Abstract.
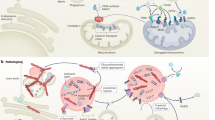
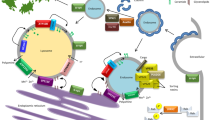
For several decades there has been a controversy on the contribution of genetic factors to the pathogenesis of sporadic idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (PD). The identification of families in which typical parkinsonism is inherited as an autosomal dominant or recessive trait sheds light on genes that cause phenotypes resembling sporadic PD. These genes are involved in molecular pathways leading to neurodegeneration and dysfunction of the nigrostriatal system. The present article gives insight into molecular pathways to neurodegeneration deciphered by the functional characterization of five genes identified in inherited forms of typical levodopa-responsive parkinsonism. There is increasing evidence that genes involved in monogenic forms of the disease may act as susceptibility factors also in the common sporadic form of PD. Transgenic animal models based on disease genes identified in monogenic forms of typical parkinsonism replicate important features of PD including protein aggregation and progressive motor symptoms. This implicates novel perspectives for neuroprotective therapeutic approaches that might be beneficial also to sporadic PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Sleiman PM, Healy DG, Quinn N, Lees AJ, Wood NW (2003) The role of pathogenic DJ-1 mutations in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 54:283–286
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Canet-Aviles RM, Wilson MA, Miller DW, Ahmad R, McLendon C, Bandyopadhyay S, Baptista MJ, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Cookson MR (2004) The Parkinson’s disease protein DJ-1 is neuroprotective due to cysteinesulfinic acid-driven mitochondrial localization. PNAS 101:9103–9108
Chiba-Falek O, Nussbaum RL (2001) Effect of allelic variation at the NACP-Rep1 repeat upstream of the α-synuclein gene (SNCA) on transcription in a cell culture luciferase reporter system. Hum Mol Genet 10:3101–3109
Cookson MR, Lockhart PJ, McLendon C, O’Farrell C, Schlossmacher M, Farrer MJ (2003) RING finger 1 mutations in parkin produce altered localization of the protein. Hum Mol Genet 12:2957–2965
Farrer M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Muenter M, DeVrieze FW, Crook R, Perez-Tur J, Lincoln S, Maraganore D, Adler C, Newman S, MacElwee K, McCarthy P, Miller C, Waters C, Hardy J (1999) A chromosome 4p haplotype segregating with Parkinson’s disease and postural tremor. Hum Mol Genet 8:81–85
Farrer M, Kachergus J, Forno L, Lincoln S, Wang DS, Hulihan M, Maraganore D, Gwinn-Hardy K, Wszolek Z, Dickson D, Langston JW (2004) Comparison of kindreds with parkinsonism and alpha-synuclein genomic multiplications. Ann Neurol 55:174–179
Feany MB, Bender WW (2000) A Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 404:394–398
Foroud T, Uniacke SK, Liu L, Pankratz N, Rudolph A, Halter C, Shults C, Marder K, Conneally PM, Nichols WC; Parkinson Study Group (2003) Heterozygosity for a mutation in the parkin gene leads to later onset Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 60:796–801
Hering R, Strauss K, Tao X, Bauer A, Mietz EM, Petrovic S, Bauer P, Schaible W, Woitalla D, Müller T, Schöls L, Klein C, Berg D, Meyer PT, Schulz JB, Wollnik B, Tong L, Krüger R, Riess O (2004) Novel E64D mutation in DJ-1 gene is causative of early onset Parkinson’s Disease.Hum Mutat (in press)
Holzmann C, Krüger R, Saecker AMM, Schmitt I, Schöls L, Berger K, Riess O (2003) Characterization of α-synuclein promoter polymorphisms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 110:67–76
Krüger R, Kuhn W, Leenders KL, Sprengelmeyer R, Müller T,Woitalla D, Portman AT, Maguire RP, Veenma L, Schröder U, Schöls L, Epplen JT, Riess O, Przuntek H (2001) Familial parkinsonism with synuclein pathology:Clinical and PET studies of A30P mutation carriers. Neurology 56:1355–1362
Krüger R, Kuhn W, Müller T, Kühnl N, Fuchs GA, Berg D, Storch A, Hungs M, Woitalla D, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schöls L, Riess O (1999) Increased susceptibility to sporadic Parkinson’s disease by a certain combined alphasynuclein/apolipoprotein E genotype. Ann Neurol 45:611–617
Krüger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schöls L, Riess O (1998) Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeroupolos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in parkinson’s disease. Nature 395:451–452
Liu Y, Fallon L, Lashuel HA, Liu Z, Lansbury PT (2002) The UCH-L1 gene encodes two opposing enzymatic activities that affect alpha-synuclein degradation and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility. Cell 111:209–218
Lücking CB, Dürr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denefle P, Wood NW, Agid Y, Brice A (2000) Association between early-onset Parkinson’s disease and mutations in the Parkin gene. New Engl J Med 342:1560–1567
