Abstract
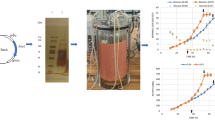
Aspergillus foetidus was used to produce transferases that can be utilized in the synthesis of isooligosaccharides. Maltose and corn steep liquor were found to be the best carbon and nitrogen substrates at optimum concentration of 1% and 3% respectively. Surfactant Tween 80 and metal ions including Fe2+, Zn2+, Mg2+ and Cu2+ were found to have no obvious effect on the enzyme productivity. Uncontrolled pH starting with an initial value of 5.0 gave the highest transferase productivity compared with pH controlled at constant levels and control after natural fall. The optimum temperature was found to be 30 °C. Enzyme activity increased 8 fold in reactors, with better aeration and agitation condition, as compared to shake flask. The morphology of the organism was highly dependent on the nitrogen source and had great influence on enzyme productivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 June 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XD., Rakshit, S. Improved extracellular transferase enzyme production by Aspergillus foetidus for synthesis of isooligosaccharides. Bioprocess Engineering 20, 429–434 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009053
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009053