Abstract
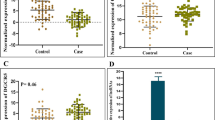
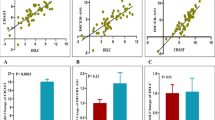
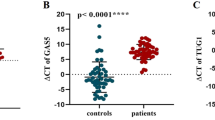
Bipolar disorders are known as chronic, recurrent, and heterogenic diseases. Regarding, diagnosis and treatment of them are very complex. The molecular mechanism and pathophysiology of bipolar disorder are slightly known. Accordingly, long noncoding RNAs are considered as one of the main factors that are dysfunctional in many diseases such as the nervous system diseases. Hence, we aim to investigate the expression of two long non coding RNAs, MALAT1 and UCA1, in patients in bipolar disorder. The levels of MALAT1 and UCA1 lncRNA were evaluated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of 50 bipolar patients and 50 healthy controls with real-time PCR. Also, ROC curve analysis and correlation analysis were performed between the gene expression and some clinical features of bipolar individuals. The significant decline of MALAT1 expression level was found in the patients compared to controls; but no significant difference was observed in the UCA1 expression level between the patients and controls. Furthermore, computational analysis of CpG Islands and miRNAs binding sites on LncRNAs, MALAT1, and UCA1 was conducted. Also, The ROC curve area (AUC) of MALAT1 was 0.80. The current results suggest that the expression level of MALAT1 could serve as a potential diagnostic biomarker for bipolar patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard D et al (2010) A long nuclear-retained non-coding RNA regulates synaptogenesis by modulating gene expression. Embo J 29:3082–3093. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2010.199
Fallah H, Azari I, Neishabouri SM, Oskooei VK, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2019) Sex-specific up-regulation of lncRNAs in peripheral blood of patients with schizophrenia. Sci Rep 9:12737–12737. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49265-z
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.082701.108
Geng JF, Liu X, Zhao HB, Fan WF, Geng JJ, Liu XZ (2018) LncRNA UCA1 inhibits epilepsy and seizure-induced brain injury by regulating miR-495/Nrf2-ARE signal pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 99:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2018.03.021
Grande I, Berk M, Birmaher B, Vieta E (2016) Bipolar disorder . Lancet 387:1561–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00241-x
Guo D, Ma J, Yan L, Li T, Li Z, Han X, Shui S (2017) Down-Regulation of Lncrna MALAT1 Attenuates Neuronal cell death through suppressing Beclin1-Dependent Autophagy by regulating Mir-30a in Cerebral ischemic stroke . Cell Physiol Biochem 43:182–194. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480337
Hilty DM, Leamon MH, Lim RF, Kelly RH, Hales RE (2006) A review of bipolar disorder in adults . Psychiatry (Edgmont) 3:43–55
Hrdlickova B, de Almeida RC, Borek Z, Withoff S (2014) Genetic variation in the non-coding genome: Involvement of micro-RNAs and long non-coding RNAs in disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1910–1922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.03.011
Jianying Tian HX, Chen G, Wang H, Bi Y, Gao H (2017) Roles of lncRNA UCA 1-miR-18 a-SOX 6 axis in preventing hypoxia injury following cerebral ischemia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 10:8187–8198
Johnson R (2012) Long non-coding RNAs in Huntington’s disease neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 46:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.006
Kim KH et al (2015) Transcriptomic analysis of induced pluripotent stem cells derived from patients with bipolar disorder from an old order Amish Pedigree. PLoS One 10:e0142693. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142693
Kraus TFJ, Haider M, Spanner J, Steinmaurer M, Dietinger V, Kretzschmar HA (2017) Altered long noncoding RNA expression precedes the course of parkinson’s disease-a preliminary report. Mol Neurobiol 54:2869–2877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9854-x
Lee DY et al (2015) Dysregulation of long non-coding RNAs in mouse models of localization-related epilepsy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 462:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.04.149
Lin M, Pedrosa E, Shah A, Hrabovsky A, Maqbool S, Zheng D, Lachman HM (2011) RNA-Seq of Human neurons derived from iPS cells reveals candidate long non-coding RNAs involved in neurogenesis and neuropsychiatric disorders. PLoS One 6:e23356. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023356
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method . Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luykx J, Giuliani F, Giuliani G, Veldink J (2018) Coding and non-coding RNA dysregulation in bipolar disorder. bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/291385
Ma XY, Wang JH, Wang JL, Ma CX, Wang XC, Liu FS (2015) Malat1 as an evolutionarily conserved lncRNA, plays a positive role in regulating proliferation and maintaining undifferentiated status of early-stage hematopoietic cells. BMC Genom 16:676. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1881-x
Magalhaes JE, Sampaio Rocha-Filho PA (2018) Migraine and cerebrovascular diseases: Epidemiology, pathophysiological, and clinical considerations. Headache. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.13378
Miller BH et al (2012) MicroRNA-132 dysregulation in schizophrenia has implications for both neurodevelopment and adult brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:3125–3130. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1113793109
Pereira Fernandes D, Bitar M, Jacobs FMJ, Barry G (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in Neuronal aging. Noncoding RNA 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4020012
Riva P, Ratti A, Venturin M (2016) The long non-coding RNAs in neurodegenerative diseases: novel mechanisms of pathogenesis. Curr Alzheimer Res 13:1219–1231
Severus E, Bauer M (2013) Diagnosing bipolar disorders in DSM-5. Int J Bipolar Disord 1:14–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/2194-7511-1-14
Spadaro PA, Bredy TW (2012) Emerging role of non-coding RNA in neural plasticity, cognitive function, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Genet 3:132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00132
Tang JY, Lee JC, Chang YT, Hou MF, Huang HW, Liaw CC, Chang HW (2013) Long noncoding RNAs-related diseases, cancers, and drugs. ScientificWorldJournal 2013:943539. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/943539
Vieta E et al (2018) Bipolar disorders. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:18008. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.8
Vieta E et al (2018) Early intervention in bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry 175:411–426. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.17090972
Vucicevic D, Schrewe H, Orom UA (2014) Molecular mechanisms of long ncRNAs in neurological disorders. Front Genet 5:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00048
Wang HK, Yan H, Wang K, Wang J (2017) Dynamic regulation effect of long non-coding RNA-UCA1 on NF-kB in hippocampus of epilepsy rats . Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci 21:3113–3119
Zheng J, Yi D, Liu Y, Wang M, Zhu Y, Shi H (2017) Long nonding RNA UCA1 regulates neural stem cell differentiation by controlling miR-1/Hes1 expression. Am J Transl Res 9:3696–3704
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge pleasantly the contribution of the patients, healthy persons and institutions in this study. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. This study was conducted and supported as a project (Number: 11262) at Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, IR Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z. Sh. and B. N. participated in planning the study, data analysis, performed all experiments, and drafting the manuscript. SMH. Gh. assisted and helped in all experiments. A. Z. and J. Sh. supervised the study and drafted the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirvani Farsani, Z., Zahirodin, A., Ghaderian, S.M.H. et al. The role of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in patients with bipolar disorder. Metab Brain Dis 35, 1077–1083 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00580-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00580-9