. Glory Brown, Mrs. Frances James, Mrs. Brenda Arnold, Mrs. Shalonda Fagg and Mrs. Pamela Bryant for editorial assistance. Supported by NIH/NIGMS/MBRS S06 GM 0811, NIH/NCRR/RCMI G12RR03020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.C., Mason, C.W., Goodman, C.B. et al. Hydrogen Peroxide Induces Lysosomal Protease Alterations in PC12 Cells. Neurochem Res 32, 1499–1510 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9338-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9338-5