Abstract
Rationale
The central cholinergic system is implicated in cognitive functioning. The dysfunction of this system is expressed in many diseases like Alzheimer's disease, dementia of Lewy body, Parkinson's disease and vascular dementia. In recent animal studies, it was found that selective cholinergic modulation affects visuospatial processes even more than memory function.
Objective
In the current study, we tried to replicate those findings. In order to investigate the acute effects of cholinergic drugs on memory and visuospatial functions, a selective anticholinergic drug, biperiden, was compared to a selective acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting drug, rivastigmine, in healthy elderly subjects.
Methods
A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, cross-over study was performed in 16 healthy, elderly volunteers (eight men, eight women; mean age 66.1, SD 4.46 years). All subjects received biperiden (2 mg), rivastigmine (3 mg) and placebo with an interval of 7 days between them. Testing took place 1 h after drug intake (which was around T max for both drugs). Subjects were presented with tests for episodic memory (wordlist and picture memory), working memory tasks (N-back, symbol recall) and motor learning (maze task, pursuit rotor). Visuospatial abilities were assessed by tests with high visual scanning components (tangled lines and Symbol Digit Substitution Test).
Results
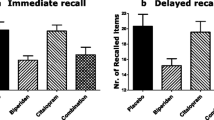
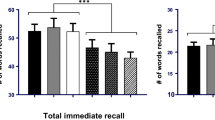
Episodic memory was impaired by biperiden. Rivastigmine impaired recognition parts of the episodic memory performance. Working memory was non-significantly impaired by biperiden and not affected by rivastigmine. Motor learning as well as visuospatial processes were impaired by biperiden and improved by rivastigmine.
Conclusions
These results implicate acetylcholine as a modulator not only of memory but also of visuospatial abilities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammons RB (1947) Acquisition of motor skill. 2. Rotary pursuit performance with continuous practice before and after a single rest. J Exp Psychol 37:393–411
Atri A, Sherman S, Norman KA, Kirchhoff BA, Nicolas MM, Greicius MD, Cramer SC, Breiter HC, Hasselmo ME, Stern CE (2004) Blockade of central cholinergic receptors impairs new learning and increases proactive interference in a word paired-associate memory task. Behav Neurosci 118:223–236
Baxter MG, Gallagher M (1996) Intact spatial learning in both young and aged rats following selective removal of hippocampal cholinergic input. Behav Neurosci 110:460–467
Baxter MG, Bucci DJ, Wiley RG, Gorman LK, Gallagher M (1995) Selective immunotoxic lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic cells—effects on learning and memory in rats. Behav Neurosci 109:714–722
Bentley P, Vuilleumier P, Thiel CM, Driver J, Dolan RJ (2003) Effects of attention and emotion on repetition priming and their modulation by cholinergic enhancement. J Neurophysiol 90:1171–1181
Bentley P, Husain M, Dolan RJ (2004) Effects of cholinergic enhancement on visual stimulation, spatial attention, and spatial working memory. Neuron 41:969–982
Birks J, Grimley Evans J, Iakovidou V, Tsolaki M (2003) Rivastigmine for Alzheimer's disease (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 3
Bittner AC, Carter RC, Krause M, Kennedy RS, Harbeson MM (1983) Performance Evaluation Tests for Environmental Research (Peter)—Moran and computer batteries. Aviat Space Environ Med 54:923–928
Bittner AC, Carter RC, Kennedy RS, Harbeson MM, Krause M (1986) Performance Evaluation Tests for Environmental Research (Peter)—evaluation of 114 measures. Percept Mot Skills 63:683–708
Blokland A (1995) Acetylcholine: a neurotransmitter for learning and memory? Brain Res Rev 21:285–300
Bond A, Lader M (1974) Use of analog scales in rating subjective feelings. Br J Med Psychol 47:211–218
Bouma A, Mulder J, Lindeboom J (1998) Neuropsychologische diagnostiek, handboek. Zwets & Zeitlinger, Lisse
Bridgeman B (2000) Interactions between vision for perception and vision for behavior. In: Rossetti Y, Revonsuo A (eds) Beyond dissociation: interaction between dissociated implicit and explicit processing. John Benjamins, Amsterdam, pp 17–40
