Abstract
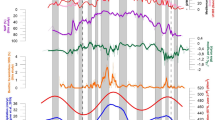
The timing of climate responses to the Bond cycle is investigated in the western Mediterranean. Periodicities had been previously reported in a marine sediment record from this region spanning the last 20 kyr, and registered by diverse paleoenvironmental proxies, in particular those associated with terrigenous input, redox conditions, productivity, sea surface temperature (SST) and salinity. Further cross-spectral analyses on these time series reveal leads–lags in the 1400 year climate cycle. Considering as reference a terrigenous input proxy (the K/Al ratio), all the paleoenvironmental proxies displayed time shifts varying from ca. 700 year to ca. 350 year. SST and salinity variations show a first leaded response with the inflow of cold and less salty Atlantic waters. Followed by a time lead of 525 year, progresively arid conditions with an increase of eolian dust transport to the area, given by the Zr/Al signal, are observed. The intensification of dust transport could have triggered a latest biological response, lead by 350 year, with an increase of productivity, as suggested by the Ba/Al ratio. Lastly changes in the Mediterranean thermohaline circulation, indicated by a selected redox proxy (the U/Th ratio), are observed. These results support that the oceanic response triggered the atmospheric response to the Bond cycle in the western Mediterranean. Changes in the North Atlantic Oscillation mode and in the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone migrations with variations in the monsoon activity or Saharan winds system, are considered as main forcing mechanisms, with a complex relationship of the involved phenomena.

(Schlitzer R, Ocean Data View, http://odv.awi.de, 2017)



(Schlitzer R, Ocean Data View, http://odv.awi.de, 2017)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alley RB, Brook EJ, Anandakrishnan S (2002) A northern lead in the orbital band: north–south phasing of Ice-Age events. Quat Sci Rev 21:431–441
Bassetti M-A, Carbonel P, Sierro FJ, Perez-Folgado M, Jouët G, Berné S (2010) Response of ostracods to abrupt climate changes in the Western Mediterranean (Gulf of Lion) during the last 30 kyr. Mar Micropaleontol 77:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2010.06.004
Béthoux JP (1979) Budgets of the Mediterranean Sea. Their dependence on the local climate and on the characteristics of the Atlantic waters. Oceanol Acta 2:157–163
Bond G, Broecker WS, Johnsen SJ, McManus J, Labeyrie L, Jouzel J, Bonani G (1993) Correlations between climate records from North Atlantic sediments and Greenland ice. Nature 365:143–147
Bond G, Showers W, Cheseby M, Lotti R, Almasi P, deMenocal P, Priore P, Cullen H, Hajdas I, Bonani G (1997) A pervasive millennial-scale cycle in North Atlantic Holocene and Glacial climates. Science 278:1257–1266
Bond G, Kromer B, Beer J, Muscheler R, Evans MN, Showers W, Hoffmann S, Lotti-Bond R, Hajdas I, Bonani G (2001) Persistent solar influence on North Atlantic climate during the Holocene. Science 294:2130–2135. doi:10.1126/science.1065680
Broecker WS (1994) Massive iceberg discharges as triggers for global climate change. Nature 372:421–424
Broecker WS (1997) Paleocean circulation during the last deglaciation; a bipolar seesaw? Paleoceanography 13:119–121
Cacho I, Grimalt JO, Pelejero C, Canals M, Sierro FJ, Flores JA, Shackleton NJ (1999) Dansgaard–Oeschger and Heinrich event imprints in the Alboran Sea paleotemperatures. Paleoceanography 14:698–705
Cacho I, Grimalt JO, Sierro FJ, Shackleton NJ, Canals M (2000) Evidences for enhanced Mediterranean thermohaline circulation during rapid climatic coolings. Earth Planet Sci Lett 183:417–429. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00296-X
Calvert SE, Pedersen TF (2007) Chapter fourteen elemental proxies for palaeoclimatic and palaeoceanographic variability in marine sediments: interpretation and application. In: Hillaire-Marcel C, De Vernal A (eds) Proxies in Late Cenozoic Paleoceanography, developments in marine geology. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 567–644
Chatfield C (1991) The analysis of time series: an introduction, 4th edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Comas MC, Ivanov MK (2003) Alboran basin (Leg 3). In: Kenyon H, Ivanov MK, Akhmetzhanov AM, Akhmanov GG (eds) Interdisciplinary geoscience research on the North East Atlantic margin, Mediterranean Sea and Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Technical Series UNESCO, pp 51–71
