Abstract
Background
In the clinical practice, prednisone (PDN) dose in children is often prescribed using the patient weight, despite dose calculation using body surface area (BSA) is assumed to be preferable, because it parallels better with PDN metabolism in human subjects.
Methods
Calculations based on body weight (W) carry the risk of underdosing, particularly in young children. Conversely, BSA estimation requires knowing the patient height, which is not always available, and more complex calculations.
Results
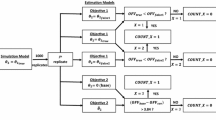
To overcome these limitations, we have developed linear equations allowing approximating the BSA-based dose using only the patient weight in kilogram. To this end, we have used anthropomorphic data from 754 pediatric patients and have validated the proposed equations with a prospective cohort of 77 children with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome. The equation estimating a dose of 60 mg/m2 was [2 × W + 8] and the equation estimating a dose of 40 mg/m2 was [W + 11].
Conclusions
Both equations performed very well and predicted reliably the BSA-based dose with an average error of 3.4% and 2.2%, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Study of Kidney Disease in Children (1979) Nephrotic syndrome in children: a randomized trial comparing two prednisone regimens in steroid-responsive patients who relapse early. J Pediatr 95:228–233
Hahn D, Hodson EM, Willis NS, Craig JC (2015) Corticosteroid therapy for nephrotic syndrome in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD001533. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858
Lombel RM, Gipson DS, Hodson EM, Kidney Disease: Improving Global O (2013) Treatment of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: new guidelines from KDIGO. Pediatr Nephrol 28:415–426
Vivarelli M, Massella L, Ruggiero B, Emma F (2017) Minimal change disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12:332–345
Feber J, Al-Matrafi J, Farhadi E, Vaillancourt R, Wolfish N (2009) Prednisone dosing per body weight or body surface area in children with nephrotic syndrome: is it equivalent? Pediatr Nephrol 24:1027–1031
Ruggiero B, Vivarelli M, Gianviti A, Benetti E, Peruzzi L, Barbano G, Corona F, Ventura G, Pecoraro C, Murer L, Ghiggeri GM, Pennesi M, Edefonti A, Coppo R, Emma F (2013) Lupus nephritis in children and adolescents: results of the Italian Collaborative Study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:1487–1496
Vivarelli M, Moscaritolo E, Tsalkidis A, Massella L, Emma F (2010) Time for initial response to steroids is a major prognostic factor in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Pediatr 156:965–971
Pasini A, Aceto G, Ammenti A, Ardissino G, Azzolina V, Bettinelli A, Cama E, Cantatore S, Crisafi A, Conti G, D'Agostino M, Dozza A, Edefonti A, Fede C, Groppali E, Gualeni C, Lavacchini A, Lepore M, Maringhini S, Mariotti P, Materassi M, Mencarelli F, Messina G, Negri A, Piepoli M, Ravaglia F, Simoni A, Spagnoletta L, Montini G, NefroKid Study G (2015) Best practice guidelines for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: recommendations versus reality. Pediatr Nephrol 30:91–101
Mosteller RD (1987) Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N Engl J Med 317:1098
Wang Y, Moss J, Thisted R (1992) Predictors of body surface area. J Clin Anesth 4:4–10
Haycock GB, Schwartz GJ, Wisotsky DH (1978) Geometric method for measuring body surface area: a height-weight formula validated in infants, children, and adults. J Pediatr 93:62–66
Gehan EA, George SL (1970) Estimation of human body surface area from height and weight. Cancer Chemother Rep 54:225–235
Verbraecken J, Van de Heyning P, De Backer W, Van Gaal L (2006) Body surface area in normal-weight, overweight, and obese adults. A comparison study. Metabolism 55:515–524
Schimmer BP, Parker KL (2001) Adrenocorticotropic hormone; adrenocortical steroids and their synthetic analogs; inhibitors of the synthesis and actions of adrenocortical hormones. In: Gilman AG, Hardman JG, Limbird LE (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. The McGraw-Hill Companies, New York, pp 1635–1648
Miura M, Satoh S, Inoue K, Kagaya H, Saito M, Inoue T, Habuchi T, Suzuki T (2008) Influence of CYP3A5, ABCB1 and NR1I2 polymorphisms on prednisolone pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Steroids 73:1052–1059
Sandrini R, Jospe N, Migeon CJ (1993) Temporal and individual variations in the dose of glucocorticoid used for the treatment of salt-losing congenital virilizing adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Acta Paediatr Suppl 388:56–60 discussion 61
Raman V, Krishnamurthy S, Harichandrakumar KT (2016) Body weight-based prednisolone versus body surface area-based prednisolone regimen for induction of remission in children with nephrotic syndrome: a randomized, open-label, equivalence clinical trial. Pediatr Nephrol 31:595–604
Saadeh SA, Baracco R, Jain A, Kapur G, Mattoo TK, Valentini RP (2011) Weight or body surface area dosing of steroids in nephrotic syndrome: is there an outcome difference? Pediatr Nephrol 26:2167–2171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 499 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emma, F., Montini, G. & Gargiulo, A. Equations to estimate prednisone dose using body weight. Pediatr Nephrol 34, 685–688 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4127-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4127-8