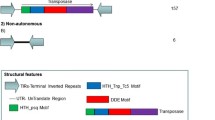
Abstract
Sequencing and annotation of a contiguous stretch of genomic DNA (112.3 kb) from the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans revealed the order, spacing and genomic context of four members of the elicitin (inf) gene family. Analysis of the GC content at the third codon position (GC3) of six genes encoded in the region, and a set of randomly selected coding regions as well as random genomic regions, showed that a high GC3 value is a general feature of Phytophthora genes that can be exploited to optimize gene prediction programs for Phytophthora species. At least one-third of the annotated 112.3-kb P. infestans sequence consisted of transposons or transposon-like elements. The most prominent were four Tc3/gypsy and Tc1/copia type retrotransposons and three DNA transposons that belong to the Tc1/mariner, Pogo and PiggyBac groups, respectively. Comparative analysis of other available genomic sequences suggests that transposable elements are highly heterogeneous and ubiquitous in the P. infestans genome.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasland R, Stewart AF (1995) The chromo shadow domain, a second chromo domain in heterochromatin-binding protein 1, HP1. Nucleic Acids Res 23:3168–3173
Ah Fong AM, Judelson HS (2004) The hAT-like DNA transposon DodoPi resides in a cluster of retro- and DNA transposons in the stramenopile Phytophthora infestans. Mol Genet Genomics 271:577–585
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Baldauf SL (2003) The deep roots of eukaryotes. Science 300:1703–1706
Baltimore D (1985) Retroviruses and retrotransposons—the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell 40:481–482
Bateman A, Birney E, Durbin R, Eddy SR, Finn RD, Sonnhammer ELL (1999) Pfam 3.1: 1313 multiple alignments and profile HMMs match the majority of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 27:260–262
Bateman A, Birney E, Durbin R, Eddy SR, Howe KL, Sonnhammer ELL (2000) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 28:263–266
Boeke JD, Corces VG (1989) Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Annu Rev Microbiol 43:403–434
Bonfield JK, Smith K, Staden R (1995) A new DNA sequence assembly program. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4992–4999
Cavalli G, Paro R (1998) Chromo-domain proteins: linking chromatin structure to epigenetic regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10:354–360
Daboussi MJ, Capy P (2003) Transposable elements in filamentous fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:275–299
Duclos J, Fauconnier A, Coelho AC, Bollen A, Cravador A, Godfroid E (1998) Identification of an elicitin gene cluster in Phytophthora cinnamomi. DNA Seq 9:231–237
Echalier G (1989) Drosophila retrotransposons—interactions with genome. Adv Virus Res 36:33–105
Erwin DC, Ribeiro OK (1996) Phytophthora diseases worldwide. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, Minn.
Feschotte C, Jiang N, Wessler SR (2002) Plant transposable elements: where genetics meets genomics. Nature Rev Genetics 3:329–341
Flavell AJ, Smith DB, Kumar A (1992) Extreme heterogeneity of Ty1-Copia group retrotransposons in plants. Mol Gen Genetics 231:233–242
Geer LY, Domrachev M, Lipman DJ, Bryant SH (2002) CDART: protein homology by domain architecture. Genome Res 12:1619–1623
Hendrix JW, Guttman SM (1970) Sterol or calcium requirement by Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae for growth on nitrate. Mycologia 62:195–198
Hraber PT, Weller JW (2001) On the species of origin: diagnosing the source of symbiotic transcripts. Genome Biol 2:37
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends Biochem Sci 23:403–405
Judelson HS (2002) Sequence variation and genomic amplification of a family of Gypsy-like elements in the oomycete genus Phytophthora. Mol Biol Evol 19:1313–1322
Kamoun S (2003) Molecular genetics of pathogenic oomycetes. Eukaryot Cell 2:191–199
Kamoun S, Styer A (2000) An improved codon usage table for Phytophthora infestans. http://www.oardc.ohio-state.edu/phytophthora/codon.htm
Kamoun S, van West P, de Jong AJ, de Groot KE, Vleeshouwers VGAA, Govers F (1997) A gene encoding a protein elicitor of Phytophthora infestans is down-regulated during infection of potato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:13–20
Kamoun S, van West P, Vleeshouwers VGAA, de Groot KE, Govers F (1998) Resistance of Nicotiana benthamiana to Phytophthora infestans is mediated by the recognition of elicitor protein INF1. Plant Cell 10:1413–1426
Kamoun S, Hraber P, Sobral B, Nuss D, Govers F (1999) Initial assessment of gene diversity for the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans based on expressed sequences. Fungal Genet Biol 28:94–106
Kim JM, Vanguri S, Boeke JD, Gabriel A, Voytas DF (1998) Transposable elements and genome organization: A comprehensive survey of retrotransposons revealed by the complete Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome sequence. Genome Res 8:464–478
Koonin EV, Zhou S, Lucchesi JC (1995) The chromo superfamily: new members, duplication of the chromo domain and possible role in delivering transcription regulators to chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4229–4233
Kroon LP, Bakker FT, Van Den Bosch GB, Bonants PJ, Flier WG (2004) Phylogenetic analysis of Phytophthora species based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Fungal Genet Biol 41:766–782