Buffett-Jerrott SE, Stewart SH (2002) Cognitive and sedative effects of benzodiazepine use. Curr Pharm Des 8:45–58
Bymaster FP, Heath I, Hendrix JC, Shannon HE (1993) Comparative behavioral and neurochemical activities of cholinergic antagonists in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:16–24
Cohen J, Braver TS, Brown JW (2002) Computational perspectives on dopamine function in prefrontal cortex—commentary. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:223–229
Corey-Bloom J (2002) The ABC of Alzheimer's disease: cognitive changes and their management in Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Int Psychogeriatr 14:51–75
Curran HV, Schifano F, Lader M (1991) Models of memory dysfunction—a comparison of the effects of scopolamine and lorazepam on memory, psychomotor performance and mood. Psychopharmacology 103:83–90
de Jong WP, Hulstijn W, Jogems-Kosterman BJM, Smits-Engelsman BCM (1996) OASIS software and its application in experimental handwriting research. In: Simmers ML, Leedham CG, Thomassen AJWM (eds) Handwriting and drawing research: basic and applied issues. IOS, Amsterdam
De Rosa E, Hasselmo ME, Baxter MG (2001) Contribution of the cholinergic basal forebrain to proactive interference from stored odor memories during associative learning in rats. Behav Neurosci 115:314–327
Dunnett SB, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1991) The basal forebrain cortical cholinergic system—interpreting the functional consequences of excitotoxic lesions. Trends Neurosci 14:494–501
Eglen RM, Choppin A, Watson N (2001) Therapeutic, opportunities from muscarinic receptor research. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:409–414
Ekstrom RB, French JW, Harmon H, Dermen D (1976) Manual for the kit of factor referenced cognitive tests. Educational Testing Service, Princeton, NY
Enz A, Amstutz R, Boddeke H, Gmelin G, Malanowski J (1993) Brain selective inhibition of acetylcholinesterase—a novel approach to therapy for Alzheimer's disease. Prog Brain Res 98:431–438
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997) Central cholinergic systems and cognition. Annu Rev Psychol 48:649–684
Fibiger HC (1991) Cholinergic mechanisms in learning, memory and dementia—a review of recent-evidence. Trends Neurosci 14:220–223
Flood JF, Cherkin A (1986) Scopolamine effects on memory retention in mice—a model of dementia. Behav Neural Biol 45:169–184
French JW (1954) Manual for kit of selected tests for reference aptitude and achievement factors. Educational Testing Service, Princeton, NY
Gold PE (2003) Acetylcholine modulation of neural systems involved in learning and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 80:194–210
Guthrie SK, Manzey L, Scott D, Giordani B, Tandon R (2000) Comparison of central and peripheral pharmacologic effects of biperiden and trihexyphenidyl in human volunteers. J Clin Psychopharmacol 20:77–83
Gutierrez H, Gutierrez R, Silva-Gandarias R, Estrada J, Miranda MI, Bermudez-Rattoni F (1999) Differential effects of 192IgG-saporin and NMDA-induced lesions into the basal forebrain on cholinergic activity and taste aversion memory formation. Brain Res 834:136–141
Hammond EJ, Meador KJ, Aungdin R, Wilder BJ (1987) Cholinergic modulation of human P3 event-related potentials. Neurology 37:346–350
Hege SG, Ellinwood EH Jr, Wilson WH, Helligers CA, Graham SM (1997) Psychomotor effects of the anxiolytic abecarnil: a comparison with lorazepam. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 131:101–107
Hollmann M, Muller-Peltzer H, Greger G, Brode E, Perucca E, Grimaldi R (1987) Pharmacokinetic-dynamic study on different oral biperiden formulations in volunteers. Pharmacopsychiatry 20:72–77
Jann MW, Shirley KL, Small GW (2002) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cholinesterase inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet 41:719–739
Jogems-Kosterman BJM, Zitman FG, van Hoof JJM, Hulstijn W (2001) Psychomotor slowing and planning deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 48:317–333
Jones CK, Shannon HE (2000) Muscarinic cholinergic modulation of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:1017–1023
