Abstract
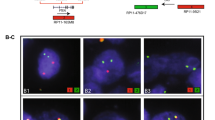
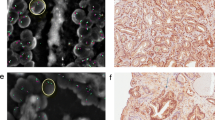
TMPRSS2–ERG, the most common gene fusion in prostate cancer, is associated with expression of a truncated protein product of the oncogene ERG. A novel anti-ERG monoclonal antibody has been recently characterized. We investigated the correlation between ERG rearrangement assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and ERG expression detected by immunohistochemistry in a large cohort of patients treated with radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Thirteen tissue microarrays comprising 305 tumors and a subset of 112 samples of nonneoplastic prostatic tissue were assessed for ERG rearrangement status by FISH and for ERG expression by immunohistochemistry. Accuracy of ERG detection by immunohistochemistry in predicting ERG status as assessed by FISH (criterion standard) was calculated in terms of sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values. Of 305 tumor foci, 103 (34%) showed ERG rearrangement by FISH. ERG was detected by immunohistochemistry in 100 (33%) cases, 99 of which were FISH positive. ERG detection by immunohistochemistry demonstrated a sensitivity and specificity of 96% and 99%, respectively, with positive and negative predictive values of 99% and 98%, respectively. None of the 112 samples of nonneoplastic prostatic tissue was rearranged by FISH or showed any ERG expression. In conclusion, ERG detection by immunohistochemistry in prostate cancer was highly predictive of ERG rearrangement as assessed by FISH in a large cohort of prostatectomy patients. Given the high yield and the easier task of performing immunohistochemistry vs. FISH, ERG assessment by immunohistochemistry may be useful for characterizing ERG status in prostate cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabbitts TH, Stocks MR (2003) Chromosomal translocation products engender new intracellular therapeutic technologies. Nat Med 9(4):383–386
Falini B, Martelli MP, Tiacci E, Ascani S, Thiede C, Pileri SA (2010) Immunohistochemical surrogates for genetic alterations of CCDN1, PML, ALK, and NPM1 genes in lymphomas and acute myeloid leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 23(3):417–431
Mehra R, Tomlins SA, Shen R, Nadeem O, Wang L, Wei JT, Pienta KJ, Ghosh D, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM, Shah RB (2007) Comprehensive assessment of TMPRSS2 and ETS family gene aberrations in clinically localized prostate cancer. Mod Pathol 20(5):538–544
Perner S, Mosquera JM, Demichelis F, Hofer MD, Paris PL, Simko J, Collins C, Bismar TA, Chinnaiyan AM, De Marzo AM, Rubin MA (2007) TMPRSS2–ERG fusion prostate cancer: an early molecular event associated with invasion. Am J Surg Pathol 31(6):882–888
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J, Kuefer R, Lee C, Montie JE, Shah RB, Pienta KJ, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM (2005) Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 310(5748):644–648
Mosquera JM, Mehra R, Regan MM, Perner S, Genega EM, Bueti G, Shah RB, Gaston S, Tomlins SA, Wei JT, Kearney MC, Johnson LA, Tang JM, Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA, Sanda MG (2009) Prevalence of TMPRSS2–ERG fusion prostate cancer among men undergoing prostate biopsy in the United States. Clin Cancer Res 15(14):4706–4711
Clark J, Merson S, Jhavar S, Flohr P, Edwards S, Foster CS, Eeles R, Martin FL, Phillips DH, Crundwell M, Christmas T, Thompson A, Fisher C, Kovacs G, Cooper CS (2007) Diversity of TMPRSS2–ERG fusion transcripts in the human prostate. Oncogene 26(18):2667–2673
Furusato B, Gao CL, Ravindranath L, Chen Y, Cullen J, McLeod DG, Dobi A, Srivastava S, Petrovics G, Sesterhenn IA (2008) Mapping of TMPRSS2–ERG fusions in the context of multi-focal prostate cancer. Mod Pathol 21(2):67–75
Scheble VJ, Braun M, Beroukhim R, Mermel CH, Ruiz C, Wilbertz T, Stiedl AC, Petersen K, Reischl M, Kuefer R, Schilling D, Fend F, Kristiansen G, Meyerson M, Rubin MA, Bubendorf L, Perner S (2010) ERG rearrangement is specific to prostate cancer and does not occur in any other common tumor. Mod Pathol 23(8):1061–1067
Petrovics G, Liu A, Shaheduzzaman S, Furusato B, Sun C, Chen Y, Nau M, Ravindranath L, Dobi A, Srikantan V, Sesterhenn IA, McLeod DG, Vahey M, Moul JW, Srivastava S (2005) Frequent overexpression of ETS-related gene-1 (ERG1) in prostate cancer transcriptome. Oncogene 24(23):3847–3852
Tomlins SA, Laxman B, Varambally S, Cao X, Yu J, Helgeson BE, Cao Q, Prensner JR, Rubin MA, Shah RB, Mehra R, Chinnaiyan AM (2008) Role of the TMPRSS2–ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Neoplasia 10(2):177–188
Klezovitch O, Risk M, Coleman I, Lucas JM, Null M, True LD, Nelson PS, Vasioukhin V (2008) A causal role for ERG in neoplastic transformation of prostate epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(6):2105–2110
