Abstract
Aim
This study estimated the prevalence of undetected, untreated and uncontrolled hypertension in Brunei Darussalam and the associations with socio-demographic and non-communicable diseases (NCDs) risk factors.
Subjects and methods
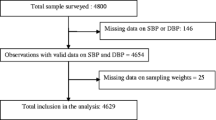
Participants were aged 18–69 years old from the national NCDs and risk factors survey in Brunei Darussalam, conducted from August 2015 to April 2016. Multiple logistic regression was applied to estimate the associations of undetected, untreated and uncontrolled hypertension with socio-demographic and NCDs risk factors.
Results
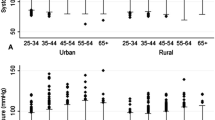
The crude prevalence of hypertension was estimated to be 40.4% [95% confidence interval (CI) = 37.2–43.6] in men and 32.3% (95% CI = 29.6–35.0) in women. Multivariable adjustment using logistic regression found that those who were currently married [odds ratio (OR) = 0.34, p < 0.001], have family history of hypertension (OR = 0.43, p < 0.001), reported buying food with low salt content (OR = 0.67, p = 0.039) and diabetic (OR = 0.28, p < 0.001) were found to be significantly less likely to have undetected hypertension. Amongst those who were previously diagnosed with hypertension, younger age groups, tobacco use and having no other NCDs diagnosis were found to have significantly higher odds of having untreated hypertension. Amongst those who were on antihypertensive treatment, having body mass index (BMI) 30 kg/m2 and above was significantly associated with lower odds of uncontrolled hypertension.
Conclusion
More than one-third (35.8%) of the adult population in Brunei Darussalam were found to have hypertension. Among them, over one-quarter (28.6%) of hypertension cases were not previously detected. Amongst those previously diagnosed with hypertension, more than one-third (35.1%) were not treated or on antihypertensive medication. Screening for hypertension should be emphasised in public health education and media campaigns so that hypertension can be detected and treated earlier.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Razak S, Daher AM, Ramli AS, Ariffin F, Mazapuspavina MY, Ambigga KS, Miskan M, Abdul-Hamid H, Mat-Nasir N, Nor-Ashikin MN, Ng KK, Nawawi H, Yusoff K; REDISCOVER Investigators (2016) Prevalence, awareness, treatment, control and socio demographic determinants of hypertension in Malaysian adults. BMC Public Health 16:351. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3008-y
Cornwell EY, Waite LJ (2012) Social network resources and management of hypertension. J Health Soc Behav 53:215–231. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022146512446832
Courtenay WH (2000) Constructions of masculinity and their influence on men’s well-being: a theory of gender and health. Soc Sci Med 50:1385–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0277-9536(99)00390-1
Cutler JA, Sorlie PD, Wolz M, Thom T, Fields LE, Roccella EJ (2008) Trends in hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rates in United States adults between 1988–1994 and 1999–2004. Hypertension 52:818–827. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.113357
Everett B, Zajacova A (2015) Gender differences in hypertension and hypertension awareness among young adults. Biodemography Soc Biol 61:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/19485565.2014.929488
He FJ, Li J, Macgregor GA (2013) Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 346:f1325 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f1325
Hussain MA, Mamun AA, Reid C, Huxley RR (2016) Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Indonesian adults aged ≥40 years: findings from the Indonesia family life survey (IFLS). PLoS One 11:e0160922. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160922
Joffres MR, Hamet P, MacLean DR, L’italien GJ, Fodor G (2001) Distribution of blood pressure and hypertension in Canada and the United States. Am J Hypertens 14:1099–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7061(01)02211-7
Johnson HM, Thorpe CT, Bartels CM, Schumacher JR, Palta M, Pandhi N, Sheehy AM, Smith MA (2014) Undiagnosed hypertension among young adults with regular primary care use. J Hypertens 32:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000000008
Kimura G, Dohi Y, Fukuda M (2010) Salt sensitivity and circadian rhythm of blood pressure: the keys to connect CKD with cardiovascular events. Hypertens Res 33:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2010.47
Lau JS, Adams SH, Boscardin WJ, Irwin CE Jr (2014) Young adults’ health care utilization and expenditures prior to the affordable care act. J Adolesc Health 54:663–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.03.001
Lee HY (2017) Socioeconomic disparities in the prevalence, diagnosis, and control of hypertension in the context of a universal health insurance system. J Korean Med Sci 32:561–567. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.561
Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H et al (2012) A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380:2224–2260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8
Lim KH, Jasvindar K, Cheong SM, Ho BK, Lim HL, Teh CH, Lau KJ, Suthahar A, Ambigga D (2016) Prevalence of smoking and its associated factors with smoking among elderly smokers in Malaysia: findings from a nationwide population-based study. Tob Induc Dis 14:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12971-016-0073-z
Maahs DM, Kinney GL, Wadwa P, Snell-Bergeon JK, Dabelea D, Hokanson J, Ehrlich J, Garg S, Eckel RH, Rewers MJ (2005) Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in an adult type 1 diabetes population and a comparable general population. Diabetes Care 28:301–306. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.28.2.301
Naing C, Aung K (2014) Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension in Myanmar: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 93:e100. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000000100
