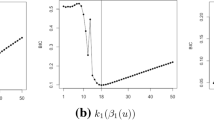
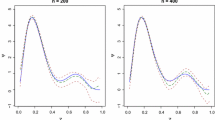
Abstract
A spline-based test statistic for a constant mean function is proposed based on the penalized residual sum-of-squares difference between the null model and a B-spline model in which the regression function is approximated with P-splines approach. When the number of knots is fixed, the limiting null distribution of the test statistic is shown to be the distribution of a linear combination of independent chi-squared random variables, each with one degree of freedom. A smoothing parameter is selected by setting a specified value equal to the expected value of the test statistic under the null hypothesis. Simulation experiments are conducted to study the proposed spline-based test statistic’s finite-sample properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcalá JT, Cristóbal JA, González-Manteiga W (1999) Goodness-of-fit test for linear models based on local polynomials. Stat Probab Lett 42: 39–46
Barry D, Hartigan J (1990) An omnibus test for departures from constant mean. Ann Stat 18: 1340–1357
Buckley M (1991) Detecting a smooth signal: optimality of cusum based procedures. Biometrika 78: 253–262
Buja A, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (1989) Linear smoother and additive models (with Discussion). Ann Stat 17: 453–555
Castaño-Martínez A, López-Blázquez F (2005) Distribution of a sum of weighted central chi-square variables. Commun Stat Theory Methods 34: 515–524
Chen JC (1994a) Testing goodness of fit of polynomial models via spline smoothing techniques. Stat Probab Lett 19: 65–76
Chen JC (1994b) Testing for no effect in nonparametric regression via spline smoothing techniques. Ann Inst Stat Math 45: 251–265
Cox D, Koh E (1989) A smoothing spline based test of model adequacy in polynomial regression. Ann Inst Stat Math 41: 383–400
Cox D, Koh E, Wahba G, Yandell B (1988) Testing the (parametric) null model hypothesis in (semiparametric) partial and generalized spline models. Ann Stat 16: 113–119
Davies RB (1973) Numerical inversion of a characteristic function. Biometrika 60: 415–417
Davies RB (1980) The distribution of a linear combination of χ2 random variables. Appl Stat 29: 323–333
de Boor C (2001) A practical guide to splines, Revised edition. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol 27. Springer, New York
Eilers PHC, Marx BD (1996) Flexible smoothing with B-splines and penalties (with Discussion). Stat Sci 11: 89–121
Eubank RL (2000) Testing for no effect by cosine series methods. Scand J Stat 27: 747–763
Eubank RL, Hart JD (1993) Commonality of cusum, von Neumann and smoothing-based goodness-of-fit tests. Biometrika 80: 89–98
Eubank RL, LaRiccia VN (1993) Testing for no effect in non-parametric regression. J Stat Plan Inference 36: 1–14
Eubank RL, Li CS, Wang S (2005) Testing lack-of-fit of parametric regression models using nonparametric regression techniques. Statistica Sinica 15: 135–152
Eubank RL, Spiegelman C (1990) Testing the goodness-of-fit of a linear model via nonparametric regression techniques. J Am Stat Assoc 85: 387–392
Gasser T, Sroka L, Jennen-Steinmetz C (1986) Residual variance and residual pattern in nonlinear regression. Biometrika 73: 625–633
Härdle W, Mammen M (1993) Comparing nonparametric versus parametric regression fits. Ann Stat 21: 1926–1947
Imhof JP (1961) Computing the distribution of quadratic forms in normal variables. Biometrika 48: 419–426
Li CS (1999) Testing lack of fit of regression models under heteroscedasticity. Can J Stat 27: 485–496
Li CS (2003) A lack-of-fit test for heteroscedastic regression models via cosine-series smoothers. Aust NZ J Stat 45: 477–489
Li CS (2005a) Using local linear kernel smoothers to test the lack of fit of nonlinear regression models. Stat Methodol 2: 267–284
Li CS (2005b) Testing lack of fit for heteroscedastic nonlinear regression models via locally weighted least squares regression. Far East J Theor Statist 16: 29–54
Lindstrom M (1999) Penalized estimation of free-knot splines. J Computat Graph Stat 8: 333–352
Müller HG (1992) Goodness-of-fit diagnostics for regression models. Scand J Stat 19: 157–172
Raz J (1990) Testing for no effect when estimating a smooth function by nonparametric regression: a randomization approach. J Am Stat Assoc 85: 132–138
Ruppert D (2002) Selecting the number of knots for penalized splines. J Computat Graph Stat 11: 735–757
Scheffé H (1959) The analysis of variance. Wiley, New York
Sen PK, Singer JM (1993) Large sample methods in statistics: an introduction with applications. Chapman and Hall, London
Sheil J, O’Muircheartaigh I (1977) The distribution of non-negative quadratic forms in normal variables. Appl Stat 26: 92–98
Smith PL (1979) Splines as a useful and convenient statistical tool. Am Stat 33: 57–62
Wold S (1974) Spline functions in data analysis. Technometrics 16: 1–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, CS. Testing for no effect via splines. Comput Stat 27, 343–357 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-011-0260-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-011-0260-6