Abstract
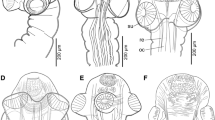
A taxonomic review of the Sebastes vulpes complex (S. vulpes, S. zonatus and S. ijimae) established the existence of two valid species, Sebastes vulpes Döderlein in Steindachner and Döderlein 1884 and Sebastes zonatus Chen and Barsukov 1976, despite evidence of hybridization between them. Similarities between the species include the following: top of cranium armed with robust nasal, preocular, postocular, tympanic and parietal spines; interorbital space flat; anterior and posterior lacrimals without distinct spines, forming two blunt lobes; thickened rays in ventral half of pectoral fin; dorsal fin usually with 13 spines and 13 soft rays; caudal fin rounded; and pored lateral-line scales usually 30–35. However, S. zonatus is distinguishable from S. vulpes in usually having distinct vertical dark bands on the dorsum (vs. usually lacking), minute cycloid scales usually present posteriorly on the lower jaw (vs. usually absent) and present on the entire basal portion of the spinous dorsal-fin membrane (vs. absent below first to ninth or to last dorsal-fin spine). Based on specimen and literature records, S. vulpes inhabits depths of 0–50 m, ranging from Hokkaido southward to Shimane and Sagami Bay, Japan, and along the southern coast of the Korean Peninsula, whereas S. zonatus inhabits depths of 50–100 m, from Hokkaido southward to Shimane and Tosa Bay, including the Seto Inland Sea, and along the southern coast of the Korean Peninsula. Sebastodes ijimae Jordan and Metz 1913 is considered to be a junior synonym of S. vulpes, based on examinations of type and other genetically assigned specimens. A lectotype is designated for S. vulpes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizawa M (2003) Myxini, Cephalaspidomorphi, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes. In: The foundation of Chiba Prefecture for the study of historical materials (ed) Checklist of animals known from Chiba Prefecture. Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, pp 304–335
Amaoka K (1988) Genus Sebastes. In: Masuda H, Amaoka K, Araga C, Uyeno T, Yoshino T (eds) The fishes of the Japanese Archipelago, 2nd edn. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp 310–313
Amaoka K, Fujii R (1999) Fishes of the Döderlein Collection. In: Nishikawa T (ed) Preliminary taxonomic and historical studies on prof. Ludwig Döderlein’s Collection of Japanese animals made in 1880–1881 and deposited at several European museums. Rep Act 1997–8 Grant-in-Aid Int Sci Res (Field Res) No. 090411155, pp 147–165
Amaoka K, Nakaya K, Yabe M (2011) Fishes of Hokkaido. Hokkaido Shimbun Sha, Sapporo
Amaoka K, Nakaya K, Yabu H, Yamamoto H (1983) Fishes and marine algae of northern Japan. Kitanihon Kaiyo Center Co Ltd, Sapporo
Barsukov VV (2003) Annotated and illustrated check-list of rockfishes of the world. In: Dorofeyeva E, Sideleva V (eds) Proc Zoo Inst Russ Acad Sci, vol 95, pp 1–320
Buonaccorsi VP, Kimbrell CA, Lynn EA, Vetter RD (2005) Limited realized dispersal and introgressive hybridization influence genetic structure and conservation strategies for brown rockfish, Sebastes auriculatus. Conserv Genet 6:697–713
Buonaccorsi VP, Narum SR, Karkoska KA, Gregory S, Deptola T, Weimer AB (2011) Characterization of a genomic divergence island between black-and-yellow and gopher Sebastes rockfishes. Mol Ecol 20:2603–2618
Burford MO (2009) Demographic history, geographical distribution and reproductive isolation of distinct lineages of blue rockfish (Sebastes mystinus), a marine fish with a high dispersal potential. J Evol Biol 22:1471–1486
Burgarella C, Lorenzo Z, Jabbour-Zahab R, Lumaret R, Guichoux E, Petit RJ, Soto Á, Gil L (2009) Detection of hybrids in nature: application to oaks (Quercus suber and Q. ilex). Heredity 102:442–452
Chen LC, Barsukov VV (1976) A study of the western North Pacific Sebastes vulpes species complex (Scorpaenidae), with description of a new species. Japan J Ichthyol 23:1–8
Cuvier G (1829) Des Sébastes (Sebastes, nob.). In: Cuvier G, Valenciennes A (eds) Histore naturelle des poissons, vol 4. Chez F. G. Levrault, Paris-Strasbourg, pp 326–350
