Abstract
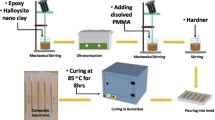
A holistic study was conducted to investigate the combined effect of three different pre-mixing processes, namely mechanical mixing, ultrasonication and centrifugation, on mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy/clay nanocomposites reinforced with different platelet-like montmorillonite (MMT) clays (Cloisite Na+, Cloisite 10A, Cloisite 15 or Cloisite 93A) at clay contents of 3–10 wt%. Furthermore, the effect of combined pre-mixing processes and material formulation on clay dispersion and corresponding material properties of resulting composites was investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), flexural and Charpy impact tests, Rockwell hardness tests and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). A high level of clay agglomeration and partially intercalated/exfoliated clay structures were observed regardless of clay type and content. Epoxy/clay nanocomposites demonstrate an overall noticeable improvement of up to 10 % in the glass transition temperature (T g) compared to that of neat epoxy, which is interpreted by the inclusion of MMT clays acting as rigid fillers to restrict the chain mobility of epoxy matrices. The impact strength of epoxy/clay nanocomposites was also found to increase by up to 24 % with the addition of 3 wt% Cloisite Na+ clays. However, their flexural strength and hardness diminished when compared to those of neat epoxy, arising from several effects including clay agglomeration, widely distributed microvoids and microcracks as well as weak interfacial bonding between clay particles and epoxy matrices, as confirmed from TEM and SEM results. Overall, it is suggested that an improved technique should be used for the combination of pre-mixing processes in order to achieve the optimal manufacturing condition of uniform clay dispersion and minimal void contents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qi B, Zhang QX, Bannister M, Mai YW (2006) Investigation of the mechanical properties of DGEBA-based epoxy resin with nanoclay additives. Compos Struct 75(1–4):514–519. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2006.04.032
Zhang D, Zhou C-H, Lin C-X, Tong D-S, Yu W-H (2010) Synthesis of clay minerals. Appl Clay Sci 50(1):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2010.06.019
Alexandre M, Dubois P (2000) Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: preparation, properties and uses of a new class of materials. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 28(1–2):1–63. doi:10.1016/S0927-796X(00)00012-7
Cho JW, Paul DR (2001) Nylon 6 nanocomposites by melt compounding. Polymer 42(3):1083–1094. doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00380-3
Yasmin A, Luo JJ, Abot JL, Daniel IM (2006) Mechanical and thermal behavior of clay/epoxy nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 66(14):2415–2422. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.03.011
Chen KH, Yang SM (2002) Synthesis of epoxy–montmorillonite nanocomposite. J Appl Polym Sci 86(2):414–421. doi:10.1002/app.10986
Shiravand F, Hutchinson JM, Calventus Y, Ferrando F (2014) Comparison of the nanostructure and mechanical performance of highly exfoliated epoxy-clay nanocomposites prepared by three different protocols. Materials 7(6):4196–4223. doi:10.3390/ma7064196
Ianchis R, Rosca ID, Ghiurea M, Spataru CI, Nicolae CA, Gabor R, Raditoiu V, Preda S, Fierascu RC, Donescu D (2015) Synthesis and properties of new epoxy-organolayered silicate nanocomposites. Appl Clay Sci 103:28–33. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2014.10.020
Wang M, Fan X, Thitsartarn W, He C (2015) Rheological and mechanical properties of epoxy/clay nanocomposites with enhanced tensile and fracture toughnesses. Polymer 58:43–52. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2014.12.042
Hussain F, Hojjati M, Okamoto M, Gorga RE (2006) Polymer-matrix nanocomposites, processing, manufacturing, and application: an overview. J Compos Mater 40(17):1511–1575. doi:10.1177/0021998306067321
Albdiry MT, Yousif BF, Ku H, Lau KT (2013) A critical review on the manufacturing processes in relation to the properties of nanoclay/polymer composites. J Compos Mater 47(9):1093–1115. doi:10.1177/0021998312445592
Salam H, Dong Y, Davies IJ (2015) Development of bio-based polymer/clay nanocomposites: a critical review. In: Dong Y, Umer R, Lau AK-T (eds) Fillers and reinforcements for advanced nanocomposites. Woodhead Publishing, UK, pp 101–132. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-100079-3.00006-5, In Imprint of Elsevier
Lan T, Pinnavaia TJ (1994) Clay-reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Chem Mater 6(12):2216–2219. doi:10.1021/cm00048a006
