Abstract
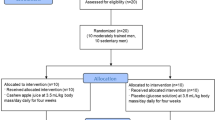
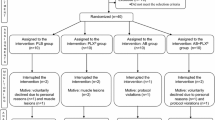
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of low-volume exercise training (100 min/week) on oxidative stress and neutrophils activation markers in older adults. Twenty-eight older adults (age range 65–78 years) were assigned into control (n = 14) or exercise (n = 14) groups. The exercise program consisted of walking 30–60 min/session, 2 days each week for 12 weeks. Blood samples were taken before starting the sessions (baseline) and when they ended. Fasting plasma and serum oxidative stress and inflammatory markers were measured using commercial kits. Cell surface expression of adhesion molecules on circulating leukocytes (CD66b and CD62L) was determined using flow cytometry. The concentrations of derivatives of reactive oxygen metabolites tended to be lower than the baseline values only in the exercise group (P = 0.05). The biological antioxidant potential, thioredoxin concentrations, and glutathione peroxidase activities significantly increased only in the exercise group (P < 0.05 for all). While CD66b expression tended to decrease only in the exercise group, CD62L expression significantly increased (P < 0.05). Our findings indicate that exercise training below the current recommended level of at least 150 min/week attenuates basal oxidative stress and neutrophil activation in older adults. Thus, our findings may encourage more people to incorporate a small amount of physical activity into their lives.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson JL, Hooper WC, Jones DP, Ashfaq S, Rhodes SD, Weintraub WS, Harrison DG, Quyyumi AA, Vaccarino V (2005) Association between novel oxidative stress markers and C-reactive protein among adults without clinical coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 178:115–121
Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C (2007) Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 297:842–857
Borg GA (1973) Perceived exertion: a note on “history” and methods. Med Sci Sports 5:90–93
Butcher LR, Thomas A, Backx K, Roberts A, Webb R, Morris K (2008) Low-intensity exercise exerts beneficial effects on plasma lipids via PPARgamma. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:1263–1270
Chen C, Jerome GJ, Laferriere D, Young DR, Vollmer WM (2009) Procedures used to standardize data collected by RT3 triaxial accelerometers in a large-scale weight-loss trial. J Phys Act Health 6:354–359
Cottam DR, Schaefer PA, Shaftan GW, Velcu L, Angus LD (2002) Effect of surgically-induced weight loss on leukocyte indicators of chronic inflammation in morbid obesity. Obes Surg 12:335–342
Fatouros IG, Jamurtas AZ, Villiotou V, Pouliopoulou S, Fotinakis P, Taxildaris K, Deliconstantinos G (2004) Oxidative stress responses in older men during endurance training and detraining. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:2065–2072
Finaud J, Lac G, Filaire E (2006) Oxidative stress: relationship with exercise and training. Sports Med 36:327–358
Frisard MI, Broussard A, Davies SS, Roberts LJ II, Rood J, de Jonge L, Fang X, Jazwinski SM, Deutsch WA, Ravussin E (2007) Aging, resting metabolic rate, and oxidative damage: results from the Louisiana Healthy Aging Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 62:752–759
Fukui T, Yamauchi K, Maruyama M, Yasuda T, Kohno M, Abe Y (2011) Significance of measuring oxidative stress in lifestyle-related diseases from the viewpoint of correlation between d-ROMs and BAP in Japanese subjects. Hypertens Res 34:1041–1045
Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, Nieman DC, Swain DP (2011) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1334–1359
Gleeson M, Bishop NC, Stensel DJ, Lindley MR, Mastana SS, Nimmo MA (2011) The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:607–615
Griffin JD, Spertini O, Ernst TJ, Belvin MP, Levine HB, Kanakura Y, Tedder TF (1990) Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines regulate surface expression of the leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 on human neutrophils, monocytes, and their precursors. J Immunol 145:576–584
