Abstract
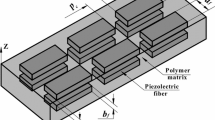
Piezoelectric distributed actuators are exhaustively utilized in control of the structural deformation/vibration. These actuators are also used in the form of smart composite of which active fiber composite (AFC) and macro-fiber composite (MFC) are the most popular smart composites. In the present work, few shortcomings of MFC/AFC actuator in its structural applications are identified and those are alleviated through the proposition of a short piezoelectric fiber-reinforced composite (SPFRC) actuator. The SPFRC is composed of equally spaced coaxial short piezoelectric fibers embedded within the polymer matrix. Every fiber is poled along its length that yields maximum piezoelectric stress/strain within the composite along the same direction in effect of co-directional applied electric field. This piezoelectric effect quantified by the coefficient (e 11) is the main parameter in its use as an actuator with a special arrangement of electrodes in microscale. The SPFRC is designed with an objective of improved magnitude of major effective coefficient (e 11), and it is performed through a continuum micro-mechanics finite element analysis of its effective electro-elastic properties. The actuation-capability of SPFRC actuator according to its present design is verified by analyzing the geometrically nonlinear electro-elastic deformations of a simply supported smart beam. The micro-mechanics analysis reveals a significant magnitude of e 11 of SPFRC although it is lesser than the case of continuous fibers within the similar composite. However, the analysis of smart beam reveals better actuation-capability of the smart composite actuator when short fibers are used instead of continuous fibers retaining the same applied voltage and electrodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
James F.T., Sedat A., Newnham R.E.: Piezolectric sensors and sensor materials. J. Electroceram. 2(4), 257–272 (1998)
Miller, S.E., Hubbard, J.E.: Observability of a Bernoulli–Euler beam using PVF2 as a distributed sensor. MIT Draper Laboratory Report (1987)
Crawley E.F., Luis J.D.: Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 25(10), 1373–1385 (1987)
Cook A.C., Vel S.S.: Multiscale analysis of laminated plates with integrated piezoelectric fiber composite actuators. Compos. Struct. 94(2), 322–336 (2012)
Prasanth S.S., Arockiarajan A.: Effective electromechanical response of macro-fiber composite (MFC): Analytical and numerical models. Int. J. Mechan. Sci. 77, 98–106 (2013)
Wilkie W.K., Inman D.J., Lloyd J.M., High J.W.: Anisotropic laminar piezocomposite actuator incorporating machined PMN–PT single-crystal fibers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 17(1), 15–28 (2006)
Bent A.A., Hagood N.W., Rodgers J.P.: Anisotropic actuation with piezoelectric fiber composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 6(3), 338–349 (1995)
High, J.W., Wilkie, W.K.: Method of fabricating NASA-standard macro-fiber composite piezoelectric actuators. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Langley Research Center (2003)
William, K.W., Robert, G.B., James, W.H., Robert, L.F., Richard, F.H., Anthony, J.Jr., Bruce, D.L., Paul, H.M.: Low-cost piezocomposite actuator for structural control applications. Proceedings SPIE 3991, Smart Structures and Materials 2000: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies 323 (2000)
Ray M.C.: Micromechanics of piezoelectric composites with improved effective piezoelectric constant. Int. J. Mechan. Mater. Design 3(4), 361–371 (2006)
Bowen C.R., Nelson L.J., Stevens R., Cain M.G., Stewart M.: Optimisation of interdigitated electrodes for piezoelectric actuators and active fibre composites. J. Electroceram. 16(4), 263–269 (2006)
Sohn J.W., Choi S.B., Kim H.S.: Vibration control of smart hull structure with optimally placed piezoelectric composite actuators. Int. J. Mechan. Sci. 53(8), 647–659 (2011)
Azzouz, M.S., Bevan, J.S., Ro, J.-J., Mei, C.: Finite element modeling of MFC/AFC actuators. Proceedings SPIE 326: Smart Structures and Materials 2001: Modeling, Signal Processing, and Control in Smart Structures (2001)
Kwak M.K., Heo S., Jeong M.: Dynamic modelling and active vibration controller design for a cylindrical shell equipped with piezoelectric sensors and actuators. J. Sound Vib. 321(3), 510–524 (2009)