Cornfortha RJ, Hoskins BJ, Thorncroft CD (2009) The impact of moist processes on the African Easterly Jet–African Easterly Wave system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 135:894–913
Debret M, Bout-Roumazeilles V, Grousset F, Desmet M, McManus JF, Massei N, Sebag D, Petit JR, Copard Y, Trentesaux A (2007) The origin of the 1500-year climate cycles in Holocene north-atlantic records. Clim Past 3:569–575. doi:10.5194/cp-3-569-2007
Debret M, Sebag D, Crosta X, Massei N, Petit JR, Chapron E, Bout-Roumazeilles V (2009) Evidence from wavelet analysis for a mid-Holocene transition in global climate forcing. Quat Sci Rev 28:2675–2688. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.06.005
Degeai JP, Devillers B, Dezileau L, Oueslati H, Bony G (2015) Major storm periods and climate forcing in the Western Mediterranean during the Late Holocene. Quat Sci Rev 129:37–56. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.10.009
deMenocal PB, Rind D (1993) Sensitivity of Asian and African climate to variations in seasonal insolation, glacial ice cover, sea surface temperatures, and Asian orography. J Geophys Res 98:7265–7287
Denton GH, Broecker WS (2008) Wobbly ocean conveyor circulation during the Holocene?. Quat Sci Rev 27:1939–1950. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.08.008
Dima M, Lohmann G (2009) Conceptual model for millennial climate variability: a possible combined solar-thermohaline circulation origin for the 1,500-year cycle. Clim Dyn 32:301–311. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0471-x
Fischer G, Wefer G (1999) Use of proxies in paleoceanography: examples from the South Atlantic. Springer, Berlin
Fletcher WJ, Debret M, Sanchez Goñi MF (2013) Mid-Holocene emergence of a low-frequency millennial oscillation in western Mediterranean climate: implications for past dynamics of the North Atlantic atmospheric westerlies. The Holocene 23:153–166. doi:10.1177/0959683612460783
Ganopolski A, Roche DM (2009) On the nature of lead–lag relationships during glacial interglacial climate transitions. Quaternary Sci Rev 28:3361–3378. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.09.019
Gasse F (2000) Hydrological changes in the African tropics since the last glacial maximum. Quat Sci Rev 19:189–211. doi:10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00061-X
Griffith EM, Paytan A (2012) Barite in the ocean-occurrence, geochemistry and palaeoceanographic applications. Sedimentology 59:1817–1835. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3091.2012.01327.x
Hosseinpour F, Wilcox E (2013) Interactions between Oceanic Saharan air layer and African Easterly Jet–African Easterly waves system. American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting, abstract GC13A-1058.
Hurrel JW (1995) Decadal trends in the North Atlantic Oscillation: regional temperatures and precipitation. Science 269:676–679. doi:10.1126/science.269.5224.676
Incarbona A, Di Stefano E, Patti B, Pelosi N, Bonomo S, Mazzola S, Sprovieri R, Tranchida G, Zgozi S, Bonanno A (2008) Holocene millennial-scale productivity variations in the Sicily Channel (Mediterranean Sea). Paleoceanography 23:PA3204. doi:10.1029/2007PA001581
Jones C, Mahowald N, Luo C (2003) The role of easterly waves on African desert dust transport. J Clim 16:3617–3628
Kelsey AM, Menk FW, Moss PT (2015) An astronomical correspondence to the 1470 year cycle of abrupt climate change. Clim Past Discuss 11:4895–4915. doi:10.5194/cpd-11-4895-2015
Knippertz P, Todd MC (2010) The central west Saharan dust hot spot and its relation to African easterly waves and extratropical disturbances. J Geophys Res 115:D12117
Lee S-Y, Chiang JCH, Matsumoto K, Tokos KS (2011) Southern Ocean wind response to North Atlantic cooling and the rise in atmospheric CO2: modeling perspective and paleoceanographic implications. Paleoceanography 26:PA1214. doi:10.1029/2010PA002004
Lionello P, Malanotte-Rizzoli P, Boscolo R, Alpert P, Artale V, Li L, Luterbacher J, May W, Trigo R, Tsimplis M, Ulbrich U, Xoplaki E (2006) The Mediterranean climate: an overview of the main characteristics and issues. In: Lionello P, Malanotte-Rizzoli P, Boscolo R (eds) Mediterranean climate variability, developments in earth and environmental sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–26
Lomb NR (1976) Least-squares frequency analysis of unequally spaced data. Astrophys Space Sci 39:447–462