Kaplan E, Fein D, Morris R, Delis D (1991) Wais-R as a neuropsychological instrument. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Kikuchi M, Wada Y, Nanbu Y, Nakajima A, Tachibana H, Takeda T, Hashimoto T (1999) EEG changes following scopolamine administration in healthy subjects—quantitative analysis during rest and photic stimulation. Neuropsychobiology 39:219–226
Kirrane RM, Mitropoulou V, Nunn M, Silverman J, Siever LJ (2001) Physostigmine and cognition in schizotypal personality disorder. Schizophr Res 48:1–5
Knoblich G, Kircher TTJ (2004) Deceiving oneself about being in control: conscious detection of changes in visuomotor coupling. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 30:657–666
Kopelman MD, Corn TH (1988) Cholinergic blockade as a model for cholinergic depletion—a comparison of the memory deficits with those of Alzheimer-type dementia and the alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. Brain 111:1079–1110
Lezak MD (1995) Neuropsychological assessment, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Lucas-Meunier E, Fossier P, Baux G, Amar M (2003) Cholinergic modulation of the cortical neuronal network. Pflugers Arch 446:17–29
Mash DC, Flynn DD, Potter LT (1985) Loss of M2 muscarine receptors in the cerebral-cortex in Alzheimer's disease and experimental cholinergic denervation. Science 228:1115–1117
Meador KJ, Moore EE, Nichols ME, Abney OL, Taylor HS, Zamrini EY, Loring DW (1993) The role of cholinergic systems in visuospatial processing and memory. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 15:832–842
Mewaldt SP, Ghoneim MM (1979) Effects and interactions of scopolamine, physostigmine and methamphetamine on human memory. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:205–210
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Poline JB, Kohn PD, Holt JL, Egan MF, Weinberger DR, Berman KF (2001) Evidence for abnormal cortical functional connectivity during working memory in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 158:1809–1817
Mintzer MZ, Griffiths RR (2003) Lorazepam and scopolamine: a single-dose comparison of effects on human memory and attentional processes. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 11:56–72
Muir JL (1997) Acetylcholine, aging, and Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56:687–696
Nordberg A, Nilsson-Hakansson L, Adem A, Lai Z, Winblad B (1989) Multiple actions of THA on cholinergic neurotransmission in Alzheimer brains. Prog Clin Biol Res 317:1169–1178
Peretti CS, Danion JM, Kauffmannmuller F, Grange D, Patat A, Rosenzweig P (1997) Effects of haloperidol and amisulpride on motor and cognitive skill learning in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 131:329–338
Petrides M, Milner B (1982) Deficits on subject-ordered tasks after frontal-lobe and temporal-lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia 20:249–262
Poirier J (2002) Evidence that the clinical effects of cholinesterase inhibitors are related to potency and targeting of action. Int J Clin Pract 127:6–19
Power AE, Vazdarjanova A, McGaugh JL (2003) Muscarinic cholinergic influences in memory consolidation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 80:178–193
Rammsayer TH, Rodewald S, Groh D (2000) Dopamine-antagonistic, anticholinergic, and GABAergic effects on declarative and procedural memory functions. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 9:61–71
Robbins TW, McAlonan G, Muir JL, Everitt BJ (1997a) Cognitive enhancers in theory and practice: studies of the cholinergic hypothesis of cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease. Behav Brain Res 83:15–23
Robbins TW, Semple J, Kumar R, Truman MI, Shorter J, Ferraro A, Fox B, Mckay G, Matthews K (1997b) Effects of scopolamine on delayed-matching-to-sample and paired associates tests of visual memory and learning in human subjects: comparison with diazepam and implications for dementia. Psychopharmacology 134:95–106
Sabbe B, Hulstijn W, van Hoof J, Tuynman-Qua HG, Zitman F (1999) Retardation in depression: assessment by means of simple motor tasks. J Affect Disord 55:39–44
Sarter M, Bruno JP (1998a) Age-related changes in rodent cortical acetylcholine and cognition: main effects of age versus age as an intervening variable. Brain Res Rev 27:143–156
