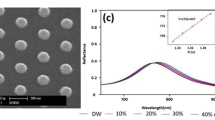
Abstract
In this study, a new type of localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) sensing substrate for phosphopeptides was explored. It has been known that LSPR response for target species is larger in the near-infrared region (NIR) than in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Several types of noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) with NIR absorption capacities have been previously demonstrated as effective LSPR-sensing nanoprobes. Herein, we demonstrate a straightforward approach with improved sensitivity by simply using layer-by-layer (LBL) spherical Au NPs self-assembled on glass slides as the LSPR-sensing substrates that are responsive in the NIR region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The modified glass slide acquired an LSPR absorption band in the NIR, which resulted from the dipole–dipole interactions between Au NPs. To enable the chip to sense phosphopeptides, the surface of the glass chip was spin-coated with thin titania film (TiO2-Glass@Au NPs). Absorption spectrophotometry was employed as a detection tool. Tryptic digest of α-casein was used as a model sample. The feasibility of using the new LSPR approach for detecting a potential risk factor leading to cancers (i.e., phosphorylated fibrinopeptide A) directly from human serum samples was demonstrated. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) was used to confirm the results.

A label free LSPR sensing of phosphopeptides using the titania coated LBL spherical Au NPs coated glass slide (TiO2-Glass@Au NPs) as the sensing chip is demonstrated in this work








Similar content being viewed by others

References
Kuong C-L, Chen W-Y, Chen Y-C (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 387:2091–2099
Okamoto T, Yamaguchi I, Kobayashi T (2000) Opt Lett 25:372–374
Nath N, Chilkoti A (2002) Anal Chem 74:504–509
Nath N, Chilkoti A (2004) Anal Chem 76:5370–5378
Nath N, Chilkoti A (2004) J Fluoresc 14:377–389
Lin H-Y, Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2006) Anal Chem 78:6873–6878
Haes AJ, Van Duyne RP (2002) J Am Chem Soc 124:10596–10604
Wang Y, Qian W, Tan Y, Ding S (2008) Biosens Bioelectron 23:1166–1170
Mayer KM, Lee S, Liao H, Rostro BC, Fuentes A, Scully PT, Nehl CL, Hafner JH (2008) ACS Nano 2:687–692
Lee S, Kathryn M, Mayer KM, Hafner JH (2009) Anal Chem 81:4450–4455
Frens G (1973) Nat Phys Sci 241:20–22
Schierhorn M, Kotov NA, Liz-Marzán LM (2002) Langmuir 18:3694–3697
Jiang C, Markutsya S, Tsukruk VV (2004) Langmuir 20:882–890
Lu C, Mohwald H, Fery A (2007) J Phys Chem C 111:10082–10087
Pinkse MWH, Uitto PM, Hilhorst MJ, Ooms B, Heck AJR (2004) Anal Chem 76:3935–3943
Liang S-S, Makamba H, Huang S-Y, Chen S-H (2006) J Chromatogr A 1116:38–45
Rinalducci S, Larsen MR, Mohammed S, Zolla L (2006) J Proteome Res 5:973–982
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jorgensen TJD (2005) Mol Cell Proteomics 4:873–886
Sano A, Nakamura H (2004) Anal Sci 20:565–566
Kweon HK, Hakansson K (2008) J Proteome Res 7:749–755
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2008) J Biomed Nanotechnol 4:73–79
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2005) Anal Chem 77:5912–5919
Hettasch JM, Strickland E, Lord ST (1993) Biochemistry 32:107–113
Selmeci L, Székely M, Soos P, Seres L, Klinga N, Geiger A, Acsady G (2006) Free Radic Res 40:952–958
Maurer MC, Trosset J-Y, Lester CC, DiBella EE, Scheraga HA (1998) Biochemistry 37:5888–5902
Ebert MP, Niemeyer D, Deininger SO, Wex T, Knippig C, Hoffmann J, Sauer J, Albrecht W, Malfertheiner P, Röcken C (2006) J Proteome Res 5:2152–2158
Ogata Y, Hepplmann CJ, Charlesworth MC, Madden BJ, Miller MN, Kalli KR, Cilby WA, Bergen HR III, Saggese DA, Muddiman DC (2006) J Proteome Res 5:3318–3325
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Science Council of Taiwan for supporting this work financially. We also thank Dr. Wei-Yu Chen and Ms. Tsai-Jung Yu for their assistance in obtaining the SEM images, and Mr. Kai-Wei Han for his assistance in preparing the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JY., Chen, YC. A label-free sensing method for phosphopeptides using two-layer gold nanoparticle-based localized surface plasma resonance spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 399, 1173–1180 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4397-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4397-x