Abstract
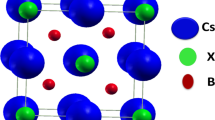
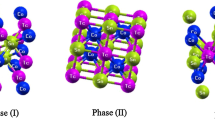
Herein, we report the study of half-Heusler ScTiX (X = Si, Ge, Pb, In, As, and Tl) compounds for the first time employing the scheme of density functional theory (DFT). The influence of on-site Coulomb interactions is taken into account, and simulations are conducted in generalized gradient approximation with the added Hubbard U term (GGA + U). All the compounds were observed to have a narrow band gap on the spin-down configuration. Though spinning the majority channel (spin-up), it is found to be metallic. Consequently, all compounds are semi-metallic or half-metallic and 100% of spin polarized at the Fermi level. Various features, comprising structural, magnetic, elastic, and electronic properties, are calculated through full-potential linearized augmented plane wave (FP-LAPW) method, since they are incorporated in the computer simulation package of WIEN2k. Equilibrium lattice constants are observed for all the compounds which exist within the domain of 6.4–6.8 A°. The IRelast package is already integrated in WIEN2K that has been used for the elastic properties. Elastic features reflect the brittle character of all the material. The total magnetic moments for all such materials are greater than 3 μB, i.e., 3 μB of MTot. Therefore, the compounds show a strong ferromagnetic behavior. These are therefore expected to be used as shape base for thin layers within metastable situations for spintronic applications. The resulted elastic properties show that ScTiSi is ductile, while all other five compounds represent brittle nature. Above findings delight the prospect of ScTiX (X = Si, Ge, Pb, In, As and Ti) compounds in developing half-metallic HH compounds for spintronics and memory storage appliances.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaughnessy, M., Fong, C.Y., Snow, R., Yang, L.H., Chen, X.S., Jiang, Z.M.: Structural and magnetic properties of single dopants of Mn and Fe for Si-based spintronic materials. Phys. Rev. B. 82, 035202 (2010)
Damewood, L., Fong, C.Y.: Local field effects in half-metals: a GW study of zincblende CrAs, MnAs, and MnC. Phys. Rev. B. 83, 113102 (2011)
Shaughnessy, M., Fong, C.Y., Snow, R., Liu, K., Pask, J.E., Yang, L.H.: Origin of large moments in Mn x Si 1 − x at small x. Appl. Phy. Lett. 95, 022515 (2009)
I. Zuti’c, J. Fabian, S. D. Sarma: Spintronics: fundamentals and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323 (2004)
Boeck, J.D., Roy, W.V., Motsnyi, V., Liu, Z., Dessein, K., Borghs, G.: Hybrid epitaxial structures for spintronics. Thin Solid Films. 412, 3–13 (2002)
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J.M., von Molnar, S., Roukes, M.L., Chtchelkanova, A.Y., Treger, D.M.: Spintronics: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science. 294, 1488–1495 (2001)
De Groot, R.A., Mueller, F.M., Engen, P.G.V., Buschow, K.H.J.: New class of materials: half-metallic ferromagnets. Phys. Rev.Lett. 50, 2024 (1983)
Hülsen, B., Scheffler, M., Kratzer, P.: Thermodynamics of the Heusler alloy Co2−xMn1+xSi: a combined density functional theory and cluster expansion study. Phys. Rev. B. 79, 094407 (2009)
Lee, S.C., Lee, T.D., Blaha, P., Schwarz, K.: Magnetic and half-metallic properties of the full-Heusler alloys co 2 Ti X ( X = Al , Ga ; Si , Ge , Sn ; Sb ). J. Appl. Phys. 97, 10C307 (2005)
Mehmood, N., Ahmad, R., Murtaza, G.: Ab initio investigations of structural, elastic, mechanical, electronic, magnetic, and optical properties of half-Heusler compounds RhCrZ (Z = Si, Ge). J. Supercond. Nov. Mag. 30, 2481–2488 (2017)
Feng, L., Liu, E.K., Zhang, W.X., Wang, W.H., Wu, G.H.: First-principles investigation of half-metallic ferromagnetism of half-Heusler compounds XYZ. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 351, 92–97 (2014)
Kaur, K., Kumar, R.: High temperature thermoelectric performance of p-type TaRhSn half Heusler compound: a computational assessment. Ceram. Int. 43, 15160–15166 (2017)
Fu, C., Zhu, T., Pei, Y., Xie, H., Wang, H., Jeffrey Snyder, G., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, X.: High band degeneracy contributes to high thermoelectric performance in p-type half-Heusler compounds. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 1400600 (2014)
