Abstract
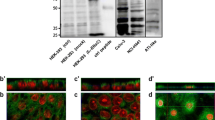
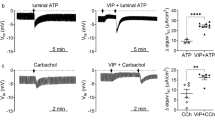
Potassium channels are required for the absorption and secretion of fluids and electrolytes in epithelia. Calu-3 cells possess a secretory phenotype, and are a model human airway submucosal gland serous cell. Short-circuit current (Isc) recordings from Calu-3 cells indicated that basal anion secretion was reduced by apical application of the K+ channel inhibitors bupivicaine, lidocaine, clofilium, and quinidine. Application of riluzole resulted in a large increase in Isc, inhibited by apical application of either bupivicane or the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) Cl− channel blocker DPC. These results suggested that one or more members of the two-pore-domain K+ (K2P) channel family could influence anion secretion. Using RT-PCR, we found that Calu-3 cells express mRNA transcripts for TASK-2 (KCNK5), TWIK-1 (KCNK1), TWIK-2 (KCNK6) and TREK-1 (KCNK2). TASK-2, TWIK-2 and TREK-1 protein were detected by Western blotting, while immunolocalization of polarized cells confirmed protein expression of TREK-1 and TWIK-2 at the plasma cell membrane. TASK-2 protein staining was localized to intracellular vesicles, located beneath the apical membrane. While the pro-secretory role of basolateral K+ channels is well established, we suggest that apically located K2Pchannels, not previously described in airway epithelial cells, also play an important role in controlling the rate of transepithelial anion secretion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bleich M, Warth R (2000) The very small-conductance K+ channel KvLQT1 and epithelial function. Pflugers Arch 440:202–206
Chavez RA, Gray AT, Zhao BB, Kindler CH, Mazurek MJ, Mehta Y et al (1999) TWIK-2, a new weak inward rectifying member of the tandem pore domain potassium channel family. J Biol Chem 274:7887–7892
Cook DI, Young JA (1989) Effect of K+ channels in the apical plasma membrane on epithelial secretion based on secondary actve Cl− transport. J Membr Biol 110:139–146
Cotton CU (2000) Basolateral potassium channels and epithelial ion transport. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23:270–272
Cowley EA, Linsdell P (2002) Characterization of basolateral K+ channels underlying anion secretion in the human airway cell line Calu-3. J Physiol 538:747–757
Cowley EA, Linsdell P (2002) Oxidant stress stimulates anion secretion from the human airway epithelial cell line Calu-3: implications for cystic fibrosis lung disease. J Physiol 543:201–209
Cowley EA (2003) Isoprostane-mediated secretion from human airway epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol 64:298–307
Cuthbert AW, MacVinish LJ (2003) Mechanisms of anion secretion in Calu-3 human airway epithelial cells by 7,8-benzoquinoline. Br J Pharmacol 40:81–90
Czirjak G, Enyedi P (2002) Formation of functional heterodimers between the TASK-1 and TASK-3 two-pore domain potassium channel subunits. J Biol Chem 277:5426–5432
Decher N, Maier M, Dittrich W, Gassenhuber J, Bruggemann A, Busch AE, Steinmeyer K (2001) Characterization of TASK-4, a novel member of the pH-sensitive, two-pore domain potassium channel family. FEBS Lett 492:84–89
Devor DC, Singh AK, Frizzell RA, Bridges RJ (1996) Modulation of Cl- secretion by benzimidazolones. I. Direct activation of a Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel. Am J Physiol 271:L775–L784
Devor DC, Singh AK, Lambert LC, DeLuca A, Frizzell RA, Bridges RJ (1999) Bicarbonate and chloride secretion in Calu-3 human airway epithelial cells. J Gen Physiol 113:743–760
Dubin RF, Robinson SK, Widdicombe JH (2004) Secretion of lactoferrin and lysozyme by cultures of human airway epithelium. Am J Physiol 286:L750–L755
Duprat F, Lesage F, Patel AJ, Fink M, Romey G, Lazdunski M (2000) The neuroprotective agent riluzole activates the two P domain K+ channels TREK-1 and TRAAK. Mol Pharmacol 57:906–912
Engelhardt JF, Yankaskas JR, Ernst SA, Yang Y, Marino CR, Boucher RC et al (1992) Submucosal glands are the predominant site of CFTR expression in the human bronchus. Nat Gen 2:240–248
Fong P, Argent BE, Guggino WB, Gray MA (2002) Characterization of vectoral chloride pathways in the human pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma cell line HPAF. Am J Physiol 285:C433–C445
Illek B, Lizarzaburu ME, Lee V, Nantz MH, Kurth MJ, Fischer H (2000) Structural determinants for activation of CFTR-mediated chloride currents by apigenin. Am J Physiol 279:C1838–C1846
Kim D, Gnatenco C (2001) TASK-5, a new member of the tandem-pore K(+) channel family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:923–930
Kindler CH, Paul M, Zou H, Liu C, Winegar BD, Gray AT, Yost CS (2003) Amide local anesthetics potently inhibit the human tandem pore domain background K+ channel TASK-2 (KCNK5). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:84–92
