Abstract
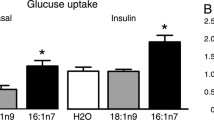
This study was designed to understand the cellular mechanisms responsible for defects in the insulin-stimulated signal transduction pathway in a type 2 diabetic animal model. We examined the in vitro PC-1 phosphodiesterase activity and glucose uptake in adipose tissue of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type 2 diabetic rats. The PC-1 activity was significantly increased in adipose tissue of diabetic rats (0.54 ± 0.08 nmol PNTP hydrolyzed/mg protein/min) compared with controls (0.29 ± 0.05 nmol PNTP hydrolyzed/mg protein/min, p < 0.05). Upon insulin stimulation (100 nM), glucose uptake in the adipose tissue of the controls (4.17 ± 1.28×10−8 μmol/mg/min) was significantly higher than that in the diabetic rats (1.26 ± 0.35×10−8; p < 0.05). These results suggest that elevated PC-1 phosphodiesterase activity and decreased glucose uptake in adipose tissues may be acquired characteristics contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E: Pathogenesis of NIDDM: a balanced overview. Diabetes Care 15: 318–368, 1992
Kahn CR: Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes 43: 1066–1084, 1994
Belli SI, Goding JW: Biochemical characterization of human PC-1 (alkaline phosphodiesterase I). Eur J Biochem 226: 433–443, 1994
Maddux BA, Sbraccia P, Kumakura S, Sasson S, Youngren JF, Fisher A, Spencer S, Grupe A, Henzel W, Stewart TA, Reaven GM, Goldfine ID: Membrane glycoprotein PC-1 and insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature 373: 448–451, 1995
Maddux BA, Goldfine ID: PC-1 inhibition of insulin receptor function occurs via direct interaction with the receptor alpha subunit. Diabetes 49: 13–19, 2000
Stefan C, Wera S, Stalmans W, Bollen M: The inhibition of the insulin receptor by the receptor protein PC-1 is not specific and results from the hydrolysis of ATP. Diabetes 45: 980–983, 1996
Ploug T, vonDeurs B, Ai H, Cushman SW, Ralston E: Analysis of GLUT4 distribution in whole skeletal muscle fibres: identification of distinct storage compartments that are reduced by insulin and muscle contractions. J Cell Biol 142: 1429–1446, 1998
Friedman JE, Dohm GL, Leggett-Frazier N, Elton CW, Tapscott EB, Pories WJ, Caro JF: Restoration of insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle of morbidly obese patients after weight loss: effect on muscle glucose transport and glucose transporter GLUT-4. J Clin Invest 89: 701–705, 1992
Virkamaka A, Ueki K, Khan CR: Protein-protein interaction in insulin signaling and the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 103: 931–943, 1999
McGrowder D, Ragoobirsingh D, Dasgupta T: Decreased insulin binding to mononuclear leucocytes and erythrocytes from dogs after S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine administration. BMC Biochem 3: 1, 2002
Masiello P, Broca C, Gross R, Roye M, Manteghetti M, Hillaire-Buys D, Novelli M, Ribes G: Experimental NIDDM: development of a new model in adult rats administered streptozotocin and nicotinamide. Diabetes 47: 224–229, 1998
World Health Organization (WHO): Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Department of non-communicable disease surveillance. Geneva: 1999
Marette A, Mauriege P, Marcotte B, Algie C, Bouchard C, Theriault G, Bukowiecki LJ, Marceau P, Biron S, Nadeau A, Despres JP: Regional variation in adipose tissue insulin action and GLUT4 glucose transporter expression in severely obesed premenopausal women. Diabetologia 40: 590–598, 1997
Youngren JF, Maddux BA, Sasson S, Sbraccia P, Tapscott EB, Swanson MS, Dohm GL, Goldfine ID: Skeletal muscle content of membrane glycoprotein PC-1 in obesity. Diabetes 45: 1324–1328, 1996
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein, utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976
Kahn CR: Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes 43: 1066–1084, 1994
Olefsky JM, Nolan JJ: Insulin resistance and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: cellular and molecular mechanism. Am J Clin Nutr 61(Suppl 1): 980S–986S, 1995.
Pedersen O: Genetics of insulin resistance. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 107: 113–118, 1999
Reaven G: Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37: 1595–1607, 1988.
Taylo SI: Insulin resistance or insulin deficiency: which is the primary cause of NIDDM? Diabetes 43: 735–740, 1994
Frittitta L, Youngren J, Vigneri R, Maddux BA, Trischitta V, Goldfine ID: PC-1 content in skeletal muscle of non-obese, non-diabetic subjects: relationship to insulin receptor tyrosine kinase and whole body insulin sensitivity. Diabetologia 39: 1190–1195, 1996
Sakoda H, Ogihara T, Anai M, Funaki M: No correlation of plasma cell-1 overexpression with insulin resistance in diabetic rats and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetes 48: 1365–1371, 1999
Kumakura S, Maddux BA, Sung CK: Overexpression of membrane glycoprotein PC-1 can influence insulin action at a post-receptor site. J Cell Biochem 68: 366–377, 1998
Mora S, Pessin JE: An adipocentric view of signaling and intracellular trafficking. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 18: 345–356, 2002
Jhun BH, Raampal AL, Liu H, Lachaal M, Jung CY: Effects of insulin on steady state kinetics of GLUT4 subcellular distribution in rat adipocytes. Evidence of constitutive GLUT4 recycling. J Biol Chem 267: 17710–17715, 1992
Slot JW, Geuze HJ, Gigengack S, James DE, Lienhard GE.: Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 7815–7819, 1991
Yang J, Holman GD: Comparison of GLUT4 and GLUT1 subcellular trafficking in basal and insulin-stimulated 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem 268: 4600–4603, 1993
Kobayashi M, Olefsky JM: Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on insulin binding, glucose transport, and intracellular glucose metabolism in isolated rat adipocytes. Diabetes 28: 87–95, 1979
Rothman DL, Schulman RG, Schulman GI: 31P nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of muscle glucose-6-phosphate: evidence for reduced insulin-dependent muscle glucose transport or phosphorylation activity in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 89: 1062–1075, 1992
Krook A, Roth RA, Jiang XJ, Zierath JR, Wallberg-Henriksson H: Insulin-stimulated Akt kinase activity is reduced in skeletal muscle from non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Diabetes 47: 1281–1286, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrett, K., McGrowder, D., Brown, P. et al. Increased PC-1 phosphodiesterase activity and inhibition of glucose uptake in adipocytes of type 2 diabetic rats. Mol Cell Biochem 293, 9–14 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-0387-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-0387-x