Martínez-Ruiz F, Kastner M, Gallego-Torres D, Rodrigo-Gámiz M, Nieto-Moreno V, Ortega-Huertas M (2015) Paleoclimate and paleoceanography over the last 20,000 year in the Mediterranean Sea Basins as indicated by sediment elemental proxies. Quat Sci Rev 107:25–46. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.09.018
Martrat B, Grimalt JO, Shackleton NJ, de Abreu L, Hutterli MA, Stocker TF (2007) Four climate cycles of recurring deep and surfacewater destabilizations on the Iberian Margin. Science 317:502–507. doi:10.1126/science.1139994
Mekonnen A, Thorncroft CD, Aiyyer AR (2006) Analysis of convection and its association with African easterly waves. J Clim 19:5405–5421
Millot C (1999) Circulation in the Western Mediterranean Sea. J Mar Syst 20:423–442
Millot C (2008) Short-term variability of the Mediterranean in- and out-flows. Geophys Res Lett 35:L15603. doi:10.1029/2008GL033762
Moreno A, Cacho I, Canals M, Grimalt JO, Sánchez Goñi MF, Shackleton N, Sierro FJ (2005) Links between marine and atmospheric processes oscillating on a millennial time-scale. A multi-proxy study of the last 50,000 year from the Alboran Sea (Western Mediterranean Sea). Quat Sci Rev 24:1623–1636. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2004.06.018
Nicholson S (2009) A revised picture of the structure of the “monsoon” and land ITCZ over West Africa. Clim Dyn 32:1155–1171. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0514-3
Nieto-Moreno V, Martínez-Ruiz F, Giralt S, Jiménez-Espejo F, Gallego-Torres D, Rodrigo-Gámiz M, García-Orellana J, Ortega-Huertas M, de Lange GJ (2011) Tracking climate variability in the western Mediterranean during the Late Holocene: a multiproxy approach. Clim Past 7:1395–1414. doi:10.5194/cp-7-1395-2011
Olsen J, Anderson NJ, Knudsen MF (2012) Variability of the North Atlantic oscillation over the past 5,200 years. Nat Geosci 5:1–14. doi:10.1038/ngeo1589
Pardo-Igúzquiza E, Rodríguez-Tovar FJ (2000) The permutation test as a nonparametric method for testing the statistical significance of power spectrum estimation in cyclostratigraphic research. Earth Planet Sci Lett 181:175–189
Pardo-Igúzquiza E, Rodríguez-Tovar FJ (2005) MAXENPER: a program for maximum entropy spectral estimation with assessment of statistical significance by the permutation test. Comput Geosci 31:555–567. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2004.11.010
Pardo-Igúzquiza E, Rodríguez-Tovar FJ (2012) Spectral and cross-spectral analysis of uneven time series with the smoothed Lomb–Scargle periodogram and Monte Carlo evaluation of statistical significance. Comput Geosci 49:207–216. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2012.06.018
Pardo-Igúzquiza E, Rodrigo-Gámiz M, Rodríguez-Tovar FJ, Martínez-Ruiz F (2014) Cross-spectral analysis of time series with uneven sampling: study of Holocene climate variability. In: Rojas Ruiz I, Ruiz Garcia G (eds) International work-conference on time series. Proceedings ITISE. Copicentro Granada SL, Granada, pp 1–6
Pena LD, Francés G, Diz P, Esparza M, Grimalt JO, Nombela MA, Alejo I (2010) Climate fluctuations during the Holocene in NW Iberia: high and low latitude linkages. Cont Shelf Res 30:1487–1496. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2010.05.009
Prahl FG, Wakeham SG (1987) Calibration of unsaturation patterns in long-chain ketone compositions for palaeotemperature assessment. Nature 330:367–369
Press HW, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (1992) Numerical recipes in Fortran, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Rodrigo-Gámiz M, Martínez-Ruiz F, Jiménez-Espejo FJ, Gallego-Torres D, Nieto-Moreno V, Romero O, Ariztegui D (2011) Impact of climate variability in the western Mediterranean during the last 20,000 years: oceanic and atmospheric responses. Quat Sci Rev 30:2018–2034. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.05.011
Rodrigo-Gámiz M, Martínez-Ruiz F, Rodríguez-Tovar FJ, Jiménez-Espejo FJ, Pardo-Igúzquiza E (2014a) Millennial- to centennial-scale climate periodicities and forcing mechanisms in the westernmost Mediterranean for the past 20,000 years. Quat Res 81:78–93. doi:10.1016/j.yqres.2013.10.009
Rodrigo-Gámiz M, Martinez-Ruiz F, Rampen SW, Schouten S, Sinninghe Damsté JS (2014b) Sea surface temperature variations in the western Mediterranean Sea over the last 20 kyr: a dual-organic proxy (UK′ 37 and LDI) approach. Paleoceanography 29:87–98. doi:10.1002/2013PA002466
Rodrigo-Gámiz M, Martínez-Ruiz F, Chiaradia M, Jiménez-Espejo FJ, Ariztegui D (2015a) Radiogenic isotopes for deciphering terrigenous input provenance in the western Mediterranean. Chem Geol 410:237–250. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.06.004
