Abstract
Background context
Laminoplasty and laminectomy with fusion are two common procedures for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Controversy remains regarding the superior surgical treatment.
Purpose
To compare short-term follow-up of laminoplasty to laminectomy with fusion for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy.
Study design/setting
Retrospective review comparing all patients undergoing surgical treatment for cervical spondylotic myelopathy by a single surgeon.
Patient sample
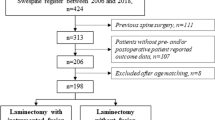
All patients undergoing laminoplasty or laminectomy with fusion by a single surgeon over a 5-year period (2007–2011).
Outcome measures
Cervical alignment and range of motion on pre- and post-operative radiographs and clinical outcome measures including Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) scores, neck disability index (NDI), short form-12 mental (SF-12M) and physical (SF-12P) composite scores and visual analog pain scores for neck (VAS-N) and arm (VAS-A).
Methods
Patients undergoing laminoplasty or laminectomy with fusion by a single surgeon were reviewed. Cohorts of 41 laminoplasty patients and 31 laminectomy with fusion patients were selected based on strict criteria. The cohorts were well matched based on pre-operative clinical scores, radiographic measurements, and demographics. The average follow-up was 19.2 months for laminoplasty and 18.2 months for laminectomy with fusion. Evaluated outcomes included Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) score, neck disability index (NDI), short form-12 (SF-12), visual analog pain scores (VAS), cervical sagittal alignment, cervical range of motion, length of stay, cost and complications.
Results
The improvement in JOA, SF-12 and VAS scores was similar in the two cohorts after surgery. There was no significant change in cervical sagittal alignment in either cohort. Range-of-motion decreased in both cohorts, but to a greater degree after laminectomy with fusion. C5 nerve root palsy and infection were the most common complications in both cohorts. Laminectomy with fusion was associated with a higher rate of C5 nerve root palsy and overall complications. The average hospital length of stay and cost were significantly less with laminoplasty.
Conclusions
This study provides evidence that laminoplasty may be superior to laminectomy with fusion in preserving cervical range of motion, reducing hospital stay and minimizing cost. However, the significance of these differences remains unclear, as laminoplasty clinical outcome scores were generally comparable to laminectomy with fusion.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao RD, Gourab K, David KS (2006) Operative treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88:1619–1640. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00014
Clarke E, Robinson PK (1956) Cervical myelopathy: a complication of cervical spondylosis. Brain 79:483–510
Fujiwara K, Yonenobu K, Ebara S, Yamashita K, Ono K (1989) The prognosis of surgery for cervical compression myelopathy. An analysis of the factors involved. J Bone Joint Surg Br 71:393–398
Suri A, Chabbra RP, Mehta VS, Gaikwad S, Pandey RM (2003) Effect of intramedullary signal changes on the surgical outcome of patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine J 3:33–45
Traynelis VC, Arnold PM, Fourney DR, Bransford RJ, Fischer DJ, Skelly AC (2013) Alternative procedures for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: arthroplasty, oblique corpectomy, skip laminectomy: evaluation of comparative effectiveness and safety. Spine 38:S210–S231. doi:10.1097/brs.0000000000000009
Lonstein JE (1977) Post-laminectomy kyphosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 128:93–100
Guigui P, Benoist M, Deburge A (1998) Spinal deformity and instability after multilevel cervical laminectomy for spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 23:440–447
Dai L, Ni B, Yuan W, Jia L (1998) Radiculopathy after laminectomy for cervical compression myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80:846–849
Kaye ID, Marascalchi BJ, Macagno AE, Lafage VA, Bendo JA, Passias PG (2015) Predictors of morbidity and mortality among patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy treated surgically. Eur Spine J 24:2910–2917. doi:10.1007/s00586-015-4010-2
Gonzalez-Feria L, Peraita-Peraita P (1975) Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a cooperative study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 78:19–33
Maurer PK, Ellenbogen RG, Ecklund J, Simonds GR, van Dam B, Ondra SL (1991) Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: treatment with posterior decompression and Luque rectangle bone fusion. Neurosurgery 28:680–683 (discussion 683–684)
Huang RC, Girardi FP, Poynton AR, Cammisa FP Jr (2003) Treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myeloradiculopathy with posterior decompression and fusion with lateral mass plate fixation and local bone graft. J Spinal Disord Tech 16:123–129
Cherubino P, Benazzo F, Borromeo U, Perle S (1990) Degenerative arthritis of the adjacent spinal joints following anterior cervical spinal fusion: clinicoradiologic and statistical correlations. Ital J Orthop Traumatol 16:533–543
Kato Y, Iwasaki M, Fuji T, Yonenobu K, Ochi T (1998) Long-term follow-up results of laminectomy for cervical myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg 89:217–223. doi:10.3171/jns.1998.89.2.0217
Hosono N, Yonenobu K, Ono K (1996) Neck and shoulder pain after laminoplasty. A noticeable complication. Spine 21:1969–1973
Ratliff JK, Cooper PR (2003) Cervical laminoplasty: a critical review. J Neurosurg 98:230–238
Nurboja B, Kachramanoglou C, Choi D (2011) Cervical laminectomy versus laminoplasty: is there a difference in outcome and post-operative pain? Neurosurgery. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e31823cf16b
Manzano GR, Casella G, Wang MY, Vanni S, Levi AD (2012) A prospective, randomized trial comparing expansile cervical laminoplasty and cervical laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy. Neurosurg 70:264–277. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182305669
