Abstract
The paper seeks to analyse the evolution of expenditure on private health insurance (PHI) in Spain. We consider the factors that influence PHI demand and level of spending before and during the economic recession, along with identifying the effect of the recession on these factors. The data is obtained from the Spanish Family Budget Survey (SFBS) for 2006 and 2012. Due to the data structure and the demand function, the analysis is performed using a sample selection model in order to avoid sample selection bias. We estimate three models: a pre-recession model (2006), a model for the recession period (2012) and a third one covering both periods (2006 and 2012) and where we include a dummy variable that establishes the effect of the economic recession. The results show that the effect of the economic recession on PHI demand is not significant, but it is on the level of spending.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
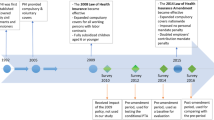
Consolidated public health expenditure fell by 9.11% between 2009 (the year with the highest consolidated public health expenditure) and 2012. This percentage is equivalent to a drop of EUR 6.126 billion (Estadística de Gasto Sanitario Público 2013).
The consolidated public health expenditure increased 26.75% from 2006 to 2009, that is, EUR 1.489 billion (Estadística de Gasto Sanitario Público 2013).
Spanish Family Budget Survey (Encuesta de Presupuestos Familiares) is conducted by the Spanish National Institute of Statistics (Instituto Nacional de Estadística, INE). www.ine.es.
A summary of the variables used and their main descriptive statistics are reported in Table 1 in the appendix.
Health insurance expenditure reported in the survey incorporates school insurance. Assuming that the cheapest health insurance in Spain is around EUR 10 per month, the minimum spending of a household that takes out insurance is EUR 120. Those families that spend less than EUR120 per year are considered as not having contracted health insurance (this expense is assumed to be spending on school insurance).
\( {\text{RECESSION}} \) is introduced only in the third model where all the observation are considered in the 2006 and 2012 model.
The 2PM estimations are also reported in Table 3 in the Appendix.
See Appendix.
There are also workers that are not public sector workers, but they actually represent a lower percentage.
References
Appleby, J. (2011). Does poor health justify NHS reform? BMJ, 342, d566.
Bacigalupe, A., & Escolar-Pujolar, A. (2014). The impact of economic crises on social inequalities in health: What do we know so far? International Journal for Equity in Health, 13(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-13-52.
Bacigalupe, A., Martín, U., Font, R., González-Rábago, Y., & Bergantiños, N. (2016). Austeridad y privatización sanitaria en época de crisis: ¿existen diferencias entre las comunidades autónomas? Gaceta Sanitaria, 30(1), 47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaceta.2015.10.003.
Baron-Epel, O., Dushenat, M., & Friedman, N. (2001). Evaluation of the consumer model: relationship between patients’ expectations, perceptions and satisfaction with care. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 13(4), 317–323. Retrieved from http://intqhc.oxfordjournals.org/content/13/4/317.abstract.
Besley, T., Hall, J., & Preston, I. (1999). The demand for private health insurance: Do waiting lists matter? Journal of Public Economics, 72(2), 155–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-2727(98)00108-X.
Boletín Oficial del Estado. (2012). Real Decreto-ley 16/2012, de 20 de abril, de medidas urgentes para garantizar la sostenibilidad del Sistema Nacional de Salud y mejorar la calidad y seguridad de sus prestaciones. Disponible En URL: https://www.Boe.es/boe/dias/2012/…, 31278. https://doi.org/BOE-A-2012-5403.
Calero, R., & Gallarza, M. G. (2011). Percepciones del Usuario vs. Percepciones del Gestor del Servicio Sanitario : Un Análisis Cualitativo en el Ambito del “Modelo Alzira.” Anales de Estudios Económicos Y Empresariales, XXI, 9–37.
Cortès-Franch, I., & González López-Valcárcel, B. (2014). Crisis económico-financiera y salud en España. Evidencia y perspectivas. Informe SESPAS 2014. Gaceta sanitaria/S.E.S.P.A.S, 28 Suppl 1(< br/> Notice: Undefined index: numeroInicial in/var/www/html/includes_ws/modulos/meta-scholar.php on line 48<br/>), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaceta.2014.03.011.
Costa, J., & García, J. (2003). Demand for private health insurance: How important is the quality gap? Health Economics, 12(7), 587–599. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.756.
Costa, J., & Rovira, J. (2005). Why some people go private and others do not: Supplementary health insurance in Spain. Public Finance & Management, 5(4), 523–543. Retrieved from https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=bsx&AN=19763465&lang=es&site=eds-live.
