Abstract
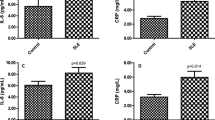
We aimed to determine in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients the Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 and C-reactive gene (CRP) polymorphisms and allele frequency and to investigate the relationship between clinical parameters and gene polymorphisms. We enrolled in this study 31 PsA and 41 healthy control subjects. PsA diagnosis was according to CASPAR criteria. Bath ankylosing spondylitis diseases activity index, Maastricht ankylosing spondylitis enthesitis score, and Bath ankylosing spondylitis functional index were measured. C, A, and T alleles of CRP and A and G alleles of TLR 4 were determined using the analysis of melting curves after real-time PCR. CRP A, C, and T allele frequency in controls was 26.8, 73.2, and 36.6 %, respectively. In the PsA patient group, A, C, and T allele frequency was 9.7, 87.1, and 12.9 %, respectively. Between control and PsA groups, there was a significant difference in A, C, and T allele frequency (P = 0.008, 0.038, and 0.001, respectively). The frequency of CRP gene polymorphisms (CA, AA, CT, TA, and TT alleles) in the control group was 56.1 % and in the PsA group was 22.6 %. There was a significant difference between the two groups (P = 0.004). The absence of a CRP gene polymorphism was a risk factor for PsA (odds ratio 4.3, 95 % CI; 1.5–12.4, P = 0.005). TLR gene haploid frequency was investigated, and all control subjects had the wild-type AA allele. PsA patient GA allele frequency was 6.5 %. There was no significant difference between the two groups (P = 0.182). GA mutant allele frequency was related to PsA (odds ratio 7.03, 95 % CI; 0.32–151.9, P = 0.214). We have shown that CRP gene polymorphisms are higher in control subjects than PsA patients, and TLR 4 gene polymorphisms were found to be related to PsA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mease P (2013) Psoriatic arthritis and spondyloarthritis assessment and management update. Curr Opin Rheumatol 25:287–296. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835fd8d5
Villanova F, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO (2013) Biomarkers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 72(Suppl 2):ii104-10. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-203037
Benham H, Norris P, Goodall J et al (2013) Th17 and Th22 cells in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Arthritis Res Ther 15:R136. doi:10.1186/ar4317
Genetic Képíró L, Széll M, Kovács L, Keszthelyi P, Kemény L, Gyulai R (2014) Risk and protective factors of TNFSF15 gene variants detected using single nucleotide polymorphisms in Hungarians with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Hum Immunol 75:159–162. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2013.11.006
Mavropoulos A, Rigopoulou EI, Liaskos C, Bogdanos DP, Sakkas LI (2013) The role of p38 MAPK in the aetiopathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:569751. doi:10.1155/2013/569751
O’Donnell H, Pham OH, Li LX et al (2014) Toll-like receptor and inflammasome signals converge to amplify the innate bactericidal capacity of T helper 1 cells. Immunity 40:213–224. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.12.013
Peng L, Luo YT, Liu JL (2011) The effects of atorvastatin on C-reactive protein induced Toll-like receptor 4 expression on CD14+ monocyte. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 39:664–669
Liu N, Liu JT, Ji YY, Lu PP (2010) C-reactive protein triggers inflammatory responses partly via TLR4/IRF3/NF-κB signaling pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 87:367–374. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2010.07.012
Carrasco S, Neves FS, Fonseca MH et al (2011) Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 is upregulated on peripheral blood monocytes of patients with psoriatic arthritis: a role for a gram-positive inflammatory trigger? Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:958–962
Candia L, Marquez J, Hernandez C, Zea AH, Espinoza LR (2007) Toll-like receptor-2 expression is upregulated in antigen-presenting cells from patients psoriatic arthritis: a pathogenic role for innate immunity? J Rheumatol 3:374–379
Garcia-Rodriguez S, Arias-Santiago S, Perandrés-López R et al (2013) Increased gene expression of Toll-like receptor 4 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27:242–250
Garcia-Rodriguez S, Arias-Santiago S, Perandrés-López R et al (2011) Increased gene expression of Toll-like receptor 4 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04372.x
Bogaczewicz A, Sobow T, Bogaczewicz J et al (2013) Toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphism 1196C/T does not influence the risk of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus in Polish population—a preliminary report. Lupus 22:1504–1508. doi:10.1177/0961203313511553
Yang H, Wei C, Li Q et al (2013) Association of TLR4 gene non-missense single nucleotide polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese Han population. Rheumatol Int 33:1283–1288. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2536-8