Haskell WL, Lee IM, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, Macera CA, Heath GW, Thompson PD, Bauman A (2007) Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:1423–1434
Hellsten Y, Apple FS, Sjodin B (1996) Effect of sprint cycle training on activities of antioxidant enzymes in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 81:1484–1487
Honarbakhsh S, Schachter M (2009) Vitamins and cardiovascular disease. Br J Nutr 101:1113–1131
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444:860–867
Ito W, Kobayashi N, Takeda M, Ueki S, Kayaba H, Nakamura H, Yodoi J, Chihara J (2011) Thioredoxin in allergic inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 155(Suppl 1):142–146
Jakicic JM, Marcus BH, Gallagher KI, Napolitano M, Lang W (2003) Effect of exercise duration and intensity on weight loss in overweight, sedentary women: a randomized trial. JAMA 290:1323–1330
Jankord R, Jemiolo B (2004) Influence of physical activity on serum IL-6 and IL-10 levels in healthy older men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:960–964
Kahn EB, Ramsey LT, Brownson RC, Heath GW, Howze EH, Powell KE, Stone EJ, Rajab MW, Corso P (2002) The effectiveness of interventions to increase physical activity. A systematic review. Am J Prev Med 22:73–107
Kasapoglu M, Ozben T (2001) Alterations of antioxidant enzymes and oxidative stress markers in aging. Exp Gerontol 36:209–220
Kumahara H, Schutz Y, Ayabe M, Yoshioka M, Yoshitake Y, Shindo M, Ishii K, Tanaka H (2004) The use of uniaxial accelerometry for the assessment of physical-activity-related energy expenditure: a validation study against whole-body indirect calorimetry. Br J Nutr 91:235–243
Lappalainen Z, Lappalainen J, Oksala NK, Laaksonen DE, Khanna S, Sen CK, Atalay M (2009) Diabetes impairs exercise training-associated thioredoxin response and glutathione status in rat brain. J Appl Physiol 106:461–467
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M (2004) The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol 25:677–686
Marumoto M, Suzuki S, Hosono A, Arakawa K, Shibata K, Fuku M, Goto C, Tokudome Y, Hoshino H, Imaeda N, Kobayashi M, Yodoi J, Tokudome S (2010) Changes in thioredoxin concentrations: an observation in an ultra-marathon race. Environ Health Prev Med 15:129–134
Matthews CE, Chen KY, Freedson PS, Buchowski MS, Beech BM, Pate RR, Troiano RP (2008) Amount of time spent in sedentary behaviors in the United States, 2003–2004. Am J Epidemiol 167:875–881
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (2011) 2009 The National Health and Nutrition Survey in Japan. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan, p 26
Miyazaki H, Oh-ishi S, Ookawara T, Kizaki T, Toshinai K, Ha S, Haga S, Ji LL, Ohno H (2001) Strenuous endurance training in humans reduces oxidative stress following exhausting exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:1–6
Monzillo LU, Hamdy O, Horton ES, Ledbury S, Mullooly C, Jarema C, Porter S, Ovalle K, Moussa A, Mantzoros CS (2003) Effect of lifestyle modification on adipokine levels in obese subjects with insulin resistance. Obes Res 11:1048–1054
Morris JN, Hardman AE (1997) Walking to health. Sports Med 23:306–332
Nakanishi N, Tatara K, Nakamura K, Suzuki K (2000) Association of lifestyle with serum lipid levels: a study of middle-aged Japanese men. J Epidemiol 10:216–225
Neubauer O, Konig D, Kern N, Nics L, Wagner KH (2008) No indications of persistent oxidative stress in response to an ironman triathlon. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:2119–2128
Neuman RB, Bloom HL, Shukrullah I, Darrow LA, Kleinbaum D, Jones DP, Dudley SC Jr (2007) Oxidative stress markers are associated with persistent atrial fibrillation. Clin Chem 53:1652–1657
Nijhuis J, Rensen SS, Slaats Y, van Dielen FM, Buurman WA, Greve JW (2009) Neutrophil activation in morbid obesity, chronic activation of acute inflammation. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17:2014–2018