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361
Eschmeyer WN, Fricke R, van der Laan R (2016) Catalogue of Fishes: genera, species, references. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp. Accessed 28 Feb 2018
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
FishPix. see http://fishpix.kahaku.go.jp/fishimage-e/search.html. Accessed 28 Feb 2016
Frable BW, Wagman DW, Frierson TN, Aguilar A, Sidlauskas BL (2015) A new species of Sebastes (Scorpaeniformes: Sebastidae) from the northeastern Pacific, with a redescription of the blue rockfish, S. mystinus (Jordan and Gilbert, 1881). Fish Bull 113:355–377
Funabashi M (1998) Checklist of marine fishes from the coastal region of Ibaraki Prefecture. Bull Ibaraki Nat Mus 1:75–96
Hawkins SL, Heifetz J, Kondzela CM, Pohl JE, Wilmot RL, Katugin ON, Tuponogov VN (2005) Genetic variation of rougheye rockfish (Sebastes aleutianus) and shortraker rockfish (S. borealis) inferred from allozymes. Fish Bull 103:524–535
Hyde JR, Kimbrell CA, Budrick JE, Lynn EA, Vetter RD (2008) Cryptic speciation in the vermilion rockfish (Sebastes miniatus) and the role of bathymetry in the speciation process. Mol Ecol 17:1122–1136
Hyde JR, Vetter RD (2007) The origin, evolution, and diversification of rockfishes of the genus Sebastes (Cuvier). Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:790–811
ICZN (1999) International code of zoological nomenclature, 4th edn. International Trust of Zoological Nomenclature, London
Ingram T (2010) Speciation along a depth gradient in a marine adaptive radiation. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 278:613–618
Ingram T, Kai Y (2014) The geography of morphological convergence in the radiation of Pacific Sebastes rockfishes. Am Nat 184:E115–E131
Ishida M (2009) Scorpaenidae. In: Okamura O and Amaoka K (eds) Sea fishes of Japan, 3rd edn. Yama to Keikoku Sha, Tokyo, pp 189–209
Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA (2007) CLUMPP: a cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 23:1801–1806
Johns GC, Avise JC (1998) Tests for ancient species flocks based on molecular phylogenetic appraisals of Sebastes rockfishes and other marine fishes. Evolution 52:1135–1146
Jordan DS, Evermann BW (1898) The fishes of North and Middle America: a descriptive catalogue of the species of fish-like vertebrates found in the waters of North America, north of the Isthmus of Panama, part II. Bull US Nat Mus 47:i–xxx, 1241–2183
Jordan DS, Metz CW (1913) A catalog of the fishes known from the waters of Korea. Mem Carnegie Mus 6:1–65
Jordan DS, Hubbs CL (1925) Record of fishes obtained in Japan, 1922. Mem Carnegie Mus 10:93–346
Jordan DS, Starks EC (1904) A review of the Scorpaenoid fishes of Japan. Proc US Nat Mus 27:91–175
Jordan DS, Tanaka S, Snyder JO (1913) A catalogue of the fishes of Japan. J Coll Sci Imp Univ Tokyo 33:1–497
Kai Y, Nakabo T (2008) Taxonomic review of the Sebastes inermis species complex (Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae). Ichthyol Res 55:238–259
Kai Y, Nakabo T (2013) Taxonomic review of the Sebastes pachycephalus complex (Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae). Zootaxa 3637:541–560
Kai Y, Nakayama K, Nakabo T (2002) Genetic differences among three colour morphotypes of the black rockfish, Sebastes inermis, inferred from mtDNA and AFLP analyses. Mol Ecol 11:2591–2598
Kai Y, Nakayama K, Nakabo T (2003) Molecular phylogenetic perspective on speciation in the genus Sebastes (Scorpaenidae) from the Northwest Pacific and the position of Sebastes within the subfamily Sebastinae. Ichthyol Res 50:239–244
Kai Y, Nakayama K, Nakabo T (2011) Genetic and morphological divergence within the Sebastes pachycephalus complex (Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae). Ichthyol Res 58:333–343
Kai Y, Park KD, Nakabo T (2012) The incomplete history of mitochondrial lineages between two rockfishes, Sebastes longispinis and Sebastes hubbsi (Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae). J Fish Biol 81:954–965
