Abstract.
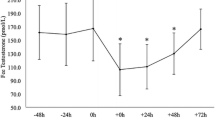
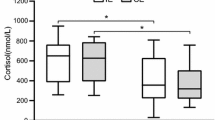
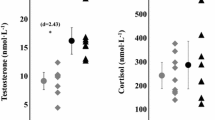
The primary objective was to evaluate the early effect of increased training mileage on testosterone (T) status in recreational joggers. Serum total (Ttot) and free (Tfree) concentrations at rest, overnight urinary Ttot excretion, and the Ttot and Tfree responses to maximal exercise were used as indicators of T status. A group of 13 male [mean (SD) age 24.5 (2.5) years] fitness joggers [maximal oxygen consumption, \( \dot V{\rm O}_{{\rm 2max}} \) , 52.9 (4.9) ml·kg–1·min–1] qualified as subjects. The training intervention consisted of a 100% increase in the habitual distance run [12 (3) miles·week–1] for 2 consecutive weeks, while maintaining the customary training intensity. Blood samples were obtained at rest and after maximal exercise tests, at the beginning and end of a control week of habitual jogging (baseline) and also following the 1st and 2nd weeks of the intervention. The \( \dot V{\rm O}_{{\rm 2max}} \) and treadmill exercise endurance time were unchanged across sampling times. Serum Ttot and Tfree concentrations averaged 565 (62) and 24 (2.6) ng·dl–1, respectively, at baseline and did not change significantly. Urinary Ttot excretion averaged 1.5 (0.21) ng·min–1 at baseline, and also remained unchanged during the intervention. Relative increases in Ttot (23%) and Tfree (22%) were observed following maximal exercise compared to rest (P<0.05). However, the exercise-related increases in serum Ttot and Tfree were not evident after adjustment for the change in plasma volume. It was concluded, that the training intervention did not alter T status in these fitness joggers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, L.J., Dressendorfer, R.H., Ferguson, M.A. et al. Maintenance of testosterone status in fitness joggers after increased training mileage. Eur J Appl Physiol 86, 498–502 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-001-0575-z
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-001-0575-z