Abstract
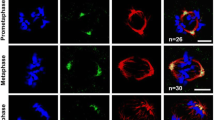
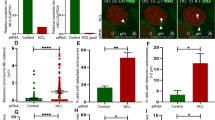
The calmodulin-binding protein nucleomorphin isoform NumA1 is a nuclear number regulator in Dictyostelium that localizes to intra-nuclear patches adjacent to the nuclear envelope and to a lesser extent the nucleoplasm. Earlier studies have shown similar patches to be nucleoli but only three nucleolar proteins have been identified in Dictyostelium. Here, actinomycin-D treatment caused the loss of NumA1 localization, while calcium and calmodulin antagonists had no effect. In keeping with a nucleolar function, NumA1 moved out of the presumptive nucleoli during mitosis redistributing to areas within the nucleus, the spindle fibers, and centrosomal region before re-accumulating in the presumptive nucleoli at telophase. Together, these data verify NumA1 as a true nucleolar protein. Prior to this study, the dynamics of specific nucleolar proteins had not been determined during mitosis in Dictyostelium. FITC-conjugated peptides equivalent to presumptive nuclear localization signals within NumA1 localized to nucleoli indicating that they also act as nucleolar localization signals. To our knowledge, these represent the first precisely defined nucleolar localization signals as well as the first nuclear/nucleolar localization signals identified in Dictyostelium. Together, these results reveal that NumA1 is a true nucleolar protein and the only nucleolar calmodulin-binding protein identified in Dictyostelium. The possible use of nuclear/nucleolar localization signal-mediated drug targeting to nucleoli is discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAPTA:
-
1,2-Bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid
- CaM:
-
Calmodulin
- CBP4a:
-
Calcium-binding protein 4a
- eif6:
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6
- hsp32:
-
Heat shock protein 32
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization signal
- NoLS:
-
Nucleolar localization signal
- NPM1:
-
Nucleophosmin
References
Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E (1998) Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 279:377–380
Balbo A, Bozzaro S (2006) Cloning of Dictyostelium eIF6 (p27BBP) and mapping its nucle(ol)ar localization subdomains. Eur J Cell Biol 85:1069–1078
Benichou J-C, Quiviger B, Ryter A (1983) Cytochemical study of the nucleolus of the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Ultrastruc Res 84:60–66
Birbach A, Bailey ST, Ghosh S, Schmid JA (2004) Cytosolic, nuclear and nucleolar localization signals determine subcellular distribution and activity of the NF-κB-inducing kinase NIK. J Cell Sci 117:3615–3624
Cappuccinelli P, Fighetti M, Rubino S (1979) A mitotic inhibitor for chromosomal studies in slime moulds. J Gen Microbiol 5:25–27
Catalano A, O’Day DH (2008) Calmodulin-binding proteins in the model organism Dictyostelium. A complete & critical review. Cell Signal 20:277–291
Catalano A, Luo W, Wang Y, O’Day DH (2010) Synthesis and biological activity of peptides equivalent to the IP22 repeat motif found in proteins from Dictyostelium and Mimivirus. Peptides 31:1799–1805
Cha H, Hancock C, Dangi S, Maiguel D, Carrier F, Shapiro P (2004) Phosphorylation regulates nucleophosmin targeting to the centrosome during mitosis as detected by cross-reactive phosphorylation-specific MKK1/MKK2 antibodies. Biochem J 378:857–865
Chan WC, White PD (2000) Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, New York
Charlesworth MC, Parish RW (1975) The isolation of nuclei and basic nucleoproteins from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem 54:307–316
Collavoli A, Hatcher CJ, He J, Okin D, Deo R, Basson CT (2003) TBX5 nuclear localization is mediated by dual cooperative intramolecular signals. J Mol Cell Cardiol 35:1191–1195
Dang CV, Lee WMF (1989) Nuclear and nucleolar targeting sequences of c-erb-A, c-myb, N-myc, p53, HSP70, and HIV Tat proteins. J Biol Chem 264:18019–18023
Fey P, Kowal AS, Gaudet P, Pilcher KE, Chisholm RL (2007) Protocols for growth and development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Nat Protoc 2:1307–1316
Gas N, Escande ML, Stevens BJ (1985) Immunolocalization of the 100 kDa nucleolar protein during the mitotic cycle in CHO cells. Biol Cell 53:209–218
Gaudet P, Pilcher KE, Fey P, Chisholm RL (2007) Transformation of Dictyostelium discoideum with plasmid DNA. Nat Protoc 2:1317–1324
Ginisty H, Sicard H, Roger B, Bouvet P (1999) Structure and functions of nucleolin. J Cell Sci 112:761–772
