Abstract
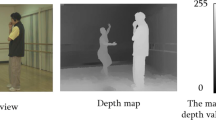
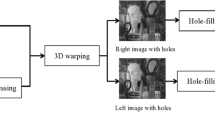
Depth-image-based rendering (DIBR) has become an important technology in 3D displaying with its great advantages. As a result, more and more 3D products copyright problems turn out. Since either the center view with depth image or the synthesized virtual views could be illegally distributed, we need to protect not only the center views but also the synthesized virtual views. In this paper, a robust watermarking method for DIBR 3D images is proposed. After applying three-level DWT to the center image, we utilize spread spectrum technology to embed the watermark into suitable coefficients of the sub-blocks of the center image, by this way we make our method robust to typical signal distortions, such as JPEG compression, noise addition and median filter. Meanwhile, in order to make the proposed method robust to some common geometric distortion attacks, SIFT-based feature points are used for geometric rectification to eliminate the effect caused by geometric distortion attacks. As the experimental results shown, the proposed method is much more robust to the common signal distortion attacks with lower BER (bit error rate) compared with existing methods. With geometric rectification, our method also performs good robustness to some simple affine transformations. In addition, the proposed watermarking method also has good robustness to the common operations of DIBR processing system.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alghoniemy M, Tewfik A (2004) Geometric invariance in image watermarking. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(2):145–153
Bas P, Chassery J-M, Macq B (2002) Geometrically invariant watermarking using feature points. IEEE Trans Image Process 11(9):1014–1028
Chan SC, Shun HY, Ng KT (2007) Image-based rendering and synthesis. IEEE Signal Process Mag 24:22–33
Deng C and Cao XB (2009) Geometrically robust image watermarking based on SIFT feature regions. Acta Photonica Sinica 1005–1010
Deng C, Gao X, Li X, Tao D (2009) A local Tchebichef moments-based robust image watermarking. Signal Process 89(8):1531–1539
Dugelay J-L, Roche S, Rey C, Doerr G (2006) Still image watermarking robust to local geometric distortions. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(9):2831–2842
Fehn C (2004) Depth-image-based rendering (dibr), compression, and transmission for a new approach on 3d-tv. SPIE Stereoscop Displays Virt Real Syst XI 5291(1):93–104
Fehn C, La Barre E, Pastoor S (2006) Interactive 3-DTV: concepts and key technologies. Proc IEEE 94(3):524–538
Fujii T, Tanimoto M (2002) Free-viewpoint TV system based on ray-space representation. Proc SPIE Three-Dimension TV, Video, Display 4864:175–189
Halici E and Alatan A (2009) Watermarking for depth-image-based rendering. IEEE Int Conf Imag Process (ICIP) 4217–4220
Hirschmüller H and Scharstein D (2007) Evaluation of cost functions for stereo matching. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Patt Recog
Hwang DC, Bae KH, Kim ES (2004) Stereo image watermarking scheme based on discrete wavelet transform and adaptive disparity estimation. Math Data/Imag Coding, Compress, Encrypt VI, Applications 5208(1):196–205
Kim HD, Lee JW, Oh TW, and Lee HK (2012) Robust DT-CWT water- marking for DIBR 3D images. IEEE Trans Broadcast 58(4)
Lee HY, Kim HS, Lee HK (2006) Robust image watermarking using local invariant features. Opt Eng 45(3):1–11
Lee MJ, Lee JW, and Lee HK (2011) Perceptual watermarking for 3D stereoscopic video using depth information. Int Conf Intell Inform Hiding Multimed Sign Process (IIHM- SP) 81–84
Levoy M and Hanrahan P (1996) Light field rendering. Proc SIGGRAPH- '96 31–42
Li LD, Guo BL, and Pa JS (2008) Feature-based image watermarking resisting geometric attacks. Innov Comput Inform Contrl (ICICIC)