Kanayama T, Kitagawa D (1983) Fishes of Iwate II, Soi-Menukerui. Iwate Fisheries Experimental Station, Kamaishi
Katayama M (1940) A catalogue of the fishes of Toyama Bay. Toyama J Nat His 3:1–28
Katayama M, Fujioka Y (1958) Fishes of Oosima-gun, Yamaguti Prefecture. Bull Fac Agr Yamaguchi Univ 9:1147–1168
Kim IS, Choi Y, Lee CL, Lee YJ, Kim BJ, Kim JH (2005) Illustrated book of Korean fishes. Kyohak Publishing Co Ltd, Seoul
Kim YU, Myoung JG, Kim YS, Han KH, Kang CB, Kim JK, Ryu JH (2005) Marine fishes of Korea, 2nd edn. Hanguel Graphics Co Ltd, Busan
Kitagawa D, Imamura H, Goto T, Ishito Y, Fujiwara K, Ueda Y (2008) Field guide of the fishes from the Tohoku district, north-eastern waters of Japan. Tokai University Press, Hadano
Lindberg GU, Krasyukova ZV (1987) Fishes of the Sea of Japan and adjacent parts of Okhotsk and Yellow Sea. Part 5. Nauka Publishers, Leningrad
Masuda H, Kobayashi Y (1994) Grand atlas of fish life modes. Tokai University Press, Tokyo
Matsubara K (1943) Studies on the scorpaenid fishes of Japan. Anatomy, phylogeny and taxonomy II. Trans Shigenkagaku Kenkyusho 2:171–486
Matsubara K (1955) Fish morphology and hierarchy, part II. Ishizakishoten, Tokyo
Matsubara K (1965) Scorpaenidae. In: Okada K, Uchida K, Uchida R (eds) New Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Fauna of Japan. Hokuryu-kan, Tokyo, pp 422–435
Mori T (1956) Fishes of San-in District including Oki Islands and its adjacent waters (Southern Japan Sea). Mem Hyogo Univ Agr 2:1–62
Muto N, Kai Y, Nakabo T (2011) Genetic and morphological differences between Sebastes vulpes and S. zonatus (Teleostei: Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae). Fish Bull 109:429–439
Muto N, Kai Y, Noda T, Nakabo T (2013) Extensive hybridization and associated geographic trends between two rockfishes Sebastes vulpes and S. zonatus (Teleostei: Scorpaeniformes: Sebastidae). J Evol Biol 26:1750–1762
Nakabo T (1993) Scorpaenidae. In: Nakabo T (ed) Fishes of Japan with pictorial keys to the species. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp 491–518, 1295–1298
Nakabo T (2000) Scorpaenidae. In: Nakabo T (ed) Fishes of Japan with pictorial keys to the species, 2nd edn. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp 565–595, 1524–1528
Nakabo T (2002) Scorpaenidae. In: Nakabo T (ed) Fishes of Japan with pictorial keys to the species, English edn. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp 565–595, 1524–1528
Nakabo T, Kai Y (2013) Sebastidae. In: Nakabo T (ed) Fishes of Japan with pictorial keys to the species, 3rd edn. Tokai University Press, Hadano, pp 668–681, 1933–1934
Narum SR, Buonaccorsi VP, Kimbrell CA, Vetter RD (2004) Genetic divergence between gopher rockfish (Sebastes carnatus) and black and yellow rockfish (Sebastes chrysomelas). Copeia 4:926–931
Nelson JS, Grande TC, Wilson MVH (2016) Fishes of the world, 5th edn. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Nishida T, Nakazono A, Oikawa S, Matsui S (2005) Changes of coastal fish fauna in the Chikuzen sea according to rise of sea water temperature in recent years. Sci Bull Fac Agr Kyushu Univ 60:187–201
Okada Y (1955) Fishes of Japan. Maruzen Co Ltd, Tokyo
Okada Y, Matsubara K (1938) Keys to the fishes and fish-like animals of Japan. Sanseido Co Ltd, Tokyo
Okada Y, Uchida K, Matsubara K (1935) Color atlas of fishes of Japan. Sanseido Co Ltd, Tokyo
Orr JW, Hawkins S (2008) Species of the rougheye rockfish complex : resurrection of Sebastes melanostictus (Matsubara, 1934) and a redescription of Sebastes aleutianus (Jordan and Evermann, 1898) (Teleostei: Scorpaeniformes). Fish Bull 106:111–134
Paepke HJ, Fricke R (1992) Kritischer Katalog der Typen der Fischsammlung des Zoologischen Museums Berlin. Teil 4: Scorpaeniformes. Mitt Zool Mus Berlin 68:267–293
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 17 May 2018
Randall JE, Eschmeyer WN (2001) Revision of the Indo-Pacific scorpionfish genus Scorpaenopsis, with descriptions of eight new species. Indo-Pacific Fishes 34:1–79
Roques S, Sévigny JM, Bernatchez L (2001) Evidence for broadscale introgressive hybridization between two redfish (genus Sebastes) in the North-west Atlantic: a rare marine example. Mol Ecol 10:149–165