Grisendi S, Mecucci C, Falini B, Pandolfi PP (2006) Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:493–505
Guerriero V Jr, Rowley DR, Means AR (1981) Production and characterization of an antibody to myosin light chain kinase and intracellular localization of the enzyme. Cell 27:449–458
Hagedorn M, Neuhaus EM, Soldati T (2006) Optimized fixation and immunofluorescence staining methods for Dictyostelium cells. Methods Mol Biol 346:327–338
Hebert MD, Matera AG (2000) Self-association of coilin reveals a common theme in nuclear body localization. Mol Biol Cell 11:4159–4171
Henderson JE, Amizuka N, Warshawsky H, Biasotto D, Lanske BMK, Goltzman D, Karaplis A (1995) Nucleolar localization of parathyroid hormone-related peptide enhances survival of chondrocytes under conditions that promote apoptotic cell death. Mol Cell Biol 15:4064–4075
Hussain S, Benavente SB, Nascimento E, Dragoni I, Kurowski A, Gillich A, Humphreys P, Frye M (2009) The nucleolar RNA methyltransferase Misu (NSun2) is required for mitotic spindle stability. J Cell Biol 186:27–40
Kakuk A, Friedlander E, Vereb G Jr, Lisboa D, Bagossi P, Toth G, Gergely P, Vereb G (2008) Nuclear and nucleolar localization signals and their targeting function in phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase PI4K230. Exp Cell Res 314:2376–2388
Kawashima K, Sameshima M, Izawa M (1979) Isolation of nucleoli from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum, strain A-3. Cell Struct Funct 4:183–191
Kieffer-Kwon P, Martianov I, Davidson I (2004) Cell-specific nucleolar localization of TBP-related factor 2. Mol Biol Cell 15:4356–4368
Kitanishi-Yumura T, Fukui Y (1987) Reorganization of microtubules during mitosis in Dictyostelium: dissociation from MTOC and selective assembly/disassembly in situ. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 8:106–117
Kubota S, Siomi H, Satoh T, Endo S, Maki M, Hatanaka M (1989) Functional similarity of HIV-I rev and HTLV-I rex proteins: identification of a new nucleolar-targeting signal in rev protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 162:963–970
Lam YW, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Lamond AI (2005) The nucleolus. J Cell Sci 118:1335–1337
Lim MJ, Wang XW (2006) Nucleophosmin and human cancer. Cancer Detect Prev 30:481–490
Lohrum MAE, Ashcroft M, Kubbutat MHG, Vousden KH (2000) Identification of a cryptic nucleolar-localization signal in MDM2. Nat Cell Biol 2:179–181
Maeda Y, Takeuchi I (1969) Cell differentiation and fine structures in the development of the cellular slime molds. Dev Growth Differ 11:232–245
Maggi LB Jr, Weber JD (2006) Nucleolar adaptation in human cancer. Cancer Invest 23:599–608
Mijatovic T, De Neve N, Gailly P, Mathieu V, Haibe-Kains B, Bontempi G, Lapeira J, Decaestecker C, Facchini V, Kiss R (2008) Nucleolus and c-Myc: potential targets of cardenolide-mediated antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1285–1296
Misteli T (2001) Protein dynamics: implications for nuclear architecture and gene expression. Science 291:843–847
Moerman AM, Klein C (1998) Dictyostelium discoideum Hsp32 is a resident nucleolar heat-shock protein. Chromosoma 107:145–154
Montanaro L, Trere D, Derenzini M (2008) Nucleolus, ribosomes, and cancer. Am J Pathol 173:301–310
Myre MA, O’Day DH (2002) Nucleomorphin. A novel, acidic, nuclear calmodulin-binding protein from Dictyostleium that regulates nuclear number. J Biol Chem 277:19735–19744
Myre MA, O’Day DH (2004a) Dictyostelium calcium-binding protein 4a interacts with nucleomorphin, a BRCT-domain protein that regulates nuclear number. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:665–671
Myre MA, O’Day DH (2004b) Dictyostelium nucleomorphin is a member of the BRCT-domain family of cell cycle checkpoint proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1675:192–197
Myre MA, O’Day DH (2005) An N-terminal nuclear localization sequence but not the calmodulin-binding domain mediates nuclear localization of nucleomorphin, a protein that regulates nuclear number in Dictyostetlium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332:157–166
Ochs R, Lischwe M, O’Leary P, Busch H (1983) Localization of nucleolar phosphoproteins B23 and C23 during mitosis. Exp Cell Res 146:139–149
Ohta Y, Ohba T, Miyamoto E (1990) Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: Localization in the interphase nucleus and the mitotic apparatus of mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5341–5345
Peterson T, Tsai RYL (2009) In search of nonribosomal nucleolar protein function and regulation. J Cell Biol 184:771–776
