Abstract
Introduction
The long-term results of total hip replacement (THR) are excellent; however, it has higher failure rates in young and active patients. Hip resurfacing arthroplasty (HRA) is an alternative in such patients and gaining popularity. This review was done to compare complications and outcomes between HRA and THA by assessing the latest level 1 studies comparing the two from the past 10 years.
Method
A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted using three databases (PubMed, EMBASE and SCOPUS) to compare the complications between THR and HRA in medium to long term follow up. The primary outcome of interest included the complication and revision rate between the two techniques. Functional outcomes and ionic levels at follow up were also compared as secondary outcomes. Risk of bias assessment was done using the Cochrane risk of bias tool.
Result
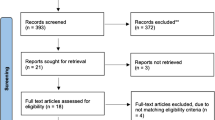
The present review included 6 level 1 studies. These included 308 THR and 304 HRA. On meta-analysis, overall complications rates were significantly lower in HRA compared to the THA group with an Odds ratio (OR) of 2.17 (95% CI 1.21, 3.88; p = 0.009). No difference was seen between the two groups in terms of revision rate (OR 1.06 95% CI 0.57, 1.99; p = 0.85). Functional outcomes in both the groups were satisfactory but the Harris Hip Score was found to be significantly better in the resurfacing group (MD 2.99 95% CI − 4.01, − 1.96, p < 0.00001). There were increased cobalt and chromium ions in the resurfacing group but no detrimental effect was seen in terms of reported poisoning.
Conclusion
Despite similar function and revision rates, HRA was seen to have lesser associated complications and ionic levels may not be a detrimental issue. Hip resurfacing provides relative ease during revisions, especially in younger patients and it may be an alternative to THR in the younger population.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wroblewski BM, Fleming PA, Siney PD (1999) Charnley low-frictional torque arthroplasty of the hip 20-to-30 year results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81(3):427–430. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.81b3.9521
Garbuz DS, Tanzer M, Greidanus NV, Masri BA, Duncan CP (2010) The John Charnley Award: metal-on-metal hip resurfacing versus large-diameter head metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(2):318–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1029-x
Grigoris P, Roberts P, Panousis K, Jin Z (2006) Hip resurfacing arthroplasty: the evolution of contemporary designs. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 220(2):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1243/095441105x69042
Mont MA, Schmalzried TP (2008) Modern metal-on-metal hip resurfacing: important observations from the first ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Suppl 3):3–11. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.H.00750
Pollard TC, Baker RP, Eastaugh-Waring SJ, Bannister GC (2006) Treatment of the young active patient with osteoarthritis of the hip. A five- to seven-year comparison of hybrid total hip arthroplasty and metal-on-metal resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88(5):592–600. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.88b5.17354
Matharu GS, McBryde CW, Pynsent WB, Pynsent PB, Treacy RB (2013) The outcome of the birmingham hip resurfacing in patients aged < 50 years up to 14 years post-operatively. Bone Joint J 95-b(9):1172–1177. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.95b9.31711
Rahman L, Muirhead-Allwood SK, Alkinj M (2010) What is the midterm survivorship and function after hip resurfacing? Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(12):3221–3227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1438-x
Nunley R, Valle C, Barrack R (2008) Is patient selection important for hip resurfacing? Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0558-z
Mont MA, Ragland PS, Etienne G, Seyler TM, Schmalzried TP (2006) Hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14(8):454–463. https://doi.org/10.5435/00124635-200608000-00003
Crawford JR, Palmer SJ, Wimhurst JA, Villar RN (2005) Bone loss at hip resurfacing: a comparison with total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int 15(4):195–198. https://doi.org/10.5301/hip.2008.5286
Harty JA, Devitt B, Harty LC, Molloy M, McGuinness A (2005) Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry analysis of peri-prosthetic stress shielding in the Birmingham resurfacing hip replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 125(10):693–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-005-0059-4
Little JP, Taddei F, Viceconti M, Murray DW, Gill HS (2007) Changes in femur stress after hip resurfacing arthroplasty: response to physiological loads. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 22(4):440–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2006.12.002
