Abstract
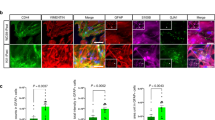
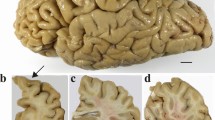
Guam parkinsonism-dementia complex (PDC) is a neurodegenerative tauopathy in ethnic Chamorro residents of the Mariana Islands that manifests clinically with parkinsonism as well as dementia and is characterized neuropathologically by prominent cortical neuron loss in association with extensive telencephalic neurofibrillary tau pathology. To further characterize cortical gray and white matter tau, alpha-synuclein and lipid peroxidation pathologies in Guam PDC, we examined the brains of 17 Chamorro PDC and control subjects using biochemical and immunohistological techniques. We observed insoluble tau pathology in both gray and white matter of PDC and Guam control cases, with frontal and temporal lobes being most severely affected. Using phosphorylation dependent anti-tau antibodies, abundant tau inclusions were detected by immunohistochemistry in both neuronal and glial cells of the neocortex, while less alpha-synuclein pathology was observed in more limited brain regions. Further, in sharp contrast to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), levels of the lipid peroxidation product 8, 12–iso-iPF2α-VI isoprostane were not elevated in Guam PDC brains relative to controls. Thus, although the tau pathologies of Guam PDC share similarities with AD, the composite Guam PDC neuropathology profile of tau, alpha-synuclein and 8, 12-iso-iPF2α-VI isoprostane reported here more closely resembles that seen in other tauopathies including frontotemporal dementias (FTDs), which may imply that Guam PDC and FTD tauopathies share underlying mechanisms of neurodegeneration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson FH, Richardson EP Jr, Okazaki H, Brody JA (1979) Neurofibrillary degeneration on Guam: frequency in Chamorros and non Chamorros with no known neurological disease. Brain 102:65–77
Behrman S, Carroll JD, Janota I, Matthews WB (1969) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Clinico-pathological study of four cases. Brain 92:663–678
Buee-Scherrer V, Buee L, Hof PR, Leveugle B, Gilles C, Loerzel AJ, Perl DP, Delacourte A (1995) Neurofibrillary degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam. Immunochemical characterization of tau proteins. Am J Pathol 146:924–932
Buee L, Bussiere T, Buee-Scherrer V, Delacourte A, Hof PR (2000) Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33:95–130
Esclaire F, Kisby G, Spencer P, Milne J, Lesort M, Hugon J (1999) The Guam cycad toxin methylazoxymethanol damages neuronal DNA and modulates tau mRNA expression and excitotoxicity. Exp Neurol 155:11–21
Forman MS, Schmidt ML, Kasturi S, Perl DP, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Tau and alpha-synuclein pathology in amygdala of parkinsonism-dementia complex patients of Guam. Am J Pathol 160:1725–1731
Forman MS, Zhukareva V, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Grossman M, Clark C, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Signature tau neuropathology in gray and white matter of corticobasal degeneration. Am J Pathol 160:2045–2053
Forman MS, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases: a decade of discoveries paves the way for therapeutic breakthroughs. Nat Med 10:1055–1063
Galasko D, Salmon DP, Craig UK, Thal LJ, Schellenberg G, Wiederholt W (2002) Clinical features and changing patterns of neurodegenerative disorders on Guam, 1997–2000. Neurology 58:90–97
Garruto RM, Fukatsu R, Yanagihara R, Gajdusek DC, Hook G, Fiori CE (1984) Imaging of calcium and aluminum in neurofibrillary tangle-bearing neurons in parkinsonism-dementia of Guam. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1875–1879
Gentleman SM, Perl D, Allsop D, Clinton J, Royston MC, Roberts GW (1991) Beta (A4)-amyloid protein and parkinsonian dementia complex of Guam. Lancet 337:55–56
Giasson BI, Jakes R, Goedert M, Duda JE, Leight S, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2000) A panel of epitope-specific antibodies detects protein domains distributed throughout human alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 59:528–533
Goedert M, Jakes R, Vanmechelen E (1995) Monoclonal antibody AT8 recognises tau protein phosphorylated at both serine 202 and threonine 205. Neurosci Lett 189:167–169
Greenberg SG, Davies P (1990) A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5827–5831
Grossman M, Farmer J, Leight S, Work M, Moore P, Van Deerlin V, Pratico D, Clark CM, Coslett HB, Chatterjee A, Gee J, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2005) Cerebrospinal fluid profile in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 57:721–729
Hirano A, Llena J (1986) Neurological features of parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam: reappraisal and comparative study with Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neuropathol 6:17–31