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) (2017) Worldwide trends in blood pressure from 1975 to 2015: a pooled analysis of 1479 population-based measurement studies with 19·1 million participants. Lancet 389:37–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31919-5
Nieh CC, Ho LM, Sule J, Ho SH, Shi C, Shankar A, Wong TY (2015) Cross-sectional study of hypertension in a neighborhood in Singapore. Insights Blood Press 1:1. http://blood-pressure.imedpub.com/crosssectional-study-of-hypertension-in-a-neighborhood-in-singapore.php?aid=7670. Accessed 28 Nov 2019
Ong SK, Lai DTC, Wong JYY, Si-Ramlee KA, Razak LA, Kassim N, Kamis Z, Koh D (2017) Cross-sectional STEPwise approach to surveillance (STEPS) population survey of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) and risk factors in Brunei Darussalam 2016. Asia Pac J Public Health 29:635–648. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010539517738072
Peltzer K, Pengpid S (2018) The prevalence and social determinants of hypertension among adults in Indonesia: a cross-sectional population-based national survey. Int J Hypertens 2018:5610725. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5610725
Piper MA, Evans CV, Burda BU, Margolis KL, O’Connor E, Smith N, Webber E, Perdue LA, Bigler KD, Whitlock EP (2014) Screening for high blood pressure in adults: a systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK269495/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK269495.pdf. Accessed 4 Jan 2020
Sandberg K, Ji H (2012) Sex differences in primary hypertension. Biol Sex Differ 3:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2042-6410-3-7
Satoh A, Arima H, Ohkubo T, Nishi N, Okuda N, Ae R, Inoue M, Kurita S, Murakami K, Kadota A, Fujiyoshi A, Sakata K, Okamura T, Ueshima H, Okayama A, Miura K; NIPPON DATA2010 Research Group (2017) Associations of socioeconomic status with prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in a general Japanese population: NIPPON DATA2010. J Hypertens 35:401–408. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000001169
Scheltens T, Bots ML, Numans ME, Grobbee DE, Hoes AW (2007) Awareness, treatment and control of hypertension: the ‘rule of halves’ in an era of risk-based treatment of hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 21:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002123
Son PT, Quang NN, Viet NL, Khai PG, Wall S, Weinehall L, Bonita R, Byass P (2012) Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Vietnam—results from a national survey. J Hum Hypertens 26:268–280. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2011.18
Springer KW, Mouzon DM (2011) “Macho men” and preventive health care: implications for older men in different social classes. J Health Soc Behav 52:212–227. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022146510393972
Stimpson JP, Wilson FA (2009) Cholesterol screening by marital status and sex in the United States. Prev Chronic Dis 6(2):A55. http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2009/apr/08_0102.htm. Accessed 31 Oct 2019
Vitale C, Fini M, Speziale G, Chierchia S (2010) Gender differences in the cardiovascular effects of sex hormones. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 24:675–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2010.00817.x
Wu AS, Dodhia H, Whitney D, Ashworth M (2019) Is the rule of halves still relevant today? A cross-sectional analysis of hypertension detection, treatment and control in an urban community. J Hypertens 37:2470–2480. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000002192
Yoon SS, Gu Q, Nwankwo T, Wright JD, Hong Y, Burt V (2015) Trends in blood pressure among adults with hypertension: United States, 2003 to 2012. Hypertension 65:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04012
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the support from Hjh Naedawati Hj Morsidi, Department of Policy and Planning, Ministry of Health, Brunei Darussalam and Dr Hjh Norhayati Hj Kassim, Head of Health Promotion Centre, and Dr Hjh Musjarena Hj Abd Mulok, Head of Primary Healthcare Services, Department of Health Services, Ministry of Health, Brunei Darussalam for her valuable input to the paper.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or non-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Sok King ONG is responsible for the conception and design of the study, data analysis, interpretation of data for the study, drafting and revising of the manuscript.
Dr. Siti Zuhrini KAHAN is responsible for the interpretation of data, drafting and revising of the manuscript.
Dr. Daphne Teck Ching LAI is responsible for the data analysis, interpretation of data, drafting and revising of the manuscript.
Mr. Khairil Azhar SI-RAMLEE is responsible for the data analysis, interpretation of data for the study, drafting and revising of the manuscript.
Dr. Amirruddin ABDULLAH is responsible for the literature review and drafting of the manuscript.
Ms. Nazurah SIDUP is responsible for the data analysis, interpretation of data and drafting of the manuscript.
Mr. Zakaria KAMIS is responsible for the interpretation of data for the study and drafting of the manuscript.
Dr. Chean Lin CHONG is responsible for the interpretation of data for the study, drafting and revising of the manuscript.
The authors declare that they have no relevant financial interests nor any conflict of interest in this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical consideration
The STEPwise approach to Surveillance (STEPS) population study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Medical and Health Research and Ethics Committee (MHREC), Ministry of Health, Brunei Darussalam.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ong, S.K., Kahan, S.Z., Lai, D.T.C. et al. Prevalence of undetected hypertension and its association with socio-demographic and non-communicable diseases risk factors in Brunei Darussalam. J Public Health (Berl.) 31, 149–160 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01287-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01287-y