Ha SR, Ryu SH, Park SJ, Rhee KY (2007) Effect of clay surface modification and concentration on the tensile performance of clay/epoxy nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng A 448(1–2):264–268. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.10.052
Wang H, Hoa SV, Wood-Adams PM (2006) New method for the synthesis of clay/epoxy nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 100(6):4286–4296. doi:10.1002/app.23859
Sundaram S, Nagalingam R, Satheesh Raja R (2008) Experimental analysis on tensile properties of FRP with nano clay. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 1–5. doi: 10.1007/s00170-008-1868-8
Kornmann X, Thomann R, Mülhaupt R, Finter J, Berglund L (2002) Synthesis of amine-cured, epoxy-layered silicate nanocomposites: the influence of the silicate surface modification on the properties. J Appl Polym Sci 86(10):2643–2652. doi:10.1002/app.11279
Wu L, Hoa SV, Minh T, Ton T (2006) Effects of composition of hardener on the curing and aging for an epoxy resin system. J Appl Polym Sci 99(2):580–588. doi:10.1002/app.22493
Devasenapathi V, Monish P, Balasivanandha Prabu S (2009) Experimental investigation of tensile creep behavior of polymer nanocomposites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(3):412–418. doi:10.1007/s00170-008-1877-7
Dong Y, Bhattacharyya D (2008) Effects of clay type, clay/compatibiliser content and matrix viscosity on the mechanical properties of polypropylene/organoclay nanocomposites. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 39(7):1177–1191. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.03.006
Umer R, Li Y, Dong Y, Haroosh HJ, Liao K (2015) The effect of graphene oxide (GO) nanoparticles on the processing of epoxy/glass fiber composites using resin infusion. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81(9):2183–2192. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7427-1
Xu Y, Hoa SV (2008) Mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy/clay nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 68(3–4):854–861. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.08.013
Jo B-W, Park S-K, Kim D-K (2008) Mechanical properties of nano-MMT reinforced polymer composite and polymer concrete. Constr Build Mater 22(1):14–20. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.02.009
Triantafillidis CS, LeBaron PC, Pinnavaia TJ (2002) Thermoset epoxy–clay nanocomposites: the dual role of α, ω-diamines as clay surface modifiers and polymer curing agents. J Solid State Chem 167(2):354–362. doi:10.1006/jssc.2001.9541
Nah C, Ryu HJ, Kim WD, Choi S-S (2002) Barrier property of clay/acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer nanocomposite. Polym Adv Technol 13(9):649–652. doi:10.1002/pat.325
Brown JM, Curliss D, Vaia RA (2000) Thermoset-layered silicate nanocomposites. Quaternary ammonium montmorillonite with primary diamine cured epoxies. Chem Mater 12(11):3376–3384. doi:10.1021/cm000477
Azeez AA, Rhee KY, Park SJ, Hui D (2013) Epoxy clay nanocomposites—processing, properties and applications: a review. Compos Part B 45(1):308–320. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.04.012
Bindu Sharmila TK, Ayswarya EP, Abraham BT, Sabura Begum PM, Thachil ET (2014) Fabrication of partially exfoliated and disordered intercalated cloisite epoxy nanocomposites via in situ polymerization: mechanical, dynamic mechanical, thermal and barrier properties. Appl Clay Sci 102:220–230. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2014.09.043
Chin I-J, Thurn-Albrecht T, Kim H-C, Russell TP, Wang J (2001) On exfoliation of montmorillonite in epoxy. Polymer 42(13):5947–5952. doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00898-3
Pascual-Sánchez V, Martín-Martínez JM (2006) Influence of the curing temperature in the mechanical and thermal properties of nanosilica filled epoxy resin coating. Macromol Symp 233(1):137–146. doi:10.1002/masy.200690010
Lee A, Lichtenhan JD (1999) Thermal and viscoelastic property of epoxy–clay and hybrid inorganic–organic epoxy nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 73(10):1993–2001. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19990906)73:10<1993::AID-APP18>3.0.CO;2-Q
Kornmann X, Lindberg H, Berglund LA (2001) Synthesis of epoxy–clay nanocomposites: influence of the nature of the clay on structure. Polymer 42(4):1303–1310. doi:10.1016/s0032-3861(00)00346-3
Kong D, Park CE (2003) Real time exfoliation behavior of clay layers in epoxy–clay nanocomposites. Chem Mater 15(2):419–424. doi:10.1021/cm0205837
Wang Q, Song C, Lin W (2003) Study of the exfoliation process of epoxy–clay nanocomposites by different curing agents. J Appl Polym Sci 90(2):511–517. doi:10.1002/app.12689
Xie F, Pollet E, Halley PJ, Avérous L (2013) Starch-based nano-biocomposites. Prog Polym Sci 38(10–11):1590–1628. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.05.002
LeBaron PC, Wang Z, Pinnavaia TJ (1999) Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: an overview. Appl Clay Sci 15(1–2):11–29. doi:10.1016/S0169-1317(99)00017-4
