Abstract
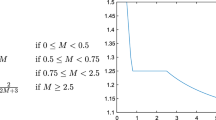
We consider online scheduling with migration on two hierarchical machines, with the goal of minimizing the makespan. In this model, one of the machines can run any job, while the other machine can only receive jobs from a subset of the input jobs. In addition, in this problem, there is a constant parameter \(M \ge 0\), called the migration factor. Jobs are presented one by one, and every arrival of a new job of size x does not only require the algorithm to assign the job to one of the machines, but it also allows the algorithm to reassign any subset of previously presented jobs, whose total size is at most \(M \cdot x\). We show that no algorithm with a finite migration factor has a competitive ratio below \(\frac{3}{2}\), and design an algorithm with this competitive ratio and migration factor 1. We prove that this is the best possible result, in the sense that no algorithm with a smaller migration factor can have a competitive ratio of \(\frac{3}{2}\). This provides tight bounds on the competitive ratio for all values \(M\ge 1\). We also find tight bounds on the competitive ratio for many other values of M.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availibility
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Code Availability
There is no software for this work.
References
Akaria I, Epstein L(2022) Bin stretching with migration on two hierarchical machines. CoRR, arXiv: abs/2206.06102
Albers S, Hellwig M (2017) On the value of job migration in online makespan minimization. Algorithmica 79(2):598–623
Azar Y, Naor JS, Rom R (1995) The competitiveness of on-line assignments. J Algorithms 18(2):221–237
Bar-Noy A, Freund A, Naor JS (2001) On-line load balancing in a hierarchical server topology. SIAM J Comput 31(2):527–549
Berndt S, Jansen K, Klein K (2020) Fully dynamic bin packing revisited. Math Program 179(1):109–155
Chen X, Lan Y, Benko A, Dósa G, Han X (2011) Optimal algorithms for online scheduling with bounded rearrangement at the end. Theor Comput Sci 412(45):6269–6278
Chen X, Xu Z, Dósa G, Han X, Jiang H (2013) Semi-online hierarchical scheduling problems with buffer or rearrangements. Inf Process Lett 113(4):127–131
Crescenzi P, Gambosi G, Penna P (2004) On-line algorithms for the channel assignment problem in cellular networks. Discrete Appl Math 137(3):237–266
Epstein L, Levin A (2009) A robust APTAS for the classical bin packing problem. Math Program 119(1):33–49
Epstein L, Levin A (2014) Robust algorithms for preemptive scheduling. Algorithmica 69(10):26–57
Epstein L, Levin A (2019) Robust algorithms for total completion time. Discrete Optim 33:70–86
Galambos G, Woeginger GJ (1993) An on-line scheduling heuristic with better worst case ratio than Graham’s list scheduling. SIAM J Comput 22(2):349–355
Gálvez W, Soto JA, Verschae J (2020) Symmetry exploitation for online machine covering with bounded migration. ACM Trans Algorithms 16(4):43:1-43:22
Jiang Y (2008) Online scheduling on parallel machines with two GoS levels. J Comb Optim 16(1):28–38
Jiang Y, He Y, Tang C (2006) Optimal online algorithms for scheduling on two identical machines under a grade of service. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci A 7(3):309–314
Lee K, Hwang H-C, Lim K (2014) Semi-online scheduling with GoS eligibility constraints. Int J Prod Econ 153:204–214
Levin V (2022) Robust algorithms for preemptive scheduling on uniform machines of non-increasing job sizes. Inf Process Lett 174:106211
Lim K, Lee K, Chang SY (2011) Improved bounds for online scheduling with eligibility constraints. Theor Comput Sci 412(39):5211–5224
Liu M, Chu C, Xu Y, Zheng F (2011) Semi-online scheduling on 2 machines under a grade of service provision with bounded processing times. J Comb Optim 21(1):138–149
Luo T, Xu Y (2015) Semi-online hierarchical load balancing problem with bounded processing times. Theor Comput Sci 607(1):75–82
Luo T, Xu Y (2016) Optimal algorithm for semi-online scheduling on two machines under GoS levels. Optim Lett 607(10):207–213
Park J, Chang SY, Lee K (2006) Online and semi-online scheduling of two machines under a grade of service provision. Operations Res Lett 34(6):692–696
Sanders P, Sivadasan N, Skutella M (2009) Online scheduling with bounded migration. Math Operations Res 34(2):481–498
Skutella M, Verschae J (2016) Robust polynomial-time approximation schemes for parallel machine scheduling with job arrivals and departures. Math Operations Res 41(3):991–1021
Tan Z, Zhang A (2011) Online hierarchical scheduling: an approach using mathematical programming. Theor Comput Sci 412(3):246–256
Wakrat I (2012). Online and semi-online scheduling with reordering and reassignment. Master’s thesis, Department of Computer Science, University of Haifa, Haifa, Israel
Wu Y, Ji M, Yang Q (2012) Optimal semi-online scheduling algorithms on two parallel identical machines under a grade of service provision. Int J Prod Econ 135(1):367–371
Zhang A, Jiang Y, Fan L, Hu J (2015) Optimal online algorithms on two hierarchical machines with tightly-grouped processing times. J Comb Optim 29:781–795
Zhang A, Jiang Y, Tan Z (2009) Online parallel machines scheduling with two hierarchies. Theor Comput Sci 410(38–40):3597–3605
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The contributions of all authors are equal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest or competing interests for this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akaria, I., Epstein, L. Online scheduling with migration on two hierarchical machines. J Comb Optim 44, 3535–3548 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-022-00906-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-022-00906-6