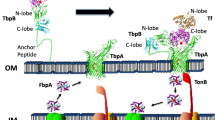
Abstract
Human hemoglobin (Hb) is a metalloprotein used by pathogens as a source of iron during invasive process. It can support the Helicobacter pylori growth and several proteins are induced during iron starvation. However, the identity of those proteins remains unknown. In this work, by in silico analysis we identified FrpB2 in H. pylori genome. This protein was annotated as an iron-regulated outer membrane protein. Multiple amino acid alignment showed the motifs necessary for Hb-binding. We demonstrate the ability of FrpB2 to bind Hb by overlay experiments. In addition, the overexpression of this gene allowed the cell growth in media without free iron but supplemented with Hb. All these results support the idea that frpB2 is a gene of H. pylori involved in iron acquisition when Hb is used as a sole iron source.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker MH, Anderson FB, Baker NE (2003) Dealing with iron: common structural principles in proteins that transport iron and heme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:3579–3583. doi:10.1073/pnas.0637295100
Beddek JA, Sheehan JB, Bossé TJ, Rycroft NA, Kroll SJ, Langford RP (2004) Two TonB systems in Actinobacillus Pleuropneumoniae: their roles in iron acquisition and virulence. Infect Immun 72:701–708. doi:10.1128/IAI.72.2.701-708.2004
Cruz-Castañeda A, Olivares-Trejo JJ (2008) Ehhmbp45 is a novel hemoglobin-binding protein identified in Entamoeba histolytica. FEBS Lett 582:2806–2810. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.06.057
De Freitas JM, Meneghini R (2001) Iron and its sensitive balance in the cell. Mutat Res 475:153–159. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(01)00066-5
Dhaenens L, Szczebara F, Husson M (1997) Identification, characterization, and immunogenicity of the lactoferrin-binding protein from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun 65:514–518
Ferguson DA, Deisenhofer J (2002) TonB-depedent receptors-structural perspectives. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta 1565:318–332
Ferguson AD, Smith BS, Deisenhofer J, Chakraborty R, Esser L, van der Helm D (2002) Structural basis of gating by the outer membrane transporter FecA. Science 295:1715–1719. doi:10.1126/science.1067313
Genco AC, Dixon WD (2001) Emerging strategies in microbial haem capture. Mol Microbiol 39:1–11. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02231.x
Letoffe S, Nato F, Goldberg ME, Wandersman C (1999) Interactions of HasA, a bacterial haemophore, with haemoglobin and with its outer membrane receptor HasR. Mol Microbiol 33:546–555. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01499.x
Létoffé S, Ghigo JM, Wandersman C (1994) Iron acquisition from heme and hemoglobin by a Serratia marcescens extracellular protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9876–9880. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.21.9876
Liu X, Olczak T, Guo CH, Dixon WD, Genco AC (2006) Identification of amino acids residues involved in heme binding and hemoprotein utilization in the Porphyromonas gingivalis heme receptor HmuR. Infect Immun 74:1222–1232. doi:10.1128/IAI.74.2.1222-1232.2006
Otto BR, Verweij-Vught AMJJ, Maclaren DM (1992) Transferrins and heme-compounds as iron sources for pathogenic bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol 18:217–233. doi:10.3109/10408419209114559
Perkins-Balding D, Baer MT, Stijiljkovic I (2003) Identification of functionally important regions of an haemoglobin receptor from Neisseria meningitides. Microbiology 149:3423–3435. doi:10.1099/mic.0.26448-0
Ratlif-Griffin DM, Stojiljkovic I (2004) Iron transport system in Neisseria meningitides. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:154–171. doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.1.154-171.2004
Rossi M, Fetherston JD, Letoffe S, Carniel E, Perry RD, Ghigo JM (2001) Identification and characterization of the hemophore-dependent heme acquisition system of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun 69:6707–6717. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.11.6707-6717.2001
Sambrook JD, Russell W (2001) Molecular cloning a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Simpson W, Olczak T, Genco AC (2000) Characterization and expression of HmuR, a TonB-dependent hemoglobin receptor of Porfiromonas gingivalis. J Bacteriol 182:5737–5748. doi:10.1128/JB.182.20.5737-5748.2000
Torres AG, Payne SM (1997) Haem iron-transport system in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol Microbiol 23:825–833. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.2641628.x
Velayudhan J, Hughes NJ, McColm AA, Bagshaw J, Clayton CL, Andrews SC, Kelly DJ (2000) Iron acquisition and virulence in Helicobacter pylori: a major role for FeoB, a high-affinity ferrous iron transporter. Mol Microbiol 37:274–286. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01987.x
Wandersman C, Stojiljkovic I (2000) Bacterial heme sources: the role of heme, hemoprotein receptors and hemophores. Curr Opin Microbiol 3:215–220. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(00)00078-3
Worst DJ, Otto BR, Graaff J (1995) Iron-repressible outer membrane proteins of Helicobacter pylori involved in heme uptake. Infect Immun 63:4161–4165
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ph.D. Norma Velázquez of Laboratorio de Bacteriología del Hospital Infantil, Federico Gómez and Ms. C. Areli Cruz-Castañeda of Posgrado en Ciencias Genómicas, UACM, for their excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grant number PIFUTP08-126 from ICyT, México.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-López, M.A., Olivares-Trejo, J.J. The gene frpB2 of Helicobacter pylori encodes an hemoglobin-binding protein involved in iron acquisition. Biometals 22, 889–894 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9240-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9240-5