Abstract
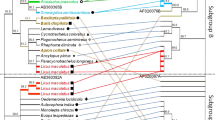
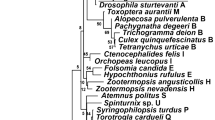
Endosymbiotic bacteria of the genus Wolbachia are widespread among arthropods and can induce cytoplasmic incompatibility, thelytokous parthenogenesis, male-killing or feminization in their hosts. Here, we report phylogenetic relationships of Wolbachia in tephritid fruit flies based on wsp gene sequences. We also report, for the first time, five distinct strains of Wolbachia in Bactrocera ascita sp. B. Four of the five Wolbachia strains found in this species were in the same groups as those found in other tephritid fruit flies, suggesting possible horizontal transmission of Wolbachia from other fruit flies into B. ascita sp. B. The unreliability of wsp-specific group primers demonstrated in this study suggests that these primers might be useful only for preliminary identification of Wolbachia. Final determination of group affiliation needs to be verified with wsp sequence data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 December 2001 / Accepted: 11 January 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamnongluk, W., Kittayapong, P., Baimai, V. et al. Wolbachia Infections of Tephritid Fruit Flies: Molecular Evidence for Five Distinct Strains in a Single Host Species. Curr Microbiol 45, 255–260 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3746-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3746-1