Sarter M, Bruno JP (1998b) Cortical acetylcholine, reality distortion, schizophrenia, and Lewy body dementia: too much or too little cortical acetylcholine? Brain Cogn 38:297–316
Sharma T, Hughes C, Aasen I, Kumari V (2004) A placebo-controlled double-blind investigation of cognitive effects of rivastigmine in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 55:27S
Siegel D (1990) A multivariate study of pursuit rotor skill development. Res Q Exerc Sport 61:201–205
Staubli U, Rogers G, Lynch G (1994) Facilitation of glutamate receptors enhances memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:777–781
Thiel CM, Bentley P, Dolan RJ (2002) Effects of cholinergic enhancement on conditioning-related responses in human auditory cortex. Eur J Neurosci 16:2199–2206
Torres EM, Perry TA, Blokland A, Wilkinson LS, Wiley RG, Lappi DA, Dunnett SB (1994) Behavioral, histochemical and biochemical consequences of selective immunolesions in discrete regions of the basal forebrain cholinergic system. Neuroscience 63:95–122
Ungerleider LG, Mishkin M (1982) Two cortical visual systems. In: Engle DJ, Goodale MA, Mansfield RJ (eds) Analysis of visual behavior. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 549–586
Vakil E, Blachstein H (1993) Rey Auditory–Verbal Learning Test—structure-analysis. J Clin Psychol 49:883–890
van Hoof JJM, Jogems-Kosterman BJM, Sabbe BGC, Zitman FG, Hulstijn W (1998) Differentiation of cognitive and motor slowing in the Digit Symbol Test (DST): differences between depression and schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 32:99–103
van Mier H, Hulstijn W, Petersen SE (1993) Changes in motor planning during the acquisition of movement patterns in a continuous task. Acta Psychologica 82:291–312
van Mier H, Tempel LW, Perlmutter JS, Raichle ME, Petersen SE (1998) Changes in brain activity during motor learning measured with PET: effects of hand of performance and practice. J Neurophysiol 80:2177–2199
Voytko ML (1996) Cognitive functions of the basal forebrain cholinergic system in monkeys: memory or attention? Behav Brain Res 75:13–25
Voytko ML, Olton DS, Richardson RT, Gorman LK, Tobin JR, Price DL (1994) Basal forebrain lesions in monkeys disrupt attention but not learning and memory. J Neurosci 14:167–186
Wechsler D (1981) The psychometric tradition-developing the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. Contemp Educ Psychol 6:82–85
Weinberger DR, Mattay V, Callicott J, Kotrla K, Santha A, van Gelderen P, Duyn J, Moonen C, Frank J (1996) fMRI applications in schizophrenia research. Neuroimage 4:S118–S126
Wenk GL, Stoehr JD, Quintana G, Mobley S, Wiley RG (1994) Behavioral, biochemical, histological, and electrophysiological effects of 192-Igg-saporin injections into the basal forebrain of rats. J Neurosci 14:5986–5995
Wezenberg E, Hulstijn W, Sabbe B, Ruigt GSF, Verkes RJ (2004) Psychomotor and cognitive effects of lorazepam and d-amphetamine in healthy subjects. Development of sensitive screening tests of psychomotor- and cognitive functions. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 14:S362
Wild R, Petit T (2004) Cholinesterase inhibitors for dementia with Lewy bodies (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library
Witte EA, Davidson MC, Marrocco RT (1997) Effects of altering brain cholinergic activity on covert orienting of attention: comparison of monkey and human performance. Psychopharmacology 132:324–334
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by NV Organon. We would like to thank them for their financial and technical support to perform this study.
We would also like to thank Jan Leijtens and Drs. Sevla Cinar for their helpful assistance in data collection and analysis.
This experiment complies with the current laws of the Netherlands.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wezenberg, E., Verkes, R.J., Sabbe, B.G.C. et al. Modulation of memory and visuospatial processes by biperiden and rivastigmine in elderly healthy subjects. Psychopharmacology 181, 582–594 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0083-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0083-7