Pansarasa O, Bertorelli L, Vecchiet J, Felzani G, Marzatico F (1999) Age-dependent changes of antioxidant activities and markers of free radical damage in human skeletal muscle. Free Radic Biol Med 27:617–622
Pasquini A, Luchetti E, Marchetti V, Cardini G, Iorio EL (2008) Analytical performances of d-ROMs test and BAP test in canine plasma. Definition of the normal range in healthy Labrador dogs. Vet Res Commun 32:137–143
Patel RS, Al Mheid I, Morris AA, Ahmed Y, Kavtaradze N, Ali S, Dabhadkar K, Brigham K, Hooper WC, Alexander RW, Jones DP, Quyyumi AA (2011) Oxidative stress is associated with impaired arterial elasticity. Atherosclerosis 218:90–95
Peternelj TT, Coombes JS (2011) Antioxidant supplementation during exercise training: beneficial or detrimental? Sports Med 41:1043–1069
Rhodes RE, Warburton DE, Murray H (2009) Characteristics of physical activity guidelines and their effect on adherence: a review of randomized trials. Sports Med 39:355–375
Roberts CK, Won D, Pruthi S, Kurtovic S, Sindhu RK, Vaziri ND, Barnard RJ (2006) Effect of a short-term diet and exercise intervention on oxidative stress, inflammation, MMP-9, and monocyte chemotactic activity in men with metabolic syndrome factors. J Appl Physiol 100:1657–1665
Rose EA, Parfitt G (2008) Can the feeling scale be used to regulate exercise intensity? Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:1852–1860
Schymeinsky J, Mocsai A, Walzog B (2007) Neutrophil activation via beta2 integrins (CD11/CD18): molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Thromb Haemost 98:262–273
Shah TJ, Leik CE, Walsh SW (2010) Neutrophil infiltration and systemic vascular inflammation in obese women. Reprod Sci 17:116–124
Simpson ME, Serdula M, Galuska DA, Gillespie C, Donehoo R, Macera C, Mack K (2003) Walking trends among U.S. adults: the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 1987–2000. Am J Prev Med 25:95–100
Sumida S, Nakamura H, Yodoi J (2004) Thioredoxin induction of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in mice in response to a single bout of swimming exercise. Gen Physiol Biophys 23:241–249
Urso ML, Clarkson PM (2003) Oxidative stress, exercise, and antioxidant supplementation. Toxicology 189:41–54
Vega A, El Bekay R, Chacon P, Ventura I, Monteseirin J (2010) Angiotensin II induces CD62L shedding in human neutrophils. Atherosclerosis 209:344–351
Viardot A, Lord RV, Samaras K (2010) The effects of weight loss and gastric banding on the innate and adaptive immune system in type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:2845–2850
Wai JP, Wen CP, Chan HT, Chiang PH, Tsai MK, Tsai SP, Chang HY (2008) Assessing physical activity in an Asian country: low energy expenditure and exercise frequency among adults in Taiwan. Asia Pacific J Clin Nutr 17:297–308
Wen CP, Wai JP, Tsai MK, Yang YC, Cheng TY, Lee MC, Chan HT, Tsao CK, Tsai SP, Wu X (2011) Minimum amount of physical activity for reduced mortality and extended life expectancy: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 378:1244–1253
West XZ, Malinin NL, Merkulova AA, Tischenko M, Kerr BA, Borden EC, Podrez EA, Salomon RG, Byzova TV (2010) Oxidative stress induces angiogenesis by activating TLR2 with novel endogenous ligands. Nature 467:972–976
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports Science and Technology of Japan; the Grant-in-Aid for the Global COE Program “Sport Science for the Promotion of Active Life” (2010–2011) and the Scientific Research (A) 23240097; the Uehara Memorial Foundation; the Nakatomi Foundation; and the Kao Corporation.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by William J. Kraemer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Miyashita, M., Kawanishi, N. et al. Low-volume exercise training attenuates oxidative stress and neutrophils activation in older adults. Eur J Appl Physiol 113, 1117–1126 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2531-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2531-5