Chen C, Tolle TB (2004) Fully exfoliated layered silicate epoxy nanocomposites. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 42(21):3981–3986. doi:10.1002/polb.20259
Gupta N, Lin T, Shapiro M (2007) Clay-epoxy nanocomposites: processing and properties. JOM 59(3):61–65. doi:10.1007/s11837-007-0041-4
Atiemo-Obeng VA, Penney W, Armenante PM (2004) Solid–liquid mixing. In: Handbook of industrial mixing: science and practice, 1st ed. Wiley, Hoboken. 543–584. doi:10.1002/0471451452.ch10
Usuki A, Kojima Y, Kawasumi M, Okada A, Fukushima Y, Kurauchi T, Kamigaito O (1993) Synthesis of nylon 6-clay hybrid. J Mater Res 8(05):1179–1184. doi:10.1557/JMR.1993.1179
Park JY, Davis TB, Sullivan PL (2010) Parametric study on the fabrication of clay-containing thermosetting nanocomposites. J Reinf Plast Compos 29(5):755–770. doi:10.1177/0731684408100698
Yasmin A, Abot JL, Daniel IM (2003) Processing of clay/epoxy nanocomposites by shear mixing. Scr Mater 49(1):81–86. doi:10.1016/S1359-6462(03)00173-8
Cravotto G, Cintas P (2011) Introduction to sonochemistry: a historical and conceptual overview. In: Chen D, Sharma SK, Mudhoo A (eds) Handbook on applications of ultrasound: sonochemistry for sustainability. CRC/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, pp 23–40. doi:10.1201/b11012-3
Suslick KS (1990) Sonochemistry. Science 247(4949):1439–1445
Kaboorani A, Riedl B, Blanchet P (2013) Ultrasonication technique: a method for dispersing nanoclay in wood adhesives. J Nanomater 2013:9. doi:10.1155/2013/341897
Lam C-K, Lau K-T, Cheung H-Y, Ling H-Y (2005) Effect of ultrasound sonication in nanoclay clusters of nanoclay/epoxy composites. Mater Lett 59(11):1369–1372. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2004.12.048
Bittmann B, Haupert F, Schlarb AK (2009) Ultrasonic dispersion of inorganic nanoparticles in epoxy resin. Ultrason Sonochem 16(5):622–628. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.01.006
Bittmann B, Haupert F, Schlarb AK (2011) Preparation of TiO2/epoxy nanocomposites by ultrasonic dispersion and their structure property relationship. Ultrason Sonochem 18(1):120–126. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.03.011
Dean K, Krstina J, Tian W, Varley RJ (2007) Effect of ultrasonic dispersion methods on thermal and mechanical properties of organoclay epoxy nanocomposites. Macromol Mater Eng 292(4):415–427. doi:10.1002/mame.200600435
Saber-Samandari S, Khatibi AA, Basic D (2007) An experimental study on clay/epoxy nanocomposites produced in a centrifuge. Compos Part B 38(1):102–107. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2006.03.010
Kabakov D, Tate JS, Koo JH (2011) Effect of dispersion techniques on thermal and mechanical properties of phenolic/E-glass nanocomposites. J Fire Sci 29(5):387–402. doi:10.1177/0734904110396160
Agubra V, Owuor P, Hosur M (2013) Influence of nanoclay dispersion methods on the mechanical behavior of E-glass/epoxy nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 3(3):550. doi:10.3390/nano3030550
Ford TC, Graham JM (1991) An introduction to centrifugation. BIOS Scientific Pub, Oxford, pp 1–20
Bordes P, Pollet E, Avérous L (2009) Nano-biocomposites: biodegradable polyester/nanoclay systems. Prog Polym Sci 34(2):125–155. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.10.002
Becker O, Cheng Y-B, Varley RJ, Simon GP (2003) Layered silicate nanocomposites based on various high-functionality epoxy resins: the influence of cure temperature on morphology, mechanical properties and free volume. Macromolecules 36(5):1616–1625. doi:10.1021/ma0213448
Akbari B, Bagheri R (2007) Deformation mechanism of epoxy/clay nanocomposite. Eur Polym J 43(3):782–788. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2006.11.028
Tjong SC (2006) Structural and mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 53(3–4):73–197. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2006.06.001
Zhang H, Popp M, Hartwig A, Madler L (2012) Synthesis of polymer/inorganic nanocomposite films using highly porous inorganic scaffolds. Nanoscale 4(7):2326–2332. doi:10.1039/C2NR12029A
Krishnamachari P, Zhang J, Lou J, Yan J, Uitenham L (2009) Biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/clay nanocomposites by melt intercalation: a study of morphological, thermal and mechanical properties. Int J Polym Anal Charact 14(4):336–350. doi:10.1080/10236660902871843
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salam, H., Dong, Y., Davies, I.J. et al. The effects of material formulation and manufacturing process on mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy/clay nanocomposites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87, 1999–2012 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8572-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8572-x