Prado A, Ramos I, Frehlick LJ, Muga A, Ausio J (2004) Nucleoplasmin: a nuclear chaperone. Biochem Cell Biol 82:437–445
Robertson R (2007) Hand it to the nucleolus. J Cell Biol 85:52–52
Roos U-P, De Brabander M, De Mey J (1984) Indirect immunofluorescence of microtubules in Dictyostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res 151:183–193
Russo G, Ricciardelli G, Pietropaolo C (1997) Different domains cooperate to target the human ribosomal L7a protein to the nucleus and to the nucleoli. J Biol Chem 272:5229–5235
Sansam CL, Wells KS, Emeson RB (2003) Modulation of RNA editing by functional nucleolar sequestration of ADAR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14018–14023
Schally AV, Nagy A (1999) Cancer chemotherapy based on targeting of cytotoxic peptide conjugates to their receptors on tumors. Eur J Endocrinol 141:1–14
Siomi H, Shida H, Nam SH, Nosaka T, Maki M, Hatanaka M (1988) Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing. Cell 55:197–209
Sirri V, Urcuqui-Inchima S, Roussel P, Hernandez-Verdun D (2008) Nucleolus: the fascinating nuclear body. Histochem Cell Biol 129:13–31
Song Z, Wu M (2005) Identification of a novel nucleolar localization signal and a degradation signal in surviving-delta Ex3: a potential link between nucleolus and protein degradation. Oncogene 24:2723–2734
Stegh AH, Schickling O, Ehret A, Scaffidi C, Peterhansel C, Hofmann TG, Grummt I, Krammer PH, Peter ME (1998) DEDD, a novel death effector domain-containing protein, targeted to the nucleolus. EMBO J 17:5974–5986
Tao W, Levine AJ (1999) P19ARF stabilizes p53 by blocking nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of Mdm2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6937–6941
Theodore M, Kawai Y, Yang J, Kleshchenko Y, Reddy SP, Villalta F, Arinze IJ (2008) Multiple nuclear localization signals function in the nuclear import of the transcription factor Nrf2. J Biol Chem 283:14176–14176
Thorogate R, Torok K (2007) Role of Ca2+activation and bilobal structure of calmodulin in nuclear and nucleolar localization. Biochem J 402:71–80
Torgan CE, Daniels MP (2006) Calcineurin localization in skeletal muscle offers insights into potential new targets. J Histochem Cytochem 54:119–128
Ueki N, Kondo M, Seki N, Yano K, Oda T, Masuho Y, Muramatsu M-A (1998) NOLP: identification of a novel human nucleolar protein and determination of sequence requirements for its nucleolar localization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:97–102
Visintin R, Amon A (2000) The nucleolus: the magician’s hat for cell cycle tricks. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:372–377
Wang Y-H, Chen Y-H, Lu J-H, Tsai H-J (2005) A 23-amino acid motif spanning the basic domain targets zebrafish myogenic regulatory factor Myf5 into nucleolus. DNA Cell Biol 24:651–660
Wong EC, Saffitz JE, McDonald JM (1991) Association of calmodulin with isolated nuclei from rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:1548–1556
Xue Z, Melese T (1994) Nucleolar proteins that bind NLSs: a role in nuclear import or ribosome biogenesis? Trends Cell Biol 4:414–417
Yamaguchi H, Morita T, Amagai A, Maeda Y (2005) Changes in spatial and temporal localization of Dictyostelium homologues of TRAP1 and GRP94 revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Exp Cell Res 303:415–424
Yao YL, Yang WM (2005) Nuclear proteins: promising targets for cancer drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5:595–610
Yun C, Wang Y, Mukhopadhyay D, Backlund P, Kolli N, Yergey A, Wilkinson KD, Dasso M (2008) Nucleolar protein B23/nucleophosmin regulates the vertebrate SUMO pathway through SENP3 and SENP5 proteases. J Cell Biol 183:589–595
Zhang Y, Xiong Y (1999) Mutations in human ARF exon 2 disrupt its nucleolar localization and impair its ability to block nuclear export of MDM2 and p53. Mol Cell 3:579–591
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grant (DDD; A6807).We would like to thank Dr. Yali Wang, Wei Luo, David Xiao, and Dr. Sheng Cai for the synthesis and conjugation of all peptides used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catalano, A., O’Day, D.H. Nucleolar localization and identification of nuclear/nucleolar localization signals of the calmodulin-binding protein nucleomorphin during growth and mitosis in Dictyostelium . Histochem Cell Biol 135, 239–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-011-0785-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-011-0785-3