Joshi, G., Yan, X., Wang, H., Liu, W., Chen, G., Ren, Z.: Enhancement in thermoelectric figure-of-merit of an N-type half-Heusler compound by the nanocomposite approach. Adv. Energy Mater. 1, 643–647 (2011)
Singh, D.J., Nordstr¨Om, L.: Planewaves, pseudopotentials, and the LAPW method. Springer, New York (2006)
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, G.K.H. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, J. Luitz, R. Laskowski, F. Tran, L. D. Marks, WIEN2K, an augmented plane wave + local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties, Karlheinz Schwarz, Techn.Universit¨at WIEN, Austria, Wien, Austria (2001)
Perdew, J.P., Burke, K., Ernzerhof, M.: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996)
U. von. Barth, L. Hedin.: A local exchange-correlation potential for the spin polarized case. I. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 5, 1629 (1972)
Pant, M.M., Rajagopal, A.K.: Theory of inhomogenous magnetic electron gas. Solid State Commun. 10, 1157–1160 (1972)
Murnaghan, F.D.: The compressibility of media under extreme pressures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 30, 244–247 (1944)
Jamal, M., Bilal, M., Ahmad, I., Jalali-Asadabadi, S.: IRelast package. J. Alloy. Compd. 735, 569–579 (2018)
I. Galankis, P. H. Dederiches, Half-metallic alloys: fundamentals and applications. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Galanakis, I., Dederichs, P.H., Papanikolaou, N.: Slater-Pauling behavior and origin of the half-metallicity of the full-Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. B. 66, 174429 (2002)
Galanakis, I., Mavropoulos, P., Dederichs, P.H.: Electronic structure and Slater–Pauling behaviour in half-metallic Heusler alloys calculated from first principles. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 39, 765–775 (2006)
Ravindran, P., Fast, L., Korzhavyi, P.A., Johansson, B., Wills, J., Eriksson, O.: J. Appl.Phys. 84, 4891 (1989)
Yu, R., Zhang, X.F., de Jonghe, L.C., Ritchie, R.O.: Elastic constants and tensile properties of Al2OC by density functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B. 75, 104114 (2007)
Łepkowski, S.P., Gorczyca, I.: Ab initio study of elastic constants in InxGa1−xN and InxAl1−xN wurtzite alloys. Phys. Rev. B. 83, 203201 (2011)
Xie, M.Y., Tasnadi, F., Abrikosov, I.A., Hultman, L., Darakchieva, V.: Elastic constants, composition, and piezolectric polarization in InxAl1−xN: from ab initio calculations to experimental implications for the applicability of Vegard’s rule. Phys. Rev. B. 86, 155310 (2012)
Callaway, J.: Quantum Theory of the Solid State, second edn. Academic Press, New York (1991)
Mase, G.T.: G.E. Theory, Applications, and Numerics, second ed., CRC Press LLC, Mase, Elasticity (1999)
P. Bruesch, Phonons: theory and experiments I : lattice dynamics and models of interatomic forces, Springer-Verlag, 1982
M.H. Sadd, Elasticity: theory, applications, and numerics, Elsevier Academic Press, 2005
Yao, H., Ouyang, L., Chingw, W.: Ab initio calculation of elastic constants of ceramic crystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 3194 (2007)
G. Grimvall, Thermophysical properties of materials, Elsevier, Amsterdam 1999, enlarged and revised edition
C. Jenkins, S. Khanna “Mechanics of materials: a modern integration of mechanics and materials in structural design,” 2005
Wachter, P., Filzmoser, M., Rebizant, J.: Electronic and elastic properties of the light actinide tellurides. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 293, 199–223 (2001)
Mott, P.H., Dorgan, J.R., Roland, C.M.: The bulk modulus and Poisson’s ratio of “incompressible” materials. J. Sound Vib. 312, 572–575 (2008)
Vitos, L., Korzhavyi, P.A., Johansson, B.: Stainless steel optimization from quantum mechanical calculations. Nat. Mater. 2, 25–28 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, N., Husain, M., Yang, J. et al. First Principle Study of Structural, Electronic, Elastic, and Magnetic Properties of Half-Heusler Compounds ScTiX (X = Si, Ge, Pb, In, Sb, and Tl). J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 3915–3922 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05652-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05652-6