Costa-Font, J., & García-Villar, J. (2009). Risk attitudes and the demand for private health insurance: the importance of “captive preferences.” Annals of Public and Cooperative Economics, 80(4), 499–519. Retrieved from https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-77950669107&partnerID=tZOtx3y1.
Doiron, D., Jones, G., & Savage, E. (2008). Healthy, wealthy and insured? The role of self-assessed health in the demand for private health insurance. Health Economics, 17, 317–334.
Drechsler, D., & Jütting, J. (2007). Different countries, different needs: The role of private health insurance in developing countries. Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law, 32(3), 497–534. https://doi.org/10.1215/03616878-2007-012.
Duan, N., Manning, W. G., Morris, C. N., & Newhouse, J. P. (1983). A comparison of alternative models for the demand for medical care. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 1(2), 115–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/07350015.1983.10509330.
Duan, N., Manning, W. G., Morris, C. N., & Newhouse, J. P. (1984). Choosing between the sample-selection model and the multi-part model. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 2(3), 283–289. https://doi.org/10.1080/07350015.1984.10509396.
Duan, N., Manning, W. G., Morris, C. N., & Newhouse, J. P. (1985). Comments on selectivity bias. Advanced in Health Economics and Health Services Research, 6, 19–24.
Escribà-Agüir, V., & Fons-Martinez, J. (2014). Crisis económica y condiciones de empleo: diferencias de género y respuesta de las políticas sociales de empleo. Informe SESPAS 2014. Gaceta Sanitaria/S.E.S.P.A.S, 28 Suppl 1, 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaceta.2014.01.013.
Estadística de Gasto Sanitario Público. (2013). MSSSI Portal estadístico del SNS. Retrieved June 20, 2005, from https://www.msps.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/inforRecopilaciones/gastoSanitario2005/home.htm.
Forriol, F., & Vaquero, J. (2012). The Spanish health care system: Issues and challenges. Injury, 43(Suppl 2), S1–S2. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(13)70171-2.
Gallo, P., & Gené-Badia, J. (2013). Cuts drive health system reforms in Spain. Health Policy (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 113(1–2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2013.06.016.
Gené-Badia, J., Gallo, P., Hernández-Quevedo, C., & García-Armesto, S. (2012). Spanish health care cuts: Penny wise and pound foolish? Health Policy, 106(1), 23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2012.02.001.
Harmon, C., & Nolan, B. (2001). Health insurance and health services utilization in Ireland. Health Economics, 10(2), 135–145. Retrieved from http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=emed5&NEWS=N&AN=2001127538.
Health Barometer. Citizen´s opinion. (2013). MSSSI Portal estadístico del SNS. Retrieved June 1, 2016, from https://www.msssi.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/BarometroSanitario/home_BS.htm.
Heckman, J. J. (1979). Sample selection bias as a specification error. Econometrica, 47(1), 153–161.
Jofre, M. (2000). Public health care and private insurance demand: The waiting time as a link. Health Care Management Science, 3, 51–71.
Jurado, I. (2012). Actitudes, uso y propuestas sobre el sistema sanitario español. Encuentros Multidisciplinares, 14(41), 37–47.
Kentikelenis, A., Karanikolos, M., Papanicolas, I., Basu, S., McKee, M., & Stuckler, D. (2011). Health effects of financial crisis: Omens of a Greek tragedy. Lancet (London, England), 378(9801), 1457–1458. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61556-0.
Kiil, A. (2012). What characterises the privately insured in universal health care systems? A review of the empirical evidence. Health Policy, 106(1), 60–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2012.02.019.
Leung, S. F., & Yu, S. (1996). On the choice between sample selection and two-part models. Journal of Econometrics, 72(1–2), 197–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4076(94)01720-4.
Liu, T., & Chen, C. (2002). An analysis of private health insurance purchasing decisions with national health insurance in Taiwan. Social Science & Medicine, 55, 755–774.
Lokuge, B., Denniss, R., & Faunce, T. A. (2005). Private health insurance and regional Australia. Medical Journal of Australia, 182(6), 290–293.
López-Casasnovas, G. (2010). Las cifras del gasto sanitario en su comparativa. Errores y omisiones. Gestión Clínica Y Sanitaria, 12, 27–29.
Lopez-Casasnovas, G., Maynou, L., & Saez, M. (2015). Another look at the comparisons of the health systems expenditure indicators. Social Indicators Research, 121(1), 149–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0628-4.
Manning, W. G., Duan, N., & Rogers, W. H. (1987). Monte Carlo evidence on the choice between sample selection and two-part models. Journal of Econometrics, 35(1), 59–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4076(87)90081-9.
