Abstract
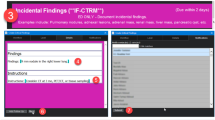
The absence of user-friendly systems for reporting complications is a major barrier to improving quality assurance (QA) programs in interventional radiology (IR) services. We describe the implementation of a QA application that is completely integrated with the radiology dictation system. We implemented an IR QA process as a module within the electronic medical record and radiologist dictation system applications used at our institution. After a radiologist completes a dictation, he or she must select from a drop-down list of complications before proceeding to the next case. Delayed QA events can be entered using the same applications. All complication entries are sent to a database, which is queried to run reports. During the study period, all the 20,034 interventional procedures were entered in the QA database, 1,144 complications were reported, 110 (9.6%) of which were classified as major. Although majority of the complications (996) were entered at the time of dictation, 148 complications (12.9%) were entered afterwards. All major complications were referred to the IR peer review committee, and 30 of these were discussed in the morbidity and mortality meetings. We studied post-lung-biopsy pneumothorax and chest tube rates and initiated a quality improvement process based on the results.The integration of the IR QA reporting system into the workflow process and the mandatory requirements for completion has the potential to minimize the work effort required to enter complication data, and improve participation in the QA process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barraclough BH, Birch J: Health care safety and quality: where have we been and where are we going? Med J Aust 184:S48–50, 2006
Becher EC, Chassin MR: Improving the quality of health care: who will lead? Health Aff (Millwood) 20:164–179, 2001
Donnelly LF, Strife JL: Performance-based assessment of radiology faculty: a practical plan to promote improvement and meet JCAHO standards. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:1398–1401, 2005
Thrall JH: Quality and safety revolution in health care. Radiology 233:3–6, 2004
Walsh K, Antony J: Improving patient safety and quality: what are the challenges and gaps in introducing an integrated electronic adverse incident and recording system within health care industry? Int J Health Care Qual Assur 20:107–115, 2007
Deitch CH, Chan WC, Sunshine JH, Zinninger MD, Cascade PN, Cochran ST: Quality assessment and improvement: what radiologists do and think. AJR Am J Roentgenol 163:1245–1254, 1994
Frank MS, Mann FA, Gillespy T: Quality assurance: a system that integrates a digital dictation system with a computer data base. AJR Am J Roentgenol 161:1101–1103, 1993
Johnson CD, Krecke KN, Roberts RM, Denham C: Quality initiatives: developing a radiology quality and safety program: a primer. Radiographics 29:951–959, 2009
Kruskal JB, Yam CS, Sosna J, Hallett DT, Milliman YJ, Kressel HY: Implementation of online radiology quality assurance reporting system for performance improvement: initial evaluation. Radiology 241:518–527, 2006
Mahgerefteh S, Kruskal JB, Yam CS, Blachar A, Sosna J: Peer review in diagnostic radiology: current state and a vision for the future. Radiographics 29:1221–1231, 2009
Kruskal JB, Anderson S, Yam CS, Sosna J: Strategies for establishing a comprehensive quality and performance improvement program in a radiology department. Radiographics 29:315–329, 2009
Kruskal JB, Siewert B, Anderson SW, Eisenberg RL, Sosna J: Managing an acute adverse event in a radiology department. Radiographics 28:1237–1250, 2008
Guidelines for establishing a quality assurance program in vascular and interventional radiology. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:S203-207, 2003
FitzGerald R: Radiological error: analysis, standard setting, targeted instruction and teamworking. Eur Radiol 15:1760–1767, 2005
Renfrew DL, Franken Jr, EA, Berbaum KS, Weigelt FH, Abu-Yousef MM: Error in radiology: classification and lessons in 182 cases presented at a problem case conference. Radiology 183:145–150, 1992
Soffa DJ, Lewis RS, Sunshine JH, Bhargavan M: Disagreement in interpretation: a method for the development of benchmarks for quality assurance in imaging. J Am Coll Radiol 1:212–217, 2004
Hahn PF, Lee MJ, Gazelle GS, Forman BH, Mueller PR: A simplified HyperCard data base for patient management in an interventional practice: experience with more than 4000 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:1443–1446, 1994
Mayo-Smith WW, Jayaraman MV, Han RS, Dupuy DE, Movson JS: Multiinstitutional computer database for recording nonvascular imaging-guided interventions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:1491–1493, 2003
McEnery KW, Suitor CT, Hildebrand S, Downs R. RadStation: client-based digital dictation system and integrated clinical information display with an embedded Web-browser. Proc AMIA Symp :561-564, 2000
McEnery KW, Suitor CT, Hildebrand S, Downs RL: Integration of radiologist peer review into clinical review workstation. J Digit Imaging 13:101–104, 2000
McEnery KW, Suitor CT, Hildebrand S, Downs RL: Radiologist's clinical information review workstation interfaced with digital dictation system. J Digit Imaging 13:45–48, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Patel, J., McEnery, K. et al. Early Experience Using an Online Reporting System for Interventional Radiology Procedure-Related Complications Integrated with a Digital Dictation System. J Digit Imaging 24, 672–679 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-010-9319-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-010-9319-0