Abstract
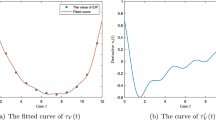
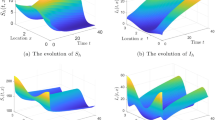
In this paper, a reaction–diffusion system is proposed to model the spatial spreading of West Nile virus in vector mosquitoes and host birds in North America. Transmission dynamics are based on a simplified model involving mosquitoes and birds, and the free boundary is introduced to model and explore the expanding front of the infected region. The spatial-temporal risk index \(R_0^F(t)\), which involves regional characteristic and time, is defined for the simplified reaction–diffusion model with the free boundary to compare with other related threshold values, including the usual basic reproduction number \(R_0\). Sufficient conditions for the virus to vanish or to spread are given. Our results suggest that the virus will be in a scenario of vanishing if \(R_0\le 1\), and will spread to the whole region if \(R_{0}^F(t_0)\ge 1\) for some \(t_0\ge 0\), while if \(R^F_0(0)<1<R_0\), the spreading or vanishing of the virus depends on the initial number of infected individuals, the area of the infected region, the diffusion rate and other factors. Moreover, some remarks on the basic reproduction numbers and the spreading speeds are presented and compared.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention, West Nile Virus: Preliminary Maps & Data for 2014. http://www.cdc.gov/westnile/statsMaps/preliminaryMapsData/index.html.
Public Health Agency of Canada: Surveillance of West Nile virus. http://healthycanadians.gc.ca/diseases-conditions-maladies-affections/disease-maladie/west-nile-nil-occidental/surveillance-eng.php.
References
Abdelrazec A, Lenhart S, Zhu H (2014) Transmission dynamics of West Nile virus in mosquitoes and corvids and non-corvids. J Math Biol 68(6):1553–1582
Allen LJS, Bolker BM, Lou Y, Nevai AL (2008) Asymptotic profiles of the steady states for an SIS epidemic reaction–diffusion model. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser A 21:1–20
Álvarez-Caudevilla P, López-Gómez J (2008) Asymptotic behaviour of principal eigenvalues for a class of cooperative systems. J Differ Equ 244(5):1093–1113
Aronson DG, Weinberger HF (1975) Nonlinear diffusion in population genetics, combustion, and nerve pulse propagation. In: Partial differential equations and related topics, Lecture Notes in Math., vol 446. Springer, Berlin, pp 5–49
Bowman C, Gumel AB, Wu J, van den Driessche P, Zhu H (2005) A mathematical model for assessing control strategies against West Nile virus. Bull Math Biol 67(5):1107–1133
CDC (2013) West Nile virus disease and other arboviral diseases in United States, 2012. MMWR 62:513–517
Chen XF, Friedman A (2000) A free boundary problem arising in a model of wound healing. SIAM J Math Anal 32:778–800
Cruz-Pacheco G, Esteva L, Montaño-Hirose JA, Vargas C (2005) Modelling the dynamics of West Nile virus. Bull Math Biol 67(6):1157–1172
Dohm DJ, Sardelis MR, Turell MJ (2002) Experimental vertical transmission of West Nile virus by Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol 39:640–644
Du YH, Guo ZM (2011) Spreading–vanishing dichotomy in the diffusive logistic model with a free boundary II. J Differ Equ 250:4336–4366
Du YH, Lin ZG (2010) Spreading–vanishing dichotomy in the diffusive logistic model with a free boundary. SIAM J Math Anal 42:377–405
Du YH, Lin ZG (2014) The diffusive competition model with a free boundary: invasion of a superior or inferior competitor. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser B 19:3105–3132
Du YH, Lou BD (2015) Spreading and vanishing in nonlinear diffusion problems with free boundaries. J Eur Math Soc 17:2673–2724
Fila M, Souplet P (2001) Existence of global solutions with slow decay and unbounded free boundary for a superlinear Stefan problem. Interfaces Free Bound 3:337–344
Fisher RA (1937) The wave of advance of advantageous genes. Ann Eugen 7:335–369
Ge J, Kim KI, Lin ZG, Zhu HP (2015) A SIS reaction–diffusion–advection model in a low-risk and high-risk domain. J Differ Equ 259:5486–5509
Ge J, Lei CX, Lin ZG (2017) Reproduction numbers and the expanding fronts for a diffusion–advection SIS model in heterogeneous time-periodic environment. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl 33:100–120
Gu H, Lin ZG, Lou BD (2015) Different asymptotic spreading speeds induced by advection in a diffusion problem with free boundaries. Proc Am Math Soc 143:1109–1117
Huang W, Han M, Liu K (2010) Dynamics of an SIS reaction–diffusion epidemic model for disease transmission. Math Biosci Eng 7:51–66
Kolmogorov AN, Petrovsky IG, Piskunov NS (1937) Ètude de l’équation de la diffusion avec croissance de la quantité de matière et son application à un problème biologique. Bull Univ Moscou Sér Internat A1:1–26 (English transl. in: Dynamics of Curved Fronts, P. Pelcé (ed.), Academic Press, 1988, 105–130)
Ladyzenskaja OA, Solonnikov VA, Ural’ceva NN (1968) Linear and quasilinear equations of parabolic type. American Mathematical Society, Providence
Lei CX, Lin ZG, Zhang QY (2014) The spreading front of invasive species in favorable habitat or unfavorable habitat. J Differ Equ 257:145–166
Lewis MA, Renclawowicz J, van den Driessche P (2006) Traveling waves and spread rates for a West Nile virus model. Bull Math Biol 68(1):3–23
Li BT, Weinberger HF, Lewis MA (2005) Spreading speeds as slowest wave speeds for cooperative systems. Math Biosci 196:82–98
Lin ZG (2007) A free boundary problem for a predator–prey model. Nonlinearity 20:1883–1892
Liu RS, Shuai JP, Wu JH, Zhu HP (2006) Modeling spatial spread of West Nile virus and impact of directional dispersal of birds. Math Biosci Eng 3(1):145–160
López-Gómez J (1996) The maximum principle and the existence of principal eigenvalues for some linear weighted boundary value problems. J Differ Equ 127(1):263–294
Maidana NA, Yang HM (2009) Spatial spreading of West Nile virus described by traveling waves. J Theor Biol 258:403–417
Smith HL (1995) Monotone dynamical systems. American Mathematical Society, Providence
van den Driessche P, Watmough J (2002) Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math Biosci 180:29–48
Wang WD, Zhao X-Q (2012) Basic reproduction numbers for reaction–diffusion epidemic models. SIAM J Appl Dyn Syst 11:1652–1673
Wang WD, Zhao X-Q (2015) Spatial invasion threshold of Lyme disease. SIAM J Appl Math 75:1142–1170
Wonham MJ, de-Camino-Beck T, Lewis MA (2004) An epidemiological model for West Nile virus: invasion analysis and control application. Proc R Soc Lond B 271:501–507
Yu X, Zhao X-Q (2016) A nonlocal spatial model for Lyme disease. J Differ Equ 261:340–372
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work is partially supported by the NSFC of China (Grant Nos. 11371311 and 11171267), the High-End Talent Plan of Yangzhou University, and NSERC and CIHR of Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Z., Zhu, H. Spatial spreading model and dynamics of West Nile virus in birds and mosquitoes with free boundary. J. Math. Biol. 75, 1381–1409 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-017-1124-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-017-1124-7
Keywords
- West Nile virus
- Vector mosquitoes
- Host birds
- Spatial spreading
- Reaction–diffusion systems
- Free boundary
- The basic reproduction number
- Risk index
- Spreading speeds