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (1994) MEGA—Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software for microcomputers. Comput Appl Biosci 10:189–191
Latijnhouwers M, de Wit PJGM, Govers F (2003) Oomycetes and fungi: similar weaponry to attack plants. Trends Microbiol 11:462–469
McLeod A, Smart CD, Fry WE (2004) Core promoter structure in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans. Eukaryot Cell 3:91–99
Mikes V, Milat ML, Ponchet M, Panabieres F, Ricci P, Blein JP (1998) Elicitins, proteinaceous elicitors of plant defense, are a new class of sterol carrier proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245:133–139
Noma K, Ohtsubo E, Ohtsubo H (1999) Non-LTR retrotransposons (LINEs) as ubiquitous components of plant genomes. Mol Gen Genet 261:71–79
O’Neill K, Zody MC, Karlsson E, Govers F, van der Vondervoort P, Weide R, Whisson S, Birch P, Ma L, Birren B, Fry W, Judelson H, Kamoun S, Nusbaum C (2004) Sequencing the Phytophthora infestans genome: preliminary studies. Abstracts of the Annual Meeting of the NSF Phytophthora Molecular Genetics Network. New Orleans, May 21–23, 2004, p. 5
Panabieres F, Marais A, LeBerre JY, Penot I, Fournier D, Ricci P (1995) Characterization of a gene cluster of Phytophthora cryptogea which codes for elicitins, proteins inducing a hypersensitive-like response in tobacco. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:996–1003
Paro R, Hogness DS (1991) The Polycomb protein shares a homologous domain with a heterochromatin-associated protein of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:263–267
Pieterse CMJ, Van West P, Verbakel HM, Brasse P, Van den Berg-Velthuis GCM, Govers F (1994) Structure and Genomic Organization of the ipib and ipio gene clusters of Phytophthora infestans. Gene 138:67–77
Plasterk RH (1996) The Tc1/mariner transposon family. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 204:125–143
Qutob D, Hraber PT, Sobral BWS, Gijzen M (2000) Comparative analysis of expressed sequences in Phytophthora sojae. Plant Physiol 123:243–253
Randall TA et al (2004) Large-scale gene discovery in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans reveals likely components of phytopathogenicity shared with true fungi. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, in press
Ricci P, Trentin F, Bonnet P, Venard P, Moutonperronnet F, Bruneteau M (1992) Differential production of parasiticein, an elicitor of necrosis and resistance in tobacco, by isolates of Phytophthora Parasitica. Plant Pathol 41:298–307
Sarkar A, Sim C, Hong YS, Hogan JR, Fraser MJ, Robertson HM, Collins FH (2003) Molecular evolutionary analysis of the widespread piggyBac transposon family and related “domesticated” sequences. Mol Genet Genomics 270:173–180
Schmidt T (1999) LINEs, SINEs and repetitive DNA: non-LTR retrotransposons in plant genomes. Plant Mol Biol 40:903–910
Schwartz S, Zhang Z, Frazer KA, Smit A, Riemer C, Bouck J, Gibbs R, Hardison R, Miller W (2000) PipMaker—a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res 10:577–586
Skalamera D, Wasson AP, Hardham AR (2004) Genes expressed in zoospores of Phytophthora nicotianae. Mol Genet Genomics 270:549–557
Smit AF, Riggs AD (1996) Tiggers and DNA transposon fossils in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1443–1448
Soanes DM, Skinner W, Keon J, Hargreaves J, Talbot NJ (2002) Genomics of phytopathogenic fungi and the development of bioinformatic resources. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:421–427
Tooley PW, Garfinkel DJ (1996) Presence of Ty1-copia group retrotransposon sequences in the potato late blight pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9:305–309
Tudor M, Lobocka M, Goodell M, Pettitt J, O’Hare K (1992) The pogo transposable element family of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet 232:126–134
Whisson SC, van der Lee T, Bryan GJ, Waugh R, Govers F, Birch PRJ (2001) Physical mapping across an avirulence locus of Phytophthora infestans using a highly representative, large-insert bacterial artificial chromosome library. Mol Genet Genomics 266:289–295
Xiong Y, Eickbush TH (1990) Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse-transcriptase sequences. EMBO J 9:3353–3362
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Sharmili Mathur for expert technical assistance, Steve Whisson for providing the BAC library and filters, Grardy van den Berg for screening the BAC library, and Pierre de Wit for critically reading the manuscript. This work was financially supported by NWO-Aspasia Grant No. 015.000.057 and USDA Cooperative Agreement No. 58-8230-6-081. The authors acknowledge Syngenta for access to the Syngenta Phytophthora Consortium EST Database, and the Broad Institute and the DOE Joint Genome Institute for depositing random genomic sequences of P. infestans and P. sojae, respectively, in the NCBI trace file archive
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W.R. McCombie
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, R.H.Y., Dawe, A.L., Weide, R. et al. Elicitin genes in Phytophthora infestans are clustered and interspersed with various transposon-like elements. Mol Genet Genomics 273, 20–32 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-1114-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-1114-0