Carver BS, Tran J, Gopalan A, Chen Z, Shaikh S, Carracedo A, Alimonti A, Nardella C, Varmeh S, Scardino PT, Cordon-Cardo C, Gerald W, Pandolfi PP (2009) Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to promote cancer progression in the prostate. Nat Genet 41(5):619–624
Furusato B, Tan SH, Young D, Dobi A, Sun C, Mohamed AA, Thangapazham R, Chen Y, McMaster G, Sreenath T, Petrovics G, McLeod DG, Srivastava S, Sesterhenn IA (2010) ERG oncoprotein expression in prostate cancer: clonal progression of ERG-positive tumor cells and potential for ERG-based stratification. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 13(3):228–237
Park K, Tomlins SA, Mudaliar KM, Chiu YL, Esgueva R, Mehra R, Suleman K, Varambally S, Brenner JC, MacDonald T, Srivastava A, Tewari AK, Sathyanarayana U, Nagy D, Pestano G, Kunju LP, Demichelis F, Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA (2010) Antibody-based detection of ERG rearrangement-positive prostate cancer. Neoplasia 12(7):590–598
Falzarano SM, Navas M, Simmerman K, Klein EA, Rubin MA, Zhou M, Magi-Galluzzi C (2010) ERG rearrangement is present in a subset of transition zone prostatic tumors. Mod Pathol 23(11):1499–1506
Falzarano SM, Zhou M, Hernandez AV, Klein EA, Rubin MA, Magi-Galluzzi C (2011) Single focus prostate cancer: pathological features and ERG fusion status. J Urol 185(2):489–494
Rubin MA, Varambally S, Beroukhim R, Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Paris PL, Hofer MD, Storz-Schweizer M, Kuefer R, Fletcher JA, Hsi BL, Byrne JA, Pienta KJ, Collins C, Sellers WR, Chinnaiyan AM (2004) Overexpression, amplification, and androgen regulation of TPD52 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 64(11):3814–3822
Espinosa I, Lee CH, Kim MK, Rouse BT, Subramanian S, Montgomery K, Varma S, Corless CL, Heinrich MC, Smith KS, Wang Z, Rubin B, Nielsen TO, Seitz RS, Ross DT, West RB, Cleary ML, van de Rijn M (2008) A novel monoclonal antibody against DOG1 is a sensitive and specific marker for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 32(2):210–218
Seth A, Watson DK (2005) ETS transcription factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur J Cancer 41(16):2462–2478
Esgueva R, Perner S, LaFargue CJ, Scheble V, Stephan C, Lein M, Fritzsche FR, Dietel M, Kristiansen G, Rubin MA (2010) Prevalence of TMPRSS2–ERG and SLC45A3-ERG gene fusions in a large prostatectomy cohort. Mod Pathol 23(4):539–546
Pflueger D, Rickman DS, Sboner A, Perner S, LaFargue CJ, Svensson MA, Moss BJ, Kitabayashi N, Pan Y, de la Taille A, Kuefer R, Tewari AK, Demichelis F, Chee MS, Gerstein MB, Rubin MA (2009) N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 (NDRG1) is fused to ERG in prostate cancer. Neoplasia 11(8):804–811
Attard G, Clark J, Ambroisine L, Fisher G, Kovacs G, Flohr P, Berney D, Foster CS, Fletcher A, Gerald WL, Moller H, Reuter V, De Bono JS, Scardino P, Cuzick J, Cooper CS (2008) Duplication of the fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG sequences identifies fatal human prostate cancer. Oncogene 27(3):253–263
Mehra R, Han B, Tomlins SA, Wang L, Menon A, Wasco MJ, Shen R, Montie JE, Chinnaiyan AM, Shah RB (2007) Heterogeneity of TMPRSS2 gene rearrangements in multifocal prostate adenocarcinoma: molecular evidence for an independent group of diseases. Cancer Res 67(17):7991–7995
Perner S, Demichelis F, Beroukhim R, Schmidt FH, Mosquera JM, Setlur S, Tchinda J, Tomlins SA, Hofer MD, Pienta KG, Kuefer R, Vessella R, Sun XW, Meyerson M, Lee C, Sellers WR, Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA (2006) TMPRSS2:ERG fusion-associated deletions provide insight into the heterogeneity of prostate cancer. Cancer Res 66(17):8337–8341
Barry M, Perner S, Demichelis F, Rubin MA (2007) TMPRSS2–ERG fusion heterogeneity in multifocal prostate cancer: clinical and biologic implications. Urology 70(4):630–633
Mohamed AA, Tan SH, Mikhalkevich N, Ponniah S, Vasioukhin V, Bieberich CJ, Sesterhenn IA, Dobi A, Srivastava S, Sreenath TL (2010) Ets family protein, erg expression in developing and adult mouse tissues by a highly specific monoclonal antibody. J Cancer 1:197–208
Birdsey GM, Dryden NH, Amsellem V, Gebhardt F, Sahnan K, Haskard DO, Dejana E, Mason JC, Randi AM (2008) Transcription factor Erg regulates angiogenesis and endothelial apoptosis through VE-cadherin. Blood 111(7):3498–3506
Anderson MK, Hernandez-Hoyos G, Diamond RA, Rothenberg EV (1999) Precise developmental regulation of Ets family transcription factors during specification and commitment to the T cell lineage. Development 126(14):3131–3148
Disclosure/Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falzarano, S.M., Zhou, M., Carver, P. et al. ERG gene rearrangement status in prostate cancer detected by immunohistochemistry. Virchows Arch 459, 441–447 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1128-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1128-4