Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study is to examine autoantibody profile of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients with lupus nephritis (LN) and to establish the correlation between the antibody reactivity and disease activity of LN.
Methods
Autoantibodies and serological parameters were measured and analyzed in 589 SLE patients. The associations of the co-positivity of anti-dsDNA, -nucleosome and –histone antibodies (3-pos) with clinical, serological and outcome parameters were analyzed.
Results
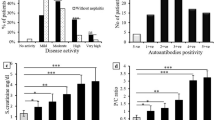
At the study entry, the prevalence for anti-dsDNA (61.52 % vs. 34.11 %, P < 0.0001), anti-nucleosome (56.09 % vs. 37.21 %, P = 0.0002) and anti-histone (49.35 % vs. 33.33 %, P = 0.0013) antibodies in patients with LN were significantly higher than that in patients without LN. Patients with 3-pos had a higher proportion of proliferative renal lesions (class III + IV). The incidence of a poor renal outcome (7.14 % vs. 2.52 %, P = 0.0174) in LN patients with 3-pos was significantly higher than those without 3-pos. Moreover, the rate of remission (73.63 % vs. 82.37 %, P = 0.0245) was significantly reduced and recurrence increased (58.90 % vs. 23.44 %, P < 0.0001) in 3-pos patients as compared to that in non 3-pos within the LN group.
Conclusion
Our data indicate a strong association between the 3-pos and renal disease activities, especially proliferative glomerulonephritis. The ability of 3-pos to predict renal flares may lead to major additional benefits in the follow-up of these patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riemekasten G, Hahn BH. Key autoantigens in SLE. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44(8):975–82.
Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(9):929–39.
Koffler D, Agnello V, Thoburn R, Kunkel HG. Systemic lupus erythematosus: prototype of immune complex nephritis in man. J Exp Med. 1971;134(3):169–79.
Jakes RW, Bae SC, Louthrenoo W, Mok CC, Navarra SV, Kwon N. Systematic review of the epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in the Asia-Pacific region: prevalence, incidence, clinical features, and mortality. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(2):159–68.
Shabana AA, El-Ghawet AE, Machaly SA, Abu Hashim EM, El-Kady BA, Shaat R. Anti-chromatin and anti-histone antibodies in Egyptian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28(6):673–8.
Isenberg DA, Ravirajan CT, Rahman A, Kalsi J. The role of antibodies to DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus–a review and introduction to an international workshop on DNA antibodies held in London, May 1996. Lupus. 1997;6(3):290–304.
Sherer Y, Gorstein A, Fritzler MJ, Shoenfeld Y. Autoantibody explosion in systemic lupus erythematosus: more than 100 different antibodies found in SLE patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004;34(2):501–37.
Kiss E, Lakos G, Szegedi G, Poor G, Szodoray P. Anti-nuscleosome antibody, a reliable indicator for lupus nephritis. Autoimmunity. 2009;42(5):393–8.
Bigler C, Lopez-Trascasa M, Potlukova E, Moll S, Danner D, Schaller M, et al. Antinucleosome antibodies as a marker of active proliferative lupus nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51(4):624–9.
Ahlin E, Mathsson L, Eloranta ML, Jonsdottir T, Gunnarsson I, Ronnblom L, et al. Autoantibodies associated with RNA are more enriched than anti-dsDNA antibodies in circulating immune complexes in SLE. Lupus. 2012;21(6):586–95.
Jaekell HP, Trabandt A, Grobe N, Werle E. Anti-dsDNA antibody subtypes and anti-C1q antibodies: toward a more reliable diagnosis and monitoring of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2006;15(6):335–45.
Cortes-Hernandez J, Ordi-Ros J, Labrador M, Bujan S, Balada E, Segarra A, et al. Antihistone and anti-double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid antibodies are associated with renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 2004;116(3):165–73.
Isenberg DA, Manson JJ, Ehrenstein MR, Rahman A. Fifty years of anti-ds DNA antibodies: are we approaching journey’s end? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(7):1052–6.
Linnik MD, Hu JZ, Heilbrunn KR, Strand V, Hurley FL, Joh T. Relationship between anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies and exacerbation of renal disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(4):1129–37.
Ho A, Magder LS, Barr SG, Petri M. Decreases in anti-double-stranded DNA levels are associated with concurrent flares in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(10):2342–9.
Cairns AP, McMillan SA, Crockard AD, Meenagh GK, Duffy EM, Armstrong DJ, et al. Antinucleosome antibodies in the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62(3):272–3.
Ng KP, Manson JJ, Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Association of antinucleosome antibodies with disease flare in serologically active clinically quiescent patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;55(6):900–4.
Amoura Z, Chabre H, Koutouzov S, Lotton C, Cabrespines A, Bach JF, et al. Nucleosome-restricted antibodies are detected before anti-dsDNA and/or antihistone antibodies in serum of MRL-Mp lpr/lpr and +/+ mice, and are present in kidney eluates of lupus mice with proteinuria. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37(11):1684–8.
Gomez-Puerta JA, Burlingame RW, Cervera R. Anti-chromatin (anti-nucleosome) antibodies: diagnostic and clinical value. Autoimmun Rev. 2008;7(8):606–11.
