Abstract
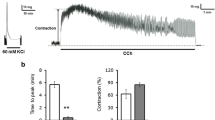
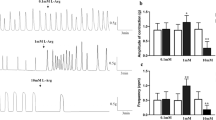
This study is aimed at elucidating with in vitro experiments the time course of alteration of ileal motility caused by in vivo exposure of ligated loops of ileum to toxin A (1 μg/ligated loop) of Clostridium difficile. In the sham-operated animals no significant alteration of motility was observed. In ligated loops directly injected with toxin A and in loops neighboring those administered with this toxin, a biphasic time course of motility alterations was observed. There was initially (2 h after toxin administration) an increase in spontaneous motility and in the amplitude of maximal contraction induced by potassium and acetylcholine. Afterwards there was a progressive depression of motility, which was more severe in loops directly injected. These results suggested a significant progressive depression of rabbit ileal motility induced by toxin A from C. difficile.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
George RH, Symonds JM, Dimock F, Brown JD, Arabi Y, Shinegawa N, Keighley MRB, Alexande-Williams J, Burdon DW (1978) Identification of Clostridium difficile as a cause of pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J 1:695
Larson HE, Parry JV, Price AB, Davies DR, Dolby J, Tyrrell DA (1977) Undescribed toxin in pseudomembranous colitis. Br Med J 14:1246–1248
Rifkin GD, Fekety FR, Silva J Jr (1977) Antibiotic-induced colitis implication of a toxin neutralized by Clostridium sordellii antitoxin. Lancet 26:1103–1106
Ho M, Yang D, Wyle FA, Mulligan ME (1996) Increased incidence of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea following decreased restriction of antibiotic use. Clin Infect Dis 23:S102–S106
Kelly CP, LaMont JT (1998) Clostridium difficile infection. Annu Rev Med 49:375–390
Lima A, Lima N (1993) Epidemiology, therapy and prevention of infection with Shiguella organisms and Clostridium difficile. Curr Op Microbiol infec Dis 6:63–71
Pothoulakis C, Lamont JT (2001) Microbes and microbial toxins: paradigms for microbial-mucosal interactions. II. The integrated response of the intestine to Clostridium difficile toxins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280:G178–G183
Settle CD, Wilcox MH (1996) Review article: antibiotic induced Clostridium difficile infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 10:835–841
Starr JM, Rogers TR, Impallomeni M (1997) Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile diarrhea and herd immunity. Lancet 8:426–428
Hall IC, O’Toole E (1935) Intestinal flora in new-born infants with a description of a new pathogenic anaerobic, Bacillus difficilis. Am J Dis Child 49:390–402
Hall A (1998) Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 23:509–514
Lyerly DM, Wilkins TD (1995) Clostridium difficile. In: Blaser MJ, Smith PD, Ravdin JI, Greenberg HB, Guerrant RL (eds) Infections of the gastrointestinal tract. Raven, New York, pp 867–891
Lyerly DM, Lockwood DE, Richardson SH, Wilkins TD (1982) Biological activities of toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun 35:1147–1150
Taylor NS, Thorne GM, Bartlett JG (1981) Comparison of two toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun 34:1036–1043
Triadafilopoulos G, Pothoulakis C, O’Brien MJ, LaMont JT (1987) Differential effects of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B on rabbit ileum. Gastroenterology 93:273–279
Chaves-Olarte E, Weidmann M, Eichel-Streiber C, Thelestam M (1997) Toxins A and B from Clostridium difficile differ with respect to enzymatic potencies, cellular substrate specificities, and surface binding to cultured cells. J Clin Invest 100:1734–1741
Burakoff R, Zhao L, Celifarco AJ, Rose KL, Donovan V, Pothoulakis C, Percy WH (1995) Effects of purified Clostridium difficile toxin A on rabbit distal colon. Gastroenterology 109:348–354
Percy WH, Burakoff R, Rose K, Desai HP, Pothoulakis C, Eglow R (1998) In vitro evidence that rabbit distal colonic muscularis mucosae has a Clostridium difficile toxin A receptor. Am J Physiol 275:G402–G409
Gilbert RJ, Triadafilopoulos G, Pothoulakis C, Gianpaolo C, LaMont JT (1989) Effect of purified Clostridium difficile toxins on intestinal smooth muscle. I. Toxin A. Am J Physiol 256:G759–G766
Cavalcante IC, Castro MV, Barreto AR et al (2006) Effect of novel A2A adenosine receptor agonist ATL 313 on Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced murine ileal enteritis. Infect Immun 74(5):2606–2612
Carneiro BA, Fujii J, Brito GA et al (2006) Caspase and bid involvement in Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced apoptosis and modulation of toxin A effects by glutamine and alanyl-glutamine in vivo and in vitro. Infect Immun 74(1):81–87
Brito GA, Fujii J, Carneiro-Filho BA, Lima AA, Obrig T, Guerrant RL (2002) Mechanism of Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced apoptosis in T84 cells. J. Infeet Dis 186(10):1438–1447
Goyal RK, Hirano I (1996) The enteric nervous system. N Engl J Med 334:1106–1115
Pothoulakis C, Castagliuolo I, Lamont JT (1998) Nerves and intestinal mast cells modulate responses to enterotoxins. News Physiol Sci 13(2):58–63
Just I, Hofmann F, Aktories K (2000) Molecular mode of action of the large Clostridium cytotoxins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 250:55–83
Just I, Hofmann F, Genth H, Gerhard R (2001) Bacterial protein toxins inhibiting low-molecular-mass GTP-binding proteins. Int J Med Microbiol 291:243–250
Sullivan NM, Pellet S, Wilkins TD (1982) Purification of toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun 35:1032–1040
Lima AA, Innes DJ, Lyerly DM, Wilkins TD, Guerrant RL (1989) Clostridium difficile toxin A. Interactions with mucus and early sequential histopathologic effects in rabbit small intestine. Laborat Invest 61:419–425
Lima AA, Lyerly DM, Wilkins TD, Innes DJ, Guerrant RL (1988) Effects of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B in rabbit small and large intestine in vivo and on cultured cells in vitro. Infect Immun 56:582–588
Diamond JM (1995) How to be physiological. Nature 376:117
Acknowledgements
We thank Alisson Ferreira Alves and Ingrid Gruber Ferreira Lima for carrying out some experiments in this work. This study was supported by the Brazilian institutions CAPES, CNPq, and FUNCAP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, C.C., Carvalho-de-Souza, J.L., Lima, A.Â.M. et al. Ileal Smooth Muscle Motility Depression on Rabbit Induced by Toxin A from Clostridium difficile . Dig Dis Sci 53, 1636–1643 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0030-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0030-z