Rostek F, Ruhland G, Bassinot FC, Müller P, Labeyrie LD, Lancelot Y, Bard E (1993) Reconstructing sea surface temperature and salinity using δ18O and alkenone records. Nature 364:319–321
Scargle JD (1982) Studies in astronomical time series analysis. II. Statistical aspects of spectral analysis of unevenly spaced data. Astrophys J 263:835–853
Scheinwald A, Billups K (2012) Millennial scale climate signals in the subtropical Northwest Atlantic. AGU Fall Meeting, Abstract PP31C–2050. San Francisco
Sierro FJ, Hodell DA, Curtis JH, Flores JA, Reguera I, Colmenero-Hidalgo E, Bárcena MA, Grimalt JO, Cacho I, Frigola J, Canals M (2005) Impact of iceberg melting on Mediterranean thermohaline circulation during Heinrich events. Paleoceanography 20:PA2019. doi:10.1029/2004PA001051
Smith AC, Wynn PM, Barker PA, Leng MJ, Noble SR, Tych W (2016) North Atlantic forcing of moisture delivery to Europe throughout the Holocene. Nat Sci Rep 6:24745. doi:10.1038/srep24745
Sorrel P, Debret M, Billeaud I, Jaccard SL, McManus JF, Tessier B (2012) Persistent non-solar forcing of Holocene storm dynamics in coastal sedimentary archives. Nat Geosci 5:892–896. doi:10.1038/ngeo161
Steig EJ, Alley RB (2002) Phase relationships between Antarctic and Greenland climate records. Ann Glaciol 35:451–456
Thompson DWJ, Wallace JM (2001) Regional climate impacts of the northern hemisphere annular mode. Science 293:85–89
Trigo RM, Pozo-Vázquez D, Osborn TJ, Castro-Díez Y, Gámiz-Fortis S, Esteban-Parra MJ (2004) North Atlantic oscillation influence on precipitation, river flow and water resources in the Iberian Peninsula. Int J Climatol 24:925–944. doi:10.1002/joc.1048
Tuenter E, Weber SL, Hilgen FJ, Lourens LJ (2007) Simulating sub-Milankovitch climate variations associated with vegetation dynamics. Clim Past 3:169–180
Urey HC (1947) The thermodynamic properties of isotopic substances. J Chem Soc 1947:562–581
Voelker AHL, Lebreiro SM, Schönfeld J, Cacho I, Erlenkeuser H, Abrantes F (2006) Mediterranean outflow strengthening during northern hemisphere coolings: a salt source for the glacial Atlantic? Earth Planet Sci Lett 245:39–55. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.03.014
Wanner H, Bütikofer J (2008) Holocene Bond Cycles: real or imaginary?. Geogr Sb ČGS 113:338–350
Wanner H, Bronnimann S, Casty C, Gyalistras D, Luterbacher J, Schmutz C, Stephenson DB, Xoplaki E (2001) North Atlantic oscillation—concepts and studies. Surv Geophys 22:321–382
Wanner H, Solomina O, Grosjean M, Ritz S, Jetel M (2011) Structure and origin of Holocene cold events. Quat Sci Rev 30:3109–3123. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.07.010
Wanner H, Mercolli L, Grosjean M, Ritz SP (2015) Holocene climate variability and change; a data-based review. J Geol Soc 172:254–263. doi:10.1144/jgs2013-101
Weedom GP (2003) Times-series analysis and cyclostratigraphy: examining stratigraphic records of environmental cycles. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Zipser EJ, Twohy CH, Chee Tsay S et al (2009) The Saharan air layer and the fate of African easterly wavesaves—NASA’s AMMA field study of tropical cyclogenesis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 90:1137–1156
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)-cofinanced Grants CGL2015-66835-P, CGL2015-66830-R, and CGL2015-71510-R (Secretaría de Estado de Investigación MINECO), Research Groups RNM 179, RNM 178 (Junta de Andalucía), and the Research Excellence Unit (UCE-PP2016-05) of the University of Granada. We are also grateful to the oceanographic cruise Training-Through-Research Programme (UNESCO-Moscow State University). M. Rodrigo-Gámiz acknowledges funding from “Ayudas para el mantenimiento de la actividad de los grupos de investigación de la UGR” within the program “Fortalecimiento de las capacidades de I + D + I” from the University of Granada, and from the Andalucía Talent Hub Program co-funded by the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program (COFUND—Grant Agreement No 291780) and the Junta de Andalucía. We thank the Editor J.-C. Duplessy and three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigo-Gámiz, M., Martínez-Ruiz, F., Rodríguez-Tovar, F. et al. Appraising timing response of paleoenvironmental proxies to the Bond cycle in the western Mediterranean over the last 20 kyr. Clim Dyn 50, 2925–2934 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3782-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3782-y