Martin-Moreno, J. M., Alonso, P., Claveria, A., Gorgojo, L., & Peiró, S. (2009). Spain: A decentralized health system in constant flux. British Medical Journal, 338, b1170.
Mossialos, E., & Thomson, S. M. S. (2004). Voluntary health insurance in the European Union. In E. Mossialos, A. Dixon, J. Figueras, & J. Kutzin (Eds.), Funding health care: Options for Europe (pp. 128–160). Buckingham, Philadelphia: Open University Press.
Nikpay, S., Buchmueller, T., & Levy, H. (2015). Early Medicaid expansion in Connecticut stemmed the growth in hospital uncompensated care. Health Affairs, 34(7), 1170–1179.
OECD. (2004). The OECD health project—Private health insurance in OECD countries. Paris: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Önen, Z., & Sayin, S. (2018). Evaluating healthcare system efficiency of OECD countries: A DEA-based study. Operations research applications in health care management (pp. 141–158). Cham: Springer.
Pettigrew, L. M., & Mathauer, I. (2016). Voluntary Health Insurance expenditure in low- and middle-income countries: Exploring trends during 1995–2012 and policy implications for progress towards universal health coverage. International Journal for Equity in Health, 15(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-016-0353-5.
Propper, C. (2000). The demand for private health care in the UK. Journal of Health Economics, 19, 855–876.
Repullo, J. R. (2012). Taxonomía práctica de la desinversión sanitaria en lo que no añade valor, para hacer sostenible el Sistema Nacional de Salud. Revista de Calidad Asistencial, 27(3), 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cali.2012.02.010.
Sagan, A., & Thomson, S. (2016a). Voluntary health insurance in Europe: Country experience. (European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies, Ed.). Copenhagen: World Health Organization.
Sagan, A., & Thomson, S. (2016b). Voluntary health insurance in Europe: Role and regulation. (European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies, Ed.). Copenhagen: World Health Organization.
Saliba, B., & Ventelou, B. (2007). Complementary health insurance in France. Who pays? Why? Who will suffer from public disengagement? Health Policy (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 81(2–3), 166–82. Retrieved from https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-33947377942&partnerID=tZOtx3y1.
Sekhri, N., & Savedoff, W. (2005). Private health insurance: Implications for developing countries. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 83(2), 127–134. Retrieved from https://www.scielosp.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0042-96862005000200013&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=en.
Siguenza, W., & Mariel, P. (2013). Valoración economica de los servicios sanitarios en la Comunidad Autonoma de Pais Vasco. Hacienda Publica Espanola/Revista de Economia Publica, (207), 71–99. Retrieved from https://www.ief.es/recursos/publicaciones/revistas/HP_resumenes.aspx\nhttp://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ecn&AN=1450852&site=ehost-live&scope=site.
Sigüenza, W., & Mariel, P. (2015). Determinantes del seguro médico privado y del uso de urgencias. Revista de Economia Aplicada, 23(68), 5–38.
Stuckler, D., Basu, S., Suhrcke, M., Coutts, A., & McKee, M. (2009). The public health effect of economic crises and alternative policy responses in Europe: An empirical analysis. Lancet (London, England), 374(9686), 315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61124-7.
Thomson, S. (2010). What role for voluntary health insurance? In J. Kutzin, C. Cashin, & M. Jakab (Eds.), Implementing health financing reform (pp. 299–325). Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe: World Health Organisation on behalf of the European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies.
Urbanos-Garrido, R. M. (2000). La prestación de los servicios sanitarios públicos en España: cálculo y análisis de la equidad horizontal interpersonal para el período 1987–1995. Hacienda Pública Española, 153(2), 139–160.
Vera-Hernández, Á. M. (1999). Duplicate coverage and demand for health care. The case of Catalonia. Health Economics, 8(7), 579–598. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1050(199911)8:7%3c579:AID-HEC478%3e3.0.CO;2-P.
Waiting List Information System. (2013). MSSSI Portal estadístico del SNS. Retrieved June 1, 2016, from https://www.msssi.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/inforRecopilaciones/listaEspera.htm.
World Health Organisation. (2010). World health report. Health system financing. The path to universal coverage. Geneva: World Health Organisation.
Acknowledgements
Alaitz Artabe acknowledges financial support from the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (ECO2017-82,111-R) and the Basque Government (IT783-13). Waleska Sigüenza acknowledges financial support from the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (ECO2017-82111-R).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Artabe, A., Sigüenza, W. The effects of the economic recession on spending on private health insurance in Spain. Int J Health Econ Manag. 19, 155–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10754-018-9251-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10754-018-9251-2