Maraganore DM, Lesnick TG, Elbaz A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Gasser T, Sharma, M, Krüger R, Riess O,Hattori N, Mellick GD, Quattrone A, Satoh JI, Toda T, Wang J, Ioannidis JPA, de Andrade M, Rocca WA, the UCH-L1 Global Genetics Consortium (2004) Collaborative reanalysis of the ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL-1) gene S18 variant and its association with Parkinson’s disease (PD). Ann Neurol 55:512–521
Miller DW, Ahmad R, Hague S, Baptista MJ, Canet-Aviles R, McLendon C, Carter DM, Zhu PP, Stadler J, Chandran J, Klinefelter GR, Blackstone C, Cookson MR (2003) L166P mutant DJ-1, causative for recessive Parkinson’s disease, is degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Biol Chem. 278:36588–36595
Miller DW, Hague SM, Clarimon J, Baptista M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Cookson MR, Singleton AB (2004) Alpha-synuclein in blood and brain from familial Parkinson disease with SNCA locus triplication. Neurology 62:1835–1838
Oliveira SA, Scott WK, Martin ER, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Hiner BC, Ondo WG, Allen FH Jr, Scott BL, Goetz CG, Small GW, Mastaglia F, Stajich JM, Zhang F, Booze MW, Winn MP, Middleton LT, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM (2003) Parkin mutations and susceptibility alleles in late-onset Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:624–629
Piccini P, Burn DJ, Ceravolo R, Maraganore D, Brooks (1999) The role of inheritance in sporadic Parkinson’s disease: evidence from a longitudinal study of dopaminergic function in twins. Ann Neurol 45:577–582
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Die SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Lorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Shimura H, Hattori N, Kubo S-I, Mizuno Y, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Iwai K, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Suzuki T (2000) Familial Parkinson disease gene product, parkin, is a ubiquitin-protein ligase. Nat Genet 25:302–305
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R,Goedert M (1997) α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Tan EK, Matsuura T, Nagamitsu S, Khajavi M, Jankovic J, Ashizawa T (2000) Polymorphism of NACP-Rep1 in Parkinson’s disease: an etiologic linkwith essential tremor? Neurology 54:1195–1198
Tanner CM, Ottman R, Goldman SM, Ellenberg J, Chan P, Mayeux R, Langston JW (1999) Parkinson’s disease in twins: an etiologic study. JAMA 281:341–246
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MMK, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Turco DD, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG, Albanese A, Nussbaum R,Gonzales-Maldonado R, Deller R, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW (2004) Hereditary earlyonset Parkinson’s disease is caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304:1158–1160
Valente EM, Bentivoglio AR, Dixon PH, Ferraris A, Ialongo T, Frontali M, Albanese A, Wood NW (2001) Localization of a novel locus for autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism, PARK6, on human chromosome 1p35-p36. Am J Hum Genet 68:895–900
VanDuijn CM, Deker MCJ, Bonifati V, Galjaard RJ, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Snijders PJLM, Testers L, Breedveld GJ, Horstink M, Sandkuijl LA, van Swieten JC, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2001) PARK7, a novel locus for autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism, on chromosome 1p36. Am J Hum Genet 69:629–634
Vaughan JR, Farrer MJ, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T, Durr A, Agid Y, Bonifati V, DeMichele G, Volpe G, Lincoln S, Breteler M, Meco G, Brice A, Marsden CD, Hardy J, Wood NW (1998) Sequencing of the α-synuclein gene in a large series of familial Parkinson’s disease fails to reveal any further mutations. Hum Mol Genet 7:751–753
Wintermeyer P, Krüger R, Kuhn W, Müller T, Woitalla D, Berg D, Becker G, Leroy E, Polymeropoulos M, Berger K, Przuntek H, Schöls L, Epplen JT, Riess O (2000) Mutation analysis and association studies of the UCHL1 gene in German Parkinson’s disease patients. Neuroreport 11:2079–2082
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Estaban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gomez Tortosa E, del Ser T, Munoz DG, de Yebenes JG (2004) The new mutation, E64K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55:164–173
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krüger, R. Genes in familial parkinsonism and their role in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 251 (Suppl 6), vi2–vi6 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-1602-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-1602-x