Kindler CH, Yost CS, Gray AT (1999) Local anesthetic inhibition of baseline potassium channels with two pore domains in tandem. Anesthesiology 90:1092–1102
Krouse ME, Talbott JF, Lee MM, Joo NS, Wine JJ (2004) Acid and base secretion in the Calu-3 model of human serous cells. Am J Physiol 287:L1274–L1283
Lam RS, App EM, Nahirney D, Szkotak AJ, Vieira-Coelho MA, King M, Duszyk M (2003) Regulation of Cl- secretion by alpha2-adrenergic receptors in mouse colonic epithelium. J Physiol 548:475–484
Lesage F, Guillemare E, Fink M, Duprat F, Lazdunski M, Romey G, Barhanin J (1996) TWIK-1, a ubiquitous human weakly inward rectifying K+ channel with a novel structure. EMBO J 15:1004–1011
Maingret F, Patel AJ, Lesage F, Lazdunski M, Honoré E (1999) Mechano- or acid stimulation, two interactive modes of activation of the TREK-1 potassium channel. J Biol Chem 274:26691–26696
McCann JD, Welsh MJ (1990) Basolateral K+ channels in airway epithelia. II. Role in Cl− secretion and evidence for two types of K+ channel. Am J Physiol 258:L343–L348
Medhurst AD, Rennie G, Chapman CG, Meadows H, Duckworth MD, Kelsell RE et al (2001) Distribution analysis of human two pore domain potassium channels in tissues of the central nervous system and periphery. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 86:101–114
Moon S, Singh M, Krouse ME, Wine JJ (1997) Calcium-stimulated Cl− secretion in Calu-3 human airway cells requires CFTR. Am J Physol 273:L1208–L1219
Niemeyer MI, Cid LP, Barros LF, Sepulveda FV (2001) Modulation of the two-pore domain acid-sensitive K+ channel TASK-2 (KCNK5) by changes in cell volume. J Biol Chem 276:43166–43174
Patel AJ, Honoré E (2001) Properties and modulation of mammalian 2P domain K+ channels. Trends Neurosci 24:339–346
Patel AJ, Honoré E, Lesage F, Fink M, Romey G, Lazdunski M (1999) Inhalational anesthetics activate two-pore-domain background K+ channels. Nat Neurosci 2:422–426
Patel AJ, Honoré E, Maingret F, Lesage F, Fink M, Duprat F, Lazdunski M (1998) A mammalian two pore domain mechano-gated S-like K+ channel. EMBO J 17:4283–4290
Patel AJ, Lazdunski M (2004) The 2P-domain K+ channels: role in apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Pflugers Arch 448:261–273
Pilewski JM, Frizzell RA (1999) Role of CFTR in airway disease. Physiol Rev 79:S215–S255
Punke MA, Licher T, Pongs O, Friederich P (2003) Inhibition of human TREK-1 channels by bupivacaine. Anesth Analg 96:1665–1673
Reyes R, Duprat F, Lesage F, Fink M, Salinas M, Farman N, Lazdunski M (1998) Cloning and expression of a novel pH-sensitive two pore domain K+ channel from human kidney. J Biol Chem 273:30863–30869
Shen BQ, Finkbeiner WE, Wine JJ, Mrsny RJ, Widdicombe JH (1994) Calu-3: a human airway epithelial cell line that shows cAMP-dependent Cl− secretion. Am J Physiol 266:L493–L501
Shorofsky SR, Filed M, Fozzard HA (1983) Electrophysiology of Cl secretion in canine trachea. J Membr Biol 72:105–115
Silva P, Stoff J, Filed M, Fine L, Forrest JN, Epstein FH (1977) mechanism of active chloride secretion by shark rectal gland: Role of Na-K-ATPase in chloride transport. Am J Physiol 233:F298–F306
Singh M, Krouse ME, Moon S, Wine JJ (1997) Most basal Isc in Calu-3 human airway cells is bicarbonate-dependent Cl− secretion. Am J Physiol 272:L690–L698
Singh S, Syme CA, Singh AK, Devor DC, Bridges RJ (2001) Benzimidazolone activators of chloride secretion: potential therapeutics for cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:600–611
Smith PL, Frizzell RA (1984) Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium: IV. Basolateral membrane K permeability parallels secretion rate. J Membr Biol 77:187–199
Szkotak AJ, Murthy M, MacVinish LJ, Duszyk M, Cuthbert AW (2004) 4-Chloro-benzo[F]isoquinoline (CBIQ) activates CFTR chloride channels and KCNN4 potassium channels in Calu-3 human airway epithelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 142:531–542
Talley EM, Sirois JE, Lei Q, Bayliss DA (2003) Two-pore-Domain (KCNK) potassium channels: dynamic roles in neuronal function. Neuroscientist 9:46–56
Wu JV, Krouse M E, Rustagi A, Joo NS, Wine JJ (2004) An inwardly rectifying potassium channel in apical membrane of Calu-3 cells. J Biol Chem 279:46558–46565
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Susan Burbidge and Jeremy Roy for assistance with cell culture. Additionally, we thank Andrew Joy for assistance with cutting Calu-3 cell sections and Dr Paul Linsdell for critical discussion of the manuscript. This work was supported by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Nova Scotia Lung Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, K.A., Cowley, E.A. Two-pore-domain potassium channels support anion secretion from human airway Calu-3 epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 451, 631–641 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-1505-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-1505-4