Lin YH, Wu JL (2011) A digital blind watermarking for depth-image-based rendering 3D images. IEEE Trans Broadcast 57(2):602–611
Loukhaoukha K, Chouinard JY, Tsai MH (2011) Optimal image watermarking algorithm based on LWT-SVD via multi-objective ant colony optimization. J Inform Hiding Multimed Sign Process 2(4):303–319
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Malvar H, Florencio D (2003) Improved spread spectrum: a new modulation technique for robust watermarking. IEEE Trans Signal Process 51(4):898–905
Scharstein D and Pal C (2007) Learning conditional random fields for stereo. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Patt Recog 1–8
Scharstein D, Szeliski R (2003) High-accuracy stereo depth maps using structured light. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Patt Recog 1:195–202
Stirmark Benchmark 4.0 May 2004 [Online]. Available: http://www.petitcolas.net/fabien/watermarking/stirmark/
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2007) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Xiang S, Kim HJ, Huang J (2008) Invariant image watermarking based on statistical features in the low-frequency domain. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 18(6):777–790
Zhang L, Tam W (2005) Stereoscopic image generation based on depth images for 3d TV. IEEE Trans Broadcast 51(2):191–199
Zheng D, Wang S, and Zhao J (2009) RST invariant image watermarking algorithm with mathematical modeling and analysis of the watermarking process. IEEE Trans Image Process 18(5)
Zitnick C, Kang SB, Uyttendaele M, Winder S, Szeliski R (2004) High -quality video view interpolation using a layered representation. ACM Trans 1111 Graph 23(3):600–608
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Algorithm 1: Watermark embedding
Find common parts in center image using formula (2): img[M][N]
\( BS=64\begin{array}{cc}\hfill :\hfill & \hfill \begin{array}{ccc}\hfill size\hfill & \hfill of\hfill & \hfill sub- block\left(64\times 64\right)\hfill \end{array}\hfill \end{array} \)
Watermark: w[⌊M/BS⌋][⌊N/BS⌋]
Hadamard matrix: p[128][128]
k = 1
for i = 1 to [⌊N/BS⌋]
for j = 1 to [⌊N/BS⌋]
if w[i][j] == 1
Watermark_seq[k] = 1
Watermark_seq[k] = − 1
end
end
end
Scramble Watermark_seq[⌊(M/BS)⌋ × ⌊(N/BS)⌋]
num = 1
for i = 1 to M
for j = 1 to N
block = block(i : i + N − 1, j : j + N − 1)
block = 3 − DWT(block)
Choose LH 3 and HL 3 as cof[128]
\( ip=\frac{\left\langle cof,\kern0.2em p\left[num\right]\right\rangle }{\left\langle p\left[num\right],\kern0.2em p\left[num\right]\right\rangle } \)
for k = 1 to 128
cof[k] = cof[k] + (Watermark_seq[num] + 6 × ip) × p[num][k]
end
Change LH 3 and HL 3 with cof[128]
block = 3 − IDWT(block)
j = j + BS
num = num + 1
end
i = i + BS
end
Algorithm 2: Watermark extraction
Watermark: watermark[3]
BS = 64
Hadamard matrix: p[128][128]
for situation[k] in formula (6)
Find common parts in watermarked image using formula (6): img[M][N]
bit_seq[⌊(M/BS)⌋ × ⌊(N/BS)⌋]
for i = 1 to M
for j = 1 to N
block = block(i : i + N − 1, j : j + N − 1)
block = 3 − DWT(block)
Choose LH 3 and HL 3 as cof[128]
\( ip=\frac{\left\langle cof,\kern0.2em p\left[num\right]\right\rangle }{\left\langle p\left[num\right],\kern0.2em p\left[num\right]\right\rangle } \)
if ip > 0
bit_seq[num] = 1
else
bit_seq[num] = − 1
end
j = j + BS
num = num + 1
end
i = i + BS
end
watermark[k]= bit_seq
end
Similarity: NC[3]
for situation[k] in formula (6)
Compute NC[k] between watermark[k] and Watermark_seq
end
Select the watermark with biggest NC between as the final extracted watermark
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, C., Wang, S. & Niu, X. A novel watermarking for DIBR 3D images with geometric rectification based on feature points. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 649–677 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3028-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3028-0