Hirano A, Kurland LT, Krooth RS, Lessell S (1961) Parkinsonism-dementia complex, an endemic disease on the island of Guam. I. Clinical features. Brain 84:642–661
Hirano A, Malamud N, Ku Rland LT (1961) Parkinsonism-dementia complex, an endemic disease on the island of Guam. II. Pathological features. Brain 84:662–679
Hirano A, Malamud N, Elizan TS, Kurland LT (1966) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam. Further pathologic studies. Arch Neurol 15:35–51
Hof PR, Perl DP, Loerzel AJ, Morrison JH (1991) Neurofibrillary tangle distribution in the cerebral cortex of parkinsonism-dementia cases from Guam: differences with Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 564:306–313
Hof PR, Perl DP, Loerzel AJ, Steele JC, Morrison JH (1994) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia from Guam: differences in neurofibrillary tangle distribution and density in the hippocampal formation and neocortex. Brain Res 650:107–116
Hong M, Zhukareva V, Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V, Wszolek Z, Reed L, Miller BI, Geschwind DH, Bird TD, McKeel D, Goate A, Morris JC, Wilhelmsen KC, Schellenberg GD, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (1998) Mutation-specific functional impairments in distinct tau isoforms of hereditary FTDP-17. Science 282:1914–1917
Hudson AJ, Rice GP (1990) Similarities of guamanian ALS/PD to post-encephalitic parkinsonism/ALS: possible viral cause. Can J Neurol Sci 17:427–433
Kosik KS, Orecchio LD, Binder L, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y, Lee G (1988) Epitopes that span the tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron 1:817–825
Kurland LT, Mulder DW (1954) Epidemiologic investigations of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. I. Preliminary report on geographic distribution and special reference to the Mariana Islands, including clinical and pathologic observations. Neurology 4:438–448
Kurland LT, Mulder DW (1955) Epidemiologic investigations of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 2. Familial aggregations indicative of dominant inheritance I. Neurology 5:182–196
Lee VM-Y, Balin BJ, Otvos L Jr, Trojanowski JQ (1991) A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science 251:675–678
Lee VM-Y, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1121–1159
Lee VM-Y, Giasson BI, Trojanowski JQ (2004) More than just two peas in a pod: common amyloidogenic properties of tau and alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 27:129–134
Mawal-Dewan M, Schmidt ML, Balin B, Perl DP, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (1996) Identification of phosphorylation sites in PHF-TAU from patients with Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:1051–1059
McGeer PL, Schwab C, McGeer EG, Haddock RL, Steele JC (1997) Familial nature and continuing morbidity of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism dementia complex of Guam. Neurology 49:400–409
Mercken M, Vandermeeren M, Lubke U, Six J, Boons J, Van de Voorde A, Martin JJ, Gheuens J (1992) Monoclonal antibodies with selective specificity for Alzheimer Tau are directed against phosphatase-sensitive epitopes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 84:265–272
Morris HR, Steele JC, Crook R, Wavrant-De Vrieze F, Onstead-Cardinale L, Gwinn-Hardy K, Wood NW, Farrer M, Lees AJ, McGeer PL, Siddique T, Hardy J, Perez-Tur J (2004) Genome-wide analysis of the parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam. Arch Neurol 61:1889–1897
Murakami N (1999) Parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam - overview of clinical aspects. J Neurol 246(Suppl 2):II16–II18
Nakano I, Hirano A (1983) Neuron loss in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam. Ann Neurol 13:87–91
Oyanagi K, Wada M (1999) Neuropathology of parkinsonism-dementia complex and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of Guam: an update. J Neurol 246(Suppl 2):II19–II27
Oyanagi K, Makifuchi T, Ohtoh T, Chen KM, Gajdusek DC, Chase TN, Ikuta F (1994) The neostriatum and nucleus accumbens in parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam: a pathological comparison with Alzheimer’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 88:122–128
Oyanagi K, Makifuchi T, Ohtoh T, Ikuta F, Chen KM, Chase TN, Gajdusek DC (1994) Topographic investigation of brain atrophy in parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurodegeneration 3:301–304
Perl DP, Hof PR, Steele JC, Purohit DP, Peterson R, Belli D (1995) Changes in the outbreak of ALS/parkinsonism-dementia complex: neuropathologic studies of asympyomatic Chamorros. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54:416
Perl DP, Hof PR, Purohit DP, Loerzel AJ, Kakulas BA (2003) Hippocampal and entorhinal cortex neurofibrillary tangle formation in Guamanian Chamorros free of overt neurologic dysfunction. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:381–388
Plato CC, Galasko D, Garruto RM, Plato M, Gamst A, Craig UK, Torres JM, Wiederholt W (2002) ALS and PDC of Guam: forty-year follow-up. Neurology 58:765–773