Xu WD, Liu SS, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2012) Lack of association of TLR4 polymorphisms with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: a meta-analysis. Joint Bone Spine 79:566–569. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2012.02.012
Myles A, Aggarwal A (2013) Lack of association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in toll-like receptors 2 and 4 with enthesitis-related arthritis category of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Indian population. Rheumatol Int 33:417–421
García-Bermúdez M, López-Mejías R, González-Juanatey C et al (2012) Lack of association between TLR4 rs4986790 polymorphism and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. DNA Cell Biol 31:1214–1220. doi:10.1089/dna.2011
Hernesniemi JA, Raitakari OT, Kähönen M et al (2008) Toll-like receptor 4 gene (Asp299Gly) polymorphism associates with carotid artery elasticity. The cardiovascular risk in young Finns study. Atherosclerosis 198:152–159
Lamb R, Zeggini E, Thomson W, Donn R (2005) Toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(5):767–769
Beygi S, Lajevardi V, Abedini R (2013) C-reactive protein in psoriasis: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. doi:10.1111/jdv.12257
Abd El-Aziz TA, Mohamed RH (2013) Human C-reactive protein gene polymorphism and metabolic syndrome are associated with premature coronary artery disease. Gene 532:216–221. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.042
Martínez-Calleja A, Quiróz-Vargas I, Parra-Rojas I, et al (2012) Haplotypes in the CRP gene associated with increased BMI and levels of CRP in subjects with type 2 diabetes or obesity from Southwestern Mexico. Exp Diabetes Res 982683. doi:10.1155/2012/982683
Shen C, Sun X, Wang H et al (2013) Association study of CRP gene and ischemic stroke in a Chinese Han population. J Mol Neurosci 49:559–566. doi:10.1007/s12031-012-9856-8
Kim HA, Chun HY, Kim SH, Park HS, Suh CH (2009) C-reactive protein gene polymorphisms in disease susceptibility and clinical manifestations of Korean systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 36(10):2238–2243. doi:10.3899/jrheum.090243
Almeida OP, Norman PE, Allcock R et al (2009) Polymorphisms of the CRP gene inhibit inflammatory response and increase susceptibility to depression: the Health in Men Study. Int J Epidemiol 38:1049–1059. doi:10.1093/ije/dyp199
Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Timpson NJ et al (2008) The association of C-reactive protein and CRP genotype with coronary heart disease: findings from five studies with 4,610 cases amongst 18,637 participants. PLoS One 3:e3011. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003011
Chang YC, Wu WM, Hsu LA (2012) Lack of association between the genetic variations in the C-reactive protein gene and the risk of psoriasis among the Taiwanese. Mol Biol Rep 39:4111–4117. doi:10.1007/s11033-011-1193-4
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H (2006) Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum 54:2665–2673
Fredriksson T, Pettersson U (1978) Severe psoriasis—oral therapy with a new retinoid. Dermatologica 157:238–244
Akkoc Y, Karatepe AG, Akar S, Kirazli Y, Akkoc N (2005) Turkish version of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index: reliability and validity. Rheumatol Int 25:280–284
Heuft-Dorenbosch L, Spoorenberg A, van Tubergen A et al (2003) Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 62:127–132
Jenkinson TR, Mallorie P, Whitelock HC, Kennedy LG, Calin A (1994) Defining spinal mobility in ankylosing spondylitis (AS): the Bath AS Metrological Index (BASMI). J Rheumatol 21:1694–1698
Ozer HT, Sarpel T, Gulek B, Alparslan ZN, Erken E (2005) The Turkish version of Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index: reliability and validity. Clin Rheumatol 24:123–128
Jönsen A, Gunnarsson I, Gullstrand B et al (2007) Association between SLE nephritis and polymorphic variants of the CRP and FcgammaRIIIa genes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:1417–1421
Szalai AJ, Alarcón GS, Calvo-Alén J et al (2005) Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US Cohort (LUMINA). XXX: association between C-reactive protein (CRP) gene polymorphisms and vascular events. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:864–868
Conflict of interest
This original article involved no financial support, and none of the authors had any conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No commercial party having a direct financial interest in the results of the research supporting this article has or will confer a benefit on the authors or on any organization with which the authors are associated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbal, A., Oğuz, S., Gökmen, F. et al. C-reactive protein gene and Toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphisms can relate to the development of psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34, 301–306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2581-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2581-7