Abstract
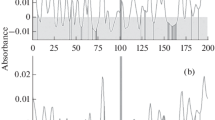
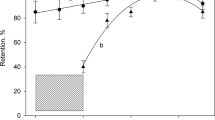
Electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ETAAS) applying a Zeeman effect background correction system (ZEBC) and a tranverse heated atomizer was used to directly determine chromium in sea water. Calcium chloride (at a concentration of 20 mg L–1) was applied as chemical modifier with optimum charring and atomization temperatures of 1600°C and 2000°C, respectively. The detection limit was 0.2 μg L–1, by injecting 20 μL aliquot of sea water sample. This detection limit could be reduced further to 0.05 μg L–1, using multiple injections (injection of five 20 μL aliquot of sea water). The accuracy of the methods developed were confirmed by analyses of different certified reference materials. Finally, interferences from major and minor components of sea water are studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 February 1997 / Revised: 26 May 1997 / Accepted: 8 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bermejo-Barrera, P., Moreda-Piñeiro, J., Moreda-Piñeiro, A. et al. Chromium determination in sea water by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry using Zeeman effect background correction and a multi-injection technique. Fresenius J Anal Chem 360, 208–212 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160050676
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160050676