Rosenberg NA (2004) Distruct: a program for the graphical display of population structure. Mol Ecol Notes 4:137–138
Rüber L, Zardoya R (2005) Rapid cladogenesis in marine fishes revisited. Evolution 59:1119–1127
Sabaj MH (2016) Standard symbolic codes for institutional resource collections in herpetology and ichthyology: an Online Reference. Version 6.5 (16 August 2016). American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists, Washington DC. http://www.asih.org/resources/standard-symbolic-codes-institutional-resource-collections-herpetology-ichthyology. Accessed 28 Feb 2018
Sanz N, Araguas RM, Fernández R, Vera M, García-Marín J (2009) Efficiency of markers and methods for detecting hybrids and introgression in stocked populations. Conserv Genet 10:225–236
Sasaki M (2003) Kitsune mebaru Sebastes vulpes Döderlein. In: Ueda Y, Maeda K, Shimada H, Takami T (eds) Fisheries and Aquatic Life in Hokkaido, Hokkaido Shimbun Sha, Sapporo, pp 194–195
Seeb LW (1998) Gene flow and introgression within and among three species of rockfishes, Sebastes auriculatus, S. caurinus, and S. maliger. J Hered 89:393–403
Shiogaki M, Ishito Y, Nomura Y, Sugimoto T (2004) Revised catalogue of the fishes collected from the waters of Aomori Prefecture. Bull Aomori Pref Fish Res Cent 4:39–80
Snyder JO (1912) Japanese shore fishes collected by the United States Bureau of Fisheries Streamer “Albatross” expedition of 1906. Proc US Nat Mus 42:399–450
Stefánsson MO, Sigurdsson T, Pampoulie C, Daníelsdóttir AK, Thorgilsson B, Ragnarsdóttir A, Gíslason D, Coughlan J, Cross TF, Bernatchez L (2009) Pleistocene genetic legacy suggests incipient species of Sebastes mentella in the Irminger Sea. Heredity 102:514–524
Steindachner F, Döderlein L (1884) Beiträge zur kenntniss der fische Japan’s. (III.). Denkschr Akad Wiss Wien 49:171–212, pls 1–7
Steindachner F, Döderlein L (1887) Beiträe zur Kenntniss der Fische Japan’s. (IV.). Denkschr Akad Wiss Wien 49:257–295, pls 1–4
Vähä JP, Primmer CR (2006) Efficiency of model-based Bayesian methods for detecting hybrid individuals under different hybridization scenarios and with different numbers of loci. Mol Ecol 15:63–72
Youn CH (2002) Fishes of Korea with pictorial key and systematic list. Acad Pub Com, Seoul
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Nakayama and M. Tagawa (FAKU) for helpful comments, G. Hardy (Ngunguru, New Zealand) for English corrections and valuable comments on the manuscript, and K. Sakai (Noto Marine Center) and T. Noda (Seikai National Fisheries Research Institute) for help in collecting specimens and valuable discussion. We also thank L. Parenti and J. Williams (USNM), W. Smith and K. Swagel (FMNH), W. Fink and D. Nelson (UMMZ), P. Hastings, H. Walker and C. Klepadlo (SIO), P. Bartsch and C. Lamour (ZMB), E. Mikschi and H. Wellendorf (NMW), M. Yabe, H. Imamura and T. Kawai (HUMZ), K. Matsuura, G. Shinohara and M. Nakae (NSMT), M. Motokawa (The Kyoto University Museum) and N. Nakayama (formerly The Kyoto University Museum), who facilitated the authors’ visits to examine specimens, J.-K. Kim (PKU), H. Endo (BSKU) and D. Catania (CAS) for loans of specimens and H.-J. Kwun (formerly PKU) for translating Korean literature. Our appreciation is also extended to the following who helped the collection of specimens and literature: Y. Koizumi and K. Koizumi (Otaru city), S. Matsui and K. Takahashi (Tomakomai city), C.-H. Jeong (Inha University) and N. Yoshimura (formerly HUMZ). This study was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 19770063 and 20370034, the Mikimoto Fund for Marine Ecology and the Sasakawa Scientific Research Grant from the Japan Science Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as 6E610D75-840F-43C9-A640-01179703E406.
This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Muto, N., Kai, Y. & Nakabo, T. Taxonomic review of the Sebastes vulpes complex (Scorpaenoidei: Sebastidae). Ichthyol Res 66, 9–29 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-018-0641-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-018-0641-8