Plato CC, Garruto RM, Galasko D, Craig UK, Plato M, Gamst A, Torres JM, Wiederholt W (2003) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam: changing incidence rates during the past 60 years. Am J Epidemiol 157:149–157
Poorkaj P, Tsuang D, Wijsman E, Steinbart E, Garruto RM, Craig UK, Chapman NH, Anderson L, Bird TD, Plato CC, Perl DP, Weiderholt W, Galasko D, Schellenberg GD (2001) TAU as a susceptibility gene for amyotropic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism dementia complex of Guam. Arch Neurol 58:1871–1878
Popescu A, Lippa CF, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2004) Lewy bodies in the amygdala: increase of alpha-synuclein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases with tau-based inclusions. Arch Neurol 61:1915–1919
Pratico D, Sung S (2004) Lipid peroxidation and oxidative imbalance: early functional events in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 6:171–175
Pratico D, Uryu K, Leight S, Trojanoswki JQ, Lee VM-Y (2001) Increased lipid peroxidation precedes amyloid plaque formation in an animal model of Alzheimer amyloidosis. J Neurosci 21:4183–4187
Pratico D, Clark CM, Liun F, Rokach J, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Increase of brain oxidative stress in mild cognitive impairment: a possible predictor of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 59:972–976
Schmidt ML, Carden MJ, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (1987) Phosphate dependent and independent neurofilament epitopes in the axonal swellings of patients with motor neuron disease and controls. Lab Invest 56:282–294
Schmidt ML, Lee VM-Y, Saido T, Perl D, Schuck T, Iwatsubo T, Trojanowski JQ (1998) Amyloid plaques in Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex contain species of A beta similar to those found in the amyloid plaques of Alzheimer’s disease and pathological aging. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 95:117–122
Sebeo J, Hof PR, Perl DP (2004) Occurrence of alpha-synuclein pathology in the cerebellum of Guamanian patients with parkinsonism-dementia complex. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 107:497–503
Spencer PS, Nunn PB, Hugon J, Ludolph AC, Ross SM, Roy DN, Robertson RC (1987) Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia linked to a plant excitant neurotoxin. Science 237:517–522
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy. A heterogeneous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Trojanowski JQ, Ishihara T, Higuchi M, Yoshiyama Y, Hong M, Zhang B, Forman MS, Zhukareva V, Lee VM-Y (2002) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism dementia complex: transgenic mice provide insights into mechanisms underlying a common tauopathy in an ethnic minority on Guam. Exp Neurol 176:1–11
Wiederholt WC (1999) Neuroepidemiologic research initiatives on Guam: past and present. Neuroepidemiology 18:279–291
Yamazaki M, Arai Y, Baba M, Iwatsubo T, Mori O, Katayama Y, Oyanagi K (2000) Alpha-synuclein inclusions in amygdala in the brains of patients with the parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:585–591
Yanagihara R, Garruto RM, Gajdusek DC, Tomita A, Uchikawa T, Konagaya Y, Chen KM, Sobue I, Plato CC, Gibbs CJ Jr (1984) Calcium and vitamin D metabolism in Guamanian Chamorros with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia. Ann Neurol 15:42–48
Yoshiyama Y, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Frontotemporal dementia and tauopathy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 1:413–421
Zhukareva V, Mann D, Pickering-Brown S, Uryu K, Shuck T, Shah K, Grossman M, Miller BL, Hulette CM, Feinstein SC, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2002) Sporadic Pick’s disease: a tauopathy characterized by a spectrum of pathological tau isoforms in gray and white matter. Ann Neurol 51:730–739
Zhukareva V, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM-Y (2004) Assessment of pathological tau proteins in frontotemporal dementias: qualitative and quantitative approaches. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 12:136–145
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support for their research from the NIH (AG14382) and thank the Chamorro families of the patients studied here for making this research possible. JQT is the William Maul Measy-Truman G. Schnabel Jr. M.D. Professor of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. VM-YL is the John H. Ware 3rd Chair of Alzheimer’s Disease Research at the University of Pennsylvania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winton, M.J., Joyce, S., Zhukareva, V. et al. Characterization of tau pathologies in gray and white matter of Guam parkinsonism-dementia complex. Acta Neuropathol 111, 401–412 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0053-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0053-0