Kim H.S., Sohn J.W., Choi S.B.: Vibration control of a cylindrical shell structure using macro fiber composite actuators. Mechan. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 39(4), 491–506 (2011)
Sohn, J.W., Kim, H.S., Kim, C.J., Ha, S.H., Choi, S.B.: Vibration suppression of hull structure using macro fiber composite actuators and sensors. Proceedings SPIE 6525: Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems 652527-1 (2007)
Sohn J.W., Kim H.S., Choi S.B., Kim K.S.: Experimental Investigation of Smart Hull Structures Based on Macro Fiber Composite Actuators. Key Eng. Mater. 326, 1419–1422 (2006)
Wickramasinghe V.K., Hagood N.W.: Durability characterization of active fiber composite actuators for helicopter rotor blade applications. J. Aircraft 41(4), 931–937 (2004)
Marinaki M., Marinakis Y., Stavroulakis GE.: Vibration control of beams with piezoelectric sensors and actuators using particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(6), 6872–6883 (2011)
Schulz, M.J., Sundaresan, M.J., Ghoshal, A., Pai, P.F.: Active fiber composites for structural health monitoring. Proceeding SPIE 3992, Smart Structures and Materials 2000: Active Materials: Behavior and Mechanics 13 (2000)
Bent, A.A.: Active fiber composite material systems for structural control applications. Proceeding SPIE 3674, Smart Structures and Materials 1999: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies 166 (1999)
Sodano H.A., Park G., Inman D.J.: An investigation into the performance of macro-fiber composites for sensing and structural vibration applications. Mechan. Syst. Sign. Process. 18(3), 683–697 (2004)
Wickramasinghe V.K., Hagood N.W.: Material characterization of active fiber composites for integral twist-actuated rotor blade application. Smart Mater. Struct. 13(5), 1155–1165 (2004)
Melnykowycz M., Kornmann X., Huber C., Barbezat M., Brunner A.J.: Performance of integrated active fiber composites in fiber reinforced epoxy laminates. Smart Mater. Struct. 15(1), 204–212 (2006)
Cesnik C.E., Shin S.: On the modeling of integrally actuated helicopter blades. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38(10), 1765–1789 (2001)
Park S., Inman D.J., Yun C.B.: An outlier analysis of MFC-based impedance sensing data for wireless structural health monitoring of railroad tracks. Eng. Struct. 30(10), 2792–2799 (2008)
Choi S.C., Park J.S., Kim J.H.: Active damping of rotating composite thin-walled beams using MFC actuators and PVDF sensors. Compos. Struct. 76(4), 362–374 (2006)
Kovalovs A., Barkanov E., Gluhihs S.: Active control of structures using macro-fiber composite (MFC). J. Phys.: Confer. Series 93(1), 012034 (2007)
Bilgen O., Kochersberger K.B., Inman D.J., Ohanian O.J.: Macro-fiber composite actuated simply supported thin airfoils. Smart Mater. Struct. 19(5), 055010 (2010)
Ikeda T.: Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity. Oxford Univercity Press, Oxford (1990)
Dunn M.L., Taya M.: Micromechanics predictions of the effective electroelastic moduli of piezoelectric composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 30(2), 161–175 (1993)
Furukawa T.: Piezoelectricity and pyroelectricity in polymers. IEEE Trans. Elect. Insul. 24(3), 375–395 (1989)
Cady W.G.: Piezolectricity. McGraw-Hill, New York (1946)
Hill R.: Elastic properties of reinforced solid: Some theoretical principles. J. Mechan. Phys. Solids 11(5), 357–372 (1963)
Odegard G.M.: Constitutive modeling of piezoelectric polymer pomposities. Acta Materialia 52(18), 5315–5330 (2004)
Cook R.D., Malkus D.S., Plesha M.E., Witt R.J.: Concepts and applications of finite element analysis. Wiley, New York (2001)
Tiersten H.F.: Linear Piezoelectric Plate Vibrations. Plenum, New York (1969)
Chia C.Y.: Non-linear Analysis of Plates. McGraw-Hill, New York (1980)
Fallah N., Ebrahimnejad M.: Finite volume analysis of adaptive beams with piezoelectric sensors and actuators. Appl. Math. Model. 38(2), 722–737 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, S., Reddy, N.H. & Pavan Kumar, A.S. Design and finite element analysis of a short piezoelectric fiber-reinforced composite actuator. Arch Appl Mech 85, 691–711 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-0982-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-0982-y