Cervera R, Vinas O, Ramos-Casals M, Font J, Garcia-Carrasco M, Siso A, et al. Anti-chromatin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a useful marker for lupus nephropathy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62(5):431–4.
Hung W, Chen Y, Lan J, Chen H, Chen D, Hsieh C, et al. Antinucleosome antibodies as a potential biomarker for the evaluation of renal pathological activity in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2011;20(13):1404–10.
van der Vlag J, Berden JH. Lupus nephritis: role of antinucleosome autoantibodies. Semin Nephrol. 2011;31(4):376–89.
Marto N, Bertolaccini ML, Calabuig E, Hughes GR, Khamashta MA. Anti-C1q antibodies in nephritis: correlation between titres and renal disease activity and positive predictive value in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(3):444–8.
Trendelenburg M, Lopez-Trascasa M, Potlukova E, Moll S, Regenass S, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, et al. High prevalence of anti-C1q antibodies in biopsy-proven active lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21(11):3115–21.
Seelen MA, Trouw LA, Daha MR. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of anti-C1q antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003;12(6):619–24.
Moroni G, Radice A, Giammarresi G, Quaglini S, Gallelli B, Leoni A, et al. Are laboratory tests useful for monitoring the activity of lupus nephritis? A 6-year prospective study in a cohort of 228 patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(2):234–7.
Katsumata Y, Miyake K, Kawaguchi Y, Okamoto Y, Kawamoto M, Gono T, et al. Anti-C1q antibodies are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus global activity but not specifically with nephritis: a controlled study of 126 consecutive patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(8):2436–44.
Meyer OC, Nicaise-Roland P, Cadoudal N, Grootenboer-Mignot S, Palazzo E, Hayem G, et al. Anti-C1q antibodies antedate patent active glomerulonephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):R87.
Becker-Merok A, Kalaaji M, Haugbro K, Nikolaisen C, Nilsen K, Rekvig OP, et al. Alpha-actinin-binding antibodies in relation to systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(6):R162.
Mason LJ, Ravirajan CT, Rahman A, Putterman C, Isenberg DA. Is alpha-actinin a target for pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies in lupus nephritis? Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(3):866–70.
Matrat A, Veysseyre-Balter C, Trolliet P, Villar E, Dijoud F, Bienvenu J, et al. Simultaneous detection of anti-C1q and anti-double stranded DNA autoantibodies in lupus nephritis: predictive value for renal flares. Lupus. 2011;20(1):28–34.
Grootscholten C, van Bruggen MC, van der Pijl JW, de Jong EM, Ligtenberg G, Derksen RH, et al. Deposition of nucleosomal antigens (histones and DNA) in the epidermal basement membrane in human lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(5):1355–62.
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25(11):1271–7.
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004;65(2):521–30.
Mosca M, Pasquariello A, Tavoni A, Moriconi L, Moneta I, Innocenti M, et al. Predictors of renal outcome in diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1997;6(4):371–8.
Austin III HA, Muenz LR, Joyce KM, Antonovych TA, Kullick ME, Klippel JH, et al. Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Contribution of renal histologic data. Am J Med. 1983;75(3):382–91.
Bertsias G, Boumpas DT. Update on the management of lupus nephritis: let the treatment fit the patient. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008;4(9):464–72.
Mosca M, Bencivelli W, Neri R, Pasquariello A, Batini V, Puccini R, et al. Renal flares in 91 SLE patients with diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2002;61(4):1502–9.
Strasser A, Huang DC, Vaux DL. The role of the bcl-2/ced-9 gene family in cancer and general implications of defects in cell death control for tumourigenesis and resistance to chemotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1333(2):F151–78.
Dieker JW, Fransen JH, van Bavel CC, Briand JP, Jacobs CW, Muller S, et al. Apoptosis-induced acetylation of histones is pathogenic in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(6):1921–33.
van Bavel CC, Fenton KA, Rekvig OP, van der Vlag J, Berden JH. Glomerular targets of nephritogenic autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(7):1892–9.
Jorgensen MH, Rekvig OP, Jacobsen RS, Jacobsen S, Fenton KA. Circulating levels of chromatin fragments are inversely correlated with anti-dsDNA antibody levels in human and murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol Lett. 2011;138(2):179–86.
Fismen S, Hedberg A, Fenton KA, Jacobsen S, Krarup E, Kamper AL, et al. Circulating chromatin-anti-chromatin antibody complexes bind with high affinity to dermo-epidermal structures in murine and human lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2009;18(7):597–607.
Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, Dennis GJ, James JA, et al. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(16):1526–33.
Acknowledgment
We are very grateful to Professor Jin Xiaoming and Zhao Ruibo for assistance in the scoring and collecting pathological data of the SLE patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The presented work was supported by National Science Foundation of China (Grant NFSC-30227738) and a grant from Heilongjiang Education Bureau, China (Grant 12521180). No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM Table 1
(DOC 34 kb)
ESM Table 2
(DOC 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sui, M., Lin, Q., Xu, Z. et al. Simultaneous Positivity for Anti-DNA, Anti-Nucleosome and Anti-Histone Antibodies is a Marker for More Severe Lupus Nephritis. J Clin Immunol 33, 378–387 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9825-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9825-6