Highsmith JM, Dhall SS, Haid RW Jr, Rodts GE Jr, Mummaneni PV (2011) Treatment of cervical stenotic myelopathy: a cost and outcome comparison of laminoplasty versus laminectomy and lateral mass fusion. J Neurosurg Spine 14:619–625. doi:10.3171/2011.1.SPINE10206
Heller JG, Edwards CC 2nd, Murakami H, Rodts GE (2001) Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy: an independent matched cohort analysis. Spine 26:1330–1336
Hukuda S, Ogata M, Mochizuki T, Shichikawa K (1988) Laminectomy versus laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy: brief report. J Bone Joint Surg Br 70:325–326
Lee CH, Lee J, Kang JD, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ (2015) Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy: a meta-analysis of clinical and radiological outcomes. J Neurosurg Spine 22:589–595. doi:10.3171/2014.10.spine1498
Bartels RH, van Tulder MW, Moojen WA, Arts MP, Peul WC (2015) Laminoplasty and laminectomy for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a systematic review. Eur Spine J 24(Suppl 2):160–167. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-2771-z
Gok B, McLoughlin GS, Sciubba DM, McGirt MJ, Chaichana KL, Wolinsky JP, Bydon A, Gokaslan ZL, Witham TF (2009) Surgical management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy with laminectomy and instrumented fusion. Neurol Res 31:1097–1101. doi:10.1179/174313209X383277
Houten JK, Cooper PR (2003) Laminectomy and posterior cervical plating for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: effects on cervical alignment, spinal cord compression, and neurological outcome. Neurosurgery 52:1081–1087 (discussion 1087–1088)
Kumar VG, Rea GL, Mervis LJ, McGregor JM (1999) Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: functional and radiographic long-term outcome after laminectomy and posterior fusion. Neurosurgery 44:771–777 (discussion 777–778)
Epstein NE (2015) Commentary on article: laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy: a meta-analysis of clinical and radiological outcomes by Chang-Hyun Lee et al. Surg Neurol Int 6:S379–S382. doi:10.4103/2152-7806.163957
Manzano GR, Casella G, Wang MY, Vanni S, Levi AD (2012) A prospective, randomized trial comparing expansile cervical laminoplasty and cervical laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy. Neurosurgery 70:264–277. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182305669
Hukuda S, Mochizuki T, Ogata M, Shichikawa K, Shimomura Y (1985) Operations for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. A comparison of the results of anterior and posterior procedures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 67:609–615
Furlan JC, Kalsi-Ryan S, Kailaya-Vasan A, Massicotte EM, Fehlings MG (2011) Functional and clinical outcomes following surgical treatment in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a prospective study of 81 cases. J Neurosurg Spine 14:348–355. doi:10.3171/2010.10.spine091029
Bartels RH, Verbeek AL, Grotenhuis JA (2007) Design of Lamifuse: a randomised, multi-centre controlled trial comparing laminectomy without or with dorsal fusion for cervical myeloradiculopathy. BMC Musculoskelet disorders 8:111. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-8-111
Vernon H, Mior S (1991) The neck disability index: a study of reliability and validity. J Manip Physiol Ther 14:409–415
Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Campbell MJ, Anderson PA (2010) Neck disability index, short form-36 physical component summary, and pain scales for neck and arm pain: the minimum clinically important difference and substantial clinical benefit after cervical spine fusion. Spine J 10:469–474. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2010.02.007
Team RDC (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Revelle W (2013) Psych: procedures for personality and psychological research, Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois, USA. http://cran.r-projectorg/package=psych. Version = 142. Accessed 01 Feb 2015
Developer TJA (2012) Epitools: epidemiology tools. R package version 0.5-7. http://cran.r-projectorg/package=epitools. Accessed 01 Feb 2015
Woods BI, Hohl J, Lee J, Donaldson W 3rd, Kang J (2011) Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:688–695. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1653-5
Nurboja B, Kachramanoglou C, Choi D (2012) Cervical laminectomy vs laminoplasty: is there a difference in outcome and postoperative pain? Neurosurgery 70:965–970. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e31823cf16b (discussion 970)
Nassr A, Eck JC, Ponnappan RK, Zanoun RR, Donaldson WF 3rd, Kang JD (2012) The incidence of C5 palsy after multilevel cervical decompression procedures: a review of 750 consecutive cases. Spine 37:174–178. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318219cfe9
Bydon M, Macki M, Kaloostian P, Sciubba DM, Wolinsky JP, Gokaslan ZL, Belzberg AJ, Bydon A, Witham TF (2014) Incidence and prognostic factors of c5 palsy: a clinical study of 1001 cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 74:595–604. doi:10.1227/neu.0000000000000322 (discussion 604-595)
Wu FL, Sun Y, Pan SF, Zhang L, Liu ZJ (2014) Risk factors associated with upper extremity palsy after expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy. Spine J 14:909–915. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2013.07.445
Yamanaka K, Tachibana T, Moriyama T, Okada F, Maruo K, Inoue S, Horinouchi Y, Yoshiya S (2014) C-5 palsy after cervical laminoplasty with instrumented posterior fusion. J Neurosurg Spine 20:1–4. doi:10.3171/2013.9.spine12952
Tetreault L, Singh A, Fawcett M, Nater A, Fehlings MG (2015) An assessment of the key predictors of perioperative complications in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy undergoing surgical treatment: results from a survey of 916 AOSpine international members. World Neurosurg. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2015.01.021
Financial and material support
No authors received financial support for any of the work reported herein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blizzard, D.J., Caputo, A.M., Sheets, C.Z. et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy with fusion for the treatment of spondylotic cervical myelopathy: short-term follow-up. Eur Spine J 26, 85–93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4746-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4746-3