Wagner M, Wagner H (1996) Preliminary results of uncemented metal on metal stemmed and resurfacing hip replacement arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199608001-00008
Vendittoli PA, Lavigne M, Roy AG, Lusignan D (2006) A prospective randomized clinical trial comparing metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty and metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing in patients less than 65 years old. Hip Int 16(Suppl 4):73–81. https://doi.org/10.5301/hip.2008.1446
Treacy RB, McBryde CW, Pynsent PB (2005) Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty. A minimum follow-up of five years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(2):167–170. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.87b2.15030
Shimmin A, Back D (2005) Femoral neck fractures following Birmingham hip resurfacing: a national review of 50 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:463–464. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.87B4.15498
Langton DJ, Jameson SS, Joyce TJ, Hallab NJ, Natu S, Nargol AV (2010) Early failure of metal-on-metal bearings in hip resurfacing and large-diameter total hip replacement: a consequence of excess wear. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(1):38–46. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.92b1.22770
Marshall DA, Pykerman K, Werle J, Lorenzetti D, Wasylak T, Noseworthy T, Dick DA, O’Connor G, Sundaram A, Heintzbergen S, Frank C (2014) Hip resurfacing versus total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review comparing standardized outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(7):2217–2230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3556-3
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 62(10):1006–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng H-Y, Corbett MS, Eldridge SM, Emberson JR, Hernán MA, Hopewell S, Hróbjartsson A, Junqueira DR, Jüni P, Kirkham JJ, Lasserson T, Li T, McAleenan A, Reeves BC, Shepperd S, Shrier I, Stewart LA, Tilling K, White IR, Whiting PF, Higgins JPT (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366:l4898. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Costa ML, Achten J, Foguet P, Parsons NR (2018) Comparison of hip function and quality of life of total hip arthroplasty and resurfacing arthroplasty in the treatment of young patients with arthritis of the hip joint at 5 years. BMJ Open 8(3):e018849. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018849
Konan S, Waugh C, Ohly N, Duncan CP, Masri BA, Garbuz DS (2021) Mid-term results of a prospective randomised controlled trial comparing large-head metal-on-metal hip replacement to hip resurfacing using patient-reported outcome measures and objective functional task-based outcomes. Hip Int 31(5):637–643. https://doi.org/10.1177/1120700020919671
Hersnaes PN, Gromov K, Otte KS, Gebuhr PH, Troelsen A (2021) Harris Hip Score and SF-36 following metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty and hip resurfacing—a randomized controlled trial with 5-years follow up including 75 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22(1):781. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04671-1
Kostretzis L, Lavigne M, Kiss M-O, Shahin M, Barry J, Vendittoli P-A (2021) Despite higher revision rate, MoM large-head THA offers better clinical scores than HR: 14 year results from a randomized controlled trial involving 48 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22(1):400. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04286-6
Bisseling P, Smolders JM, Hol A, van Susante JL (2015) Metal ion levels and functional results following resurfacing hip arthroplasty versus conventional small-diameter metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty; a 3 to 5 year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty 30(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2014.07.036
Vendittoli PA, Rivière C, Roy AG, Barry J, Lusignan D, Lavigne M (2013) Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing compared with 28 mm diameter metal-on-metal total hip replacement: a randomised study with six to nine years follow-up. Bone Joint J 95-b(11):1464–1473. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.95b11.31604
Hauptfleisch J, Pandit H, Grammatopoulos G, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere S (2012) A MRI classification of periprosthetic soft tissue masses (pseudotumours) associated with metal-on-metal resurfacing hip arthroplasty. Skeletal Radiol 41(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-011-1329-6
Funding
Nil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Ksheersagar, V., Aggarwal, S. et al. Complications and mid to long term outcomes for hip resurfacing versus total hip replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